A Glimpse into the Political Landscape of Italy: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: A Glimpse into the Political Landscape of Italy: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Glimpse into the Political Landscape of Italy: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Glimpse into the Political Landscape of Italy: A Comprehensive Guide
/the-geography-of-italy-4020744-CS-5c3df74a46e0fb00018a8a3a.jpg)
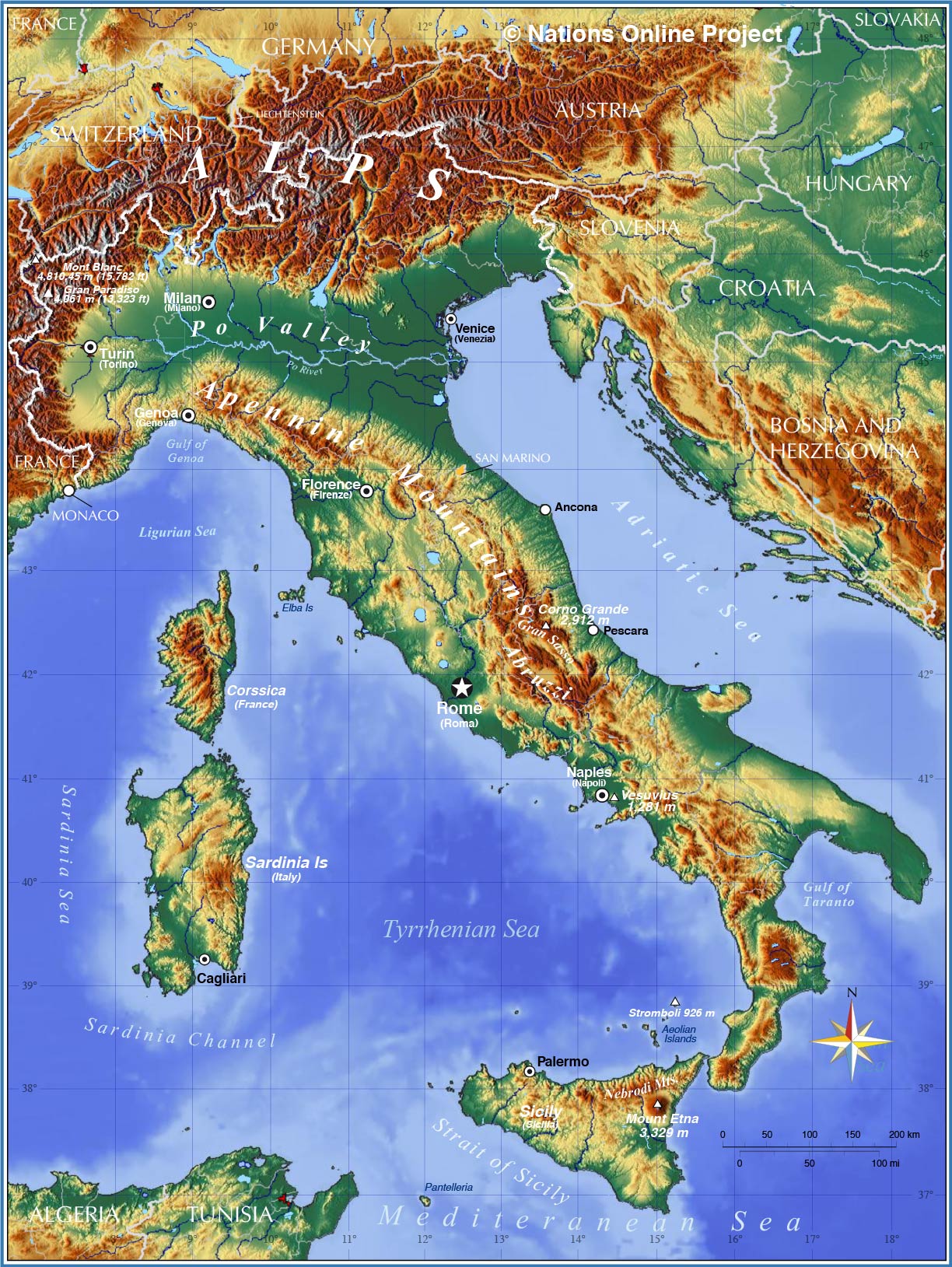
Italy, a nation steeped in history and culture, is a complex tapestry of political entities. Understanding the political map of Italy is crucial for appreciating the country’s governance, its diverse regional identities, and its multifaceted relationship with the European Union. This guide delves into the intricate structure of Italian politics, exploring its regions, provinces, and the unique challenges and opportunities they present.
The Italian Republic: A System of Decentralization
Italy is a unitary parliamentary republic, meaning it is a single, indivisible state with a central government and a legislature. However, the country has a significant degree of regional autonomy, which is reflected in the political map. The Italian Constitution, adopted in 1948, recognizes five distinct levels of government:
- State: This level comprises the national government, which is responsible for foreign affairs, defense, justice, and other core functions.
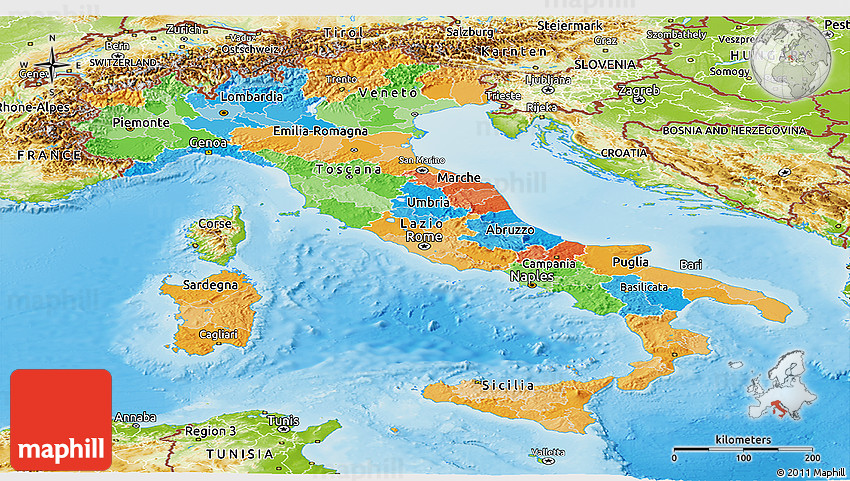
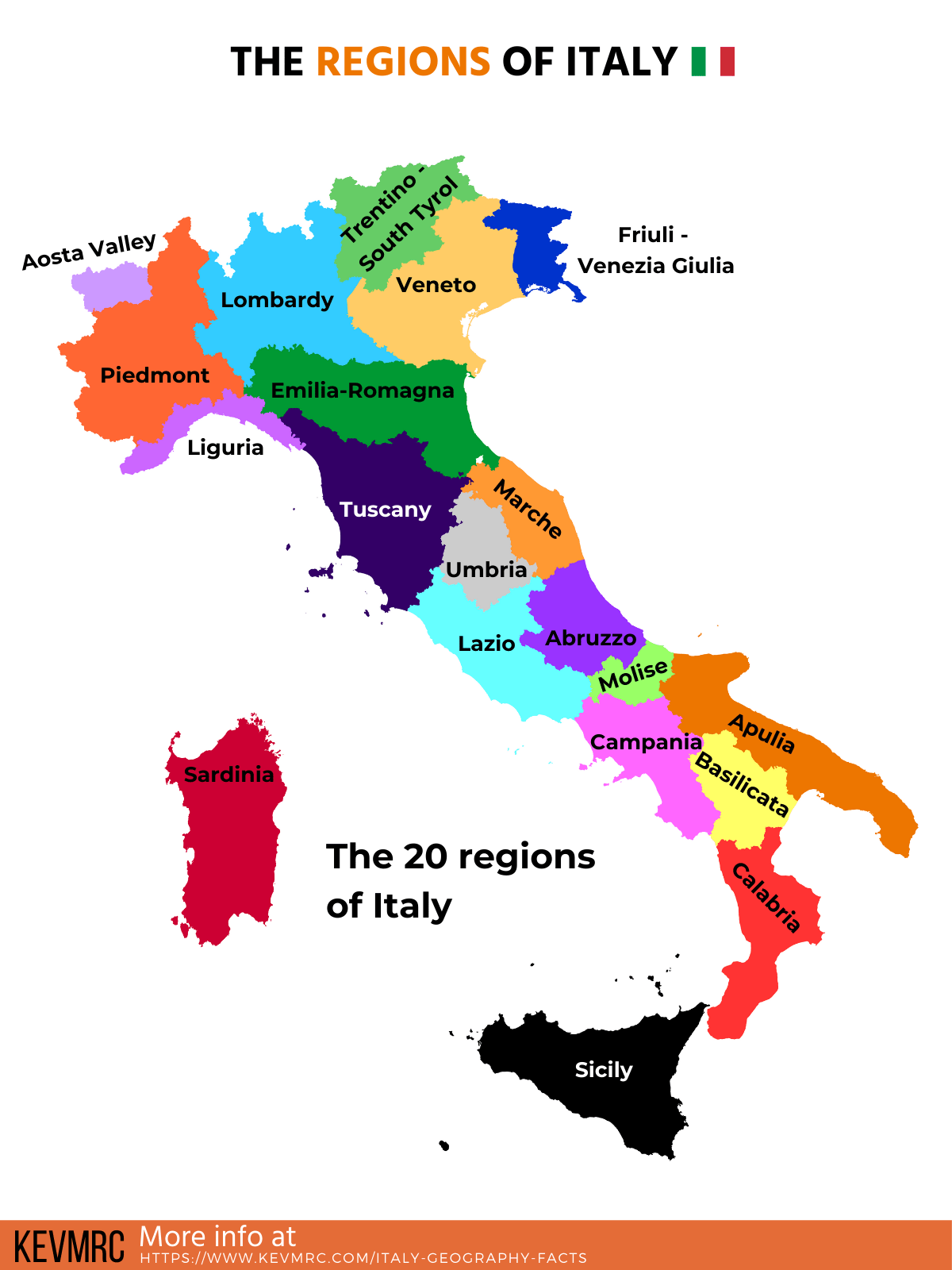
- Regions: The state is divided into 20 regions, including five autonomous regions with special status: Valle d’Aosta, Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Sardinia, and Sicily. Regions have significant powers in areas like healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
- Provinces: Regions are further divided into 107 provinces, which act as administrative subdivisions and handle local affairs.
