Ancient Greece on the World Map: A Cradle of Civilization
Related Articles: Ancient Greece on the World Map: A Cradle of Civilization
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Ancient Greece on the World Map: A Cradle of Civilization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Ancient Greece on the World Map: A Cradle of Civilization
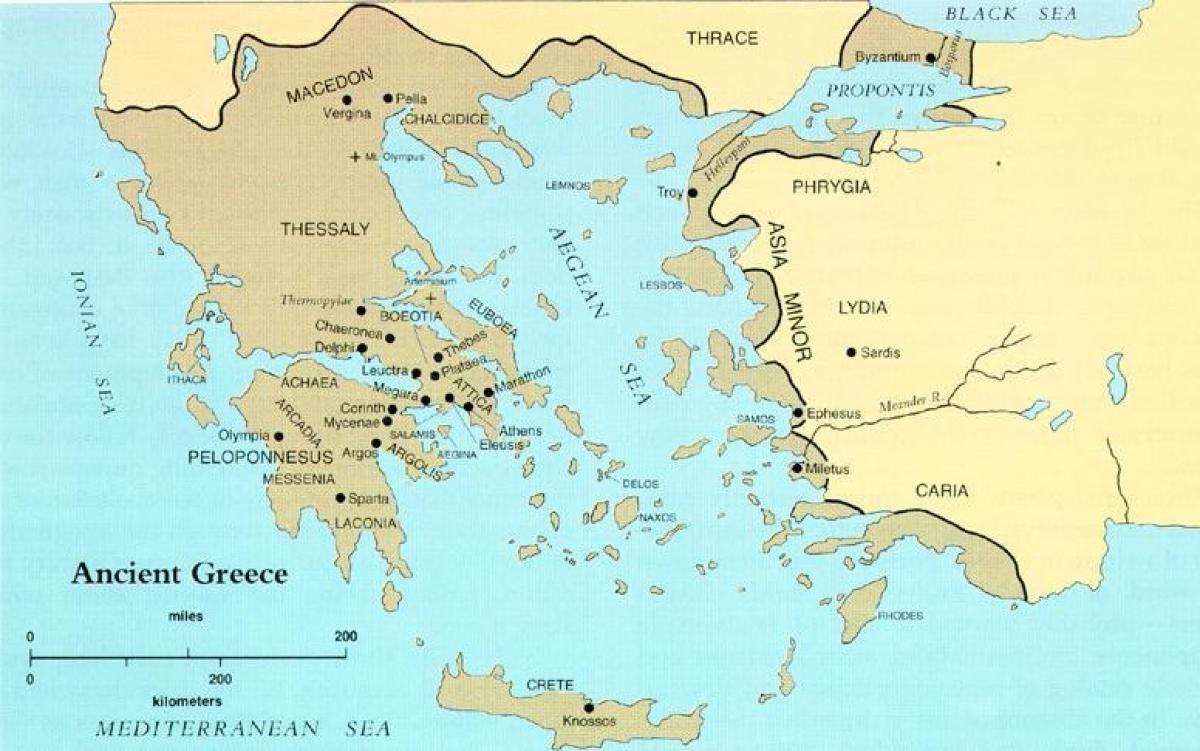
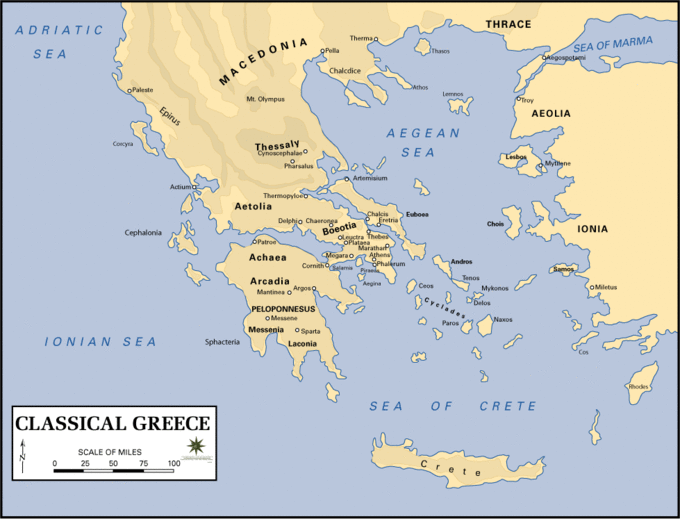
Ancient Greece, a region encompassing the southern Balkan Peninsula, the Aegean Islands, and parts of Asia Minor, holds a unique place in the tapestry of human history. Its influence on Western civilization is profound, shaping our languages, literature, art, philosophy, and even our understanding of democracy. To truly appreciate the impact of Ancient Greece, it is crucial to visualize its geographical context on a world map.
A Sea of Islands and Peninsulas:
Ancient Greece’s location played a pivotal role in its development. Situated at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa, it was a natural hub for trade and cultural exchange. The Aegean Sea, dotted with thousands of islands, provided ample opportunities for seafaring and commerce. The rugged terrain of the mainland, with its numerous mountain ranges, fostered the development of independent city-states, each with its own unique culture and political system.
The Rise of City-States:
From the 8th century BCE onwards, the Greek world was characterized by the rise of powerful city-states, such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth. These city-states were fiercely independent, often engaged in conflicts with one another. However, they also shared a common cultural heritage, language, and religious beliefs.
The Golden Age of Athens:
The 5th century BCE witnessed the Golden Age of Athens, a period marked by unprecedented cultural and intellectual flourishing. Under the leadership of Pericles, Athens became a center of art, literature, philosophy, and democracