A Land of Diverse Cultures: Exploring Montana’s Reservations
Related Articles: A Land of Diverse Cultures: Exploring Montana’s Reservations
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Land of Diverse Cultures: Exploring Montana’s Reservations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Land of Diverse Cultures: Exploring Montana’s Reservations

Montana, known for its rugged beauty and vast open spaces, is also home to a rich tapestry of Native American cultures. These cultures have thrived for centuries, shaping the state’s history, landscape, and identity. Understanding the presence and significance of Montana’s reservations is crucial to appreciating the state’s complex and multifaceted heritage.
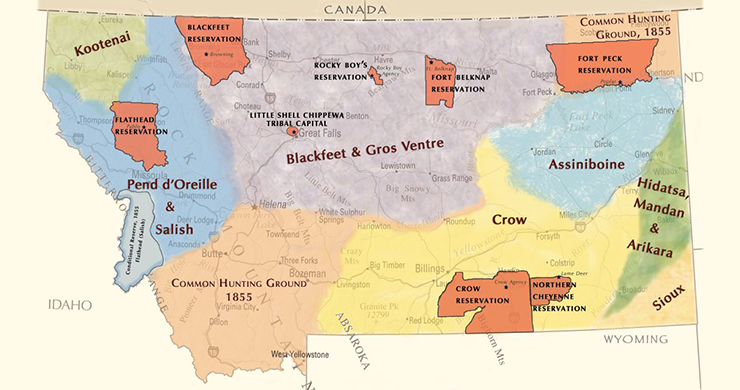
Navigating Montana’s Reservations: A Geographic Overview
Montana is home to seven federally recognized tribes: the Blackfeet Nation, the Crow Tribe, the Fort Belknap Indian Community, the Fort Peck Tribes, the Flathead Nation, the Northern Cheyenne Tribe, and the Rocky Boy’s Indian Reservation. Each reservation possesses its unique history, traditions, and governance structures.
The Blackfeet Nation: Situated in the northwestern corner of Montana, the Blackfeet Nation encompasses a vast territory, including Glacier National Park. Known for their skilled horsemanship and buffalo hunting, the Blackfeet have a rich history and cultural heritage that continues to thrive today.
The Crow Tribe: Located in southeastern Montana, the Crow Tribe has a strong connection to the land, particularly the Big Horn Mountains. Their culture is deeply intertwined with the landscape, and they have a long history of resistance and resilience.
The Fort Belknap Indian Community: Situated in north-central Montana, the Fort Belknap Indian Community is home to the Assiniboine and Gros Ventre tribes. Their culture is characterized by a strong sense of community and a deep respect for the natural world.
The Fort Peck Tribes: Located in northeastern Montana, the Fort Peck Tribes consist of the Assiniboine and Sioux tribes. Their culture is marked by a strong connection to the land and a tradition of self-governance.
The Flathead Nation: Located in western Montana, the Flathead Nation encompasses the Salish, Kootenai, and Pend d’Oreille tribes. Their culture is renowned for its artistry, storytelling, and connection to the natural world.
The Northern Cheyenne Tribe: Located in southeastern Montana, the Northern Cheyenne Tribe has a history of resilience and resistance. Their culture is characterized by their strong spiritual beliefs and their commitment to preserving their traditions.
The Rocky Boy’s Indian Reservation: Located in north-central Montana, the Rocky Boy’s Indian Reservation is home to the Chippewa Cree Tribe. Their culture is deeply rooted in the land and their traditions reflect a strong sense of community and family.
Beyond Geography: Understanding the Significance of Montana’s Reservations
Montana’s reservations are not merely geographical locations but vibrant cultural centers. They represent a legacy of resilience, self-determination, and cultural preservation. These communities have faced numerous challenges throughout history, including forced assimilation, displacement, and economic hardship. Yet, despite these obstacles, they have maintained their cultural identity and continue to thrive today.
Economic Contributions and Self-Governance:
Montana’s reservations play a significant role in the state’s economy through various enterprises, including tourism, agriculture, and gaming. They also contribute to the cultural landscape of Montana, attracting visitors from around the world who seek to experience their unique traditions and heritage.
Reservation governments are sovereign entities, operating under the framework of the Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act (ISDEAA). This autonomy empowers them to control their own affairs, including education, health care, and economic development.
Preserving Cultural Heritage:
Montana’s reservations are vital to the preservation of Native American culture. They are home to traditional languages, ceremonies, and art forms that have been passed down through generations. These traditions are a source of pride and identity for Native American communities and contribute to the richness of Montana’s cultural tapestry.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite the progress made in self-determination and cultural preservation, Montana’s reservations still face significant challenges. These include poverty, unemployment, inadequate infrastructure, and access to healthcare. However, these communities are also brimming with opportunities for economic development, education, and cultural revitalization.
FAQs about Montana’s Reservations
Q: What is the difference between a reservation and a tribe?
A: A tribe is a group of people who share a common culture, language, and history. A reservation is a designated area of land set aside by the federal government for the exclusive use of a particular tribe.
Q: Are reservations considered sovereign nations?
A: Reservations are considered sovereign entities, meaning they have a degree of self-governance and autonomy. However, their sovereignty is limited by federal law and treaties.
Q: What are the benefits of living on a reservation?
A: Living on a reservation offers a sense of community, cultural preservation, and access to tribal services. It also provides a connection to the land and a sense of belonging to a unique and vibrant heritage.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by Montana’s reservations?
A: Montana’s reservations face challenges such as poverty, unemployment, inadequate infrastructure, and access to healthcare. These challenges stem from historical injustices and ongoing economic disparities.
Tips for Visiting Montana’s Reservations
Respectful Engagement: When visiting a reservation, it is essential to approach the experience with respect and humility. Learn about the local customs and traditions, and be mindful of cultural sensitivities.
Supporting Local Businesses: Patronize local businesses and artisans on reservations to support the local economy and contribute to the community.
Seeking Permission: Before visiting sacred sites or participating in cultural ceremonies, always seek permission from the tribe or the appropriate authorities.
Learning and Engagement: Engage with local community members and learn about their history, culture, and perspectives. This will enrich your understanding of the reservation and foster a deeper appreciation for their heritage.
Conclusion
Montana’s reservations are a testament to the resilience and cultural richness of Native American communities. They offer a window into the past and a glimpse into the future, showcasing the enduring spirit of these vibrant cultures. Understanding the history, culture, and challenges of Montana’s reservations is essential for appreciating the state’s diverse heritage and fostering a more inclusive and respectful society.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Land of Diverse Cultures: Exploring Montana’s Reservations. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!