- Metropolis: Four major cities – Rome, Milan, Naples, and Turin – have special metropolitan status, granting them greater autonomy in managing their affairs.
- Municipalities: The smallest unit of government is the municipality, encompassing cities, towns, and villages.
Understanding the Regional Landscape
The Italian political map is characterized by its distinct regions, each with its own unique history, culture, and economic characteristics. These regions are not merely geographical entities; they represent distinct identities within the Italian nation.
Northern Italy: This region is generally characterized by its economic dynamism, with industrial centers like Milan, Turin, and Genoa. It is also home to the autonomous regions of Valle d’Aosta, Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, and Friuli-Venezia Giulia, each with its own distinct linguistic and cultural heritage.
Central Italy: This region is a blend of agricultural areas, historical cities like Rome and Florence, and coastal regions. It is home to a diverse mix of industries, including tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing.
Southern Italy: This region is known for its stunning landscapes, ancient ruins, and rich cultural traditions. However, it also faces challenges like economic disparities and organized crime. The autonomous region of Sicily, with its unique history and culture, is a prominent part of this region.
The Islands: Sardinia and Sicily, the two largest islands in the Mediterranean, are autonomous regions with distinct identities and significant political autonomy. They play a crucial role in shaping the Italian political landscape.
Political Parties and Coalitions
Italy’s political system is characterized by a multi-party system, with numerous political parties competing for power. The major political parties are:
- Partito Democratico (PD): A center-left party, generally considered to be the successor to the Italian Communist Party.
- Movimento 5 Stelle (M5S): A populist, anti-establishment party that gained significant popularity in recent years.
- Forza Italia (FI): A center-right party founded by former Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi.
- Lega Nord (LN): A right-wing, regionalist party that advocates for greater autonomy for the northern regions.
- Fratelli d’Italia (FdI): A right-wing, nationalist party that has grown in popularity in recent years.
These parties often form coalitions to govern, leading to complex and dynamic political scenarios.
Challenges and Opportunities
The Italian political map reflects both the strengths and weaknesses of the country’s governance system. Key challenges include:
- Regional disparities: Economic disparities between the north and south of the country, as well as between different regions, continue to be a significant issue.
- Political instability: Italy has experienced numerous government changes and political crises in recent decades.
- Organized crime: The presence of organized crime, particularly in the south, poses a serious challenge to the rule of law.
- Immigration: The influx of immigrants, particularly from North Africa, has created social and political tensions.
Despite these challenges, Italy has also experienced significant successes, including:
- Economic growth: Italy has a strong economy, with a diverse range of industries.
- Cultural heritage: The country is home to a wealth of cultural heritage, attracting millions of tourists annually.
- EU membership: Italy is a founding member of the European Union and plays a key role in shaping European policy.
FAQs about the Political Map of Italy
Q: What is the significance of the autonomous regions in Italy?
A: Autonomous regions have greater power and autonomy compared to other regions, allowing them to manage their own affairs in areas like education, healthcare, and infrastructure. This reflects the diverse cultural and linguistic identities within Italy.
Q: What is the role of provinces in the Italian political system?
A: Provinces serve as administrative subdivisions of regions, handling local affairs such as infrastructure, public services, and cultural initiatives.
Q: How does the Italian political system function?
A: Italy is a parliamentary republic with a multi-party system. The Prime Minister is elected by the Parliament, which is composed of the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate. The President of the Republic is the head of state, but his role is largely ceremonial.
Q: What are the main political parties in Italy?
A: The major political parties include the Partito Democratico (PD), Movimento 5 Stelle (M5S), Forza Italia (FI), Lega Nord (LN), and Fratelli d’Italia (FdI). These parties often form coalitions to govern, leading to complex and dynamic political scenarios.
Q: What are the major challenges facing Italy today?
A: Key challenges include regional disparities, political instability, organized crime, immigration, and economic stagnation.
Tips for Understanding the Italian Political Map
- Study the regional divisions: Familiarize yourself with the 20 regions of Italy, including the five autonomous regions.
- Research the political parties: Learn about the major political parties, their platforms, and their historical significance.
- Follow Italian news sources: Stay informed about current events and political developments in Italy.
- Visit different regions: Experiencing the diversity of Italy firsthand can provide valuable insights into the country’s political landscape.
Conclusion
The political map of Italy is a complex and dynamic reflection of the country’s history, culture, and governance. Understanding the regional divisions, the role of political parties, and the challenges and opportunities facing the country is crucial for appreciating the complexities of Italian politics. By exploring the intricacies of the Italian political landscape, we gain a deeper understanding of this fascinating and multifaceted nation.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/map-of-italy--150365156-59393b0d3df78c537b0d8aa6.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Glimpse into the Political Landscape of Italy: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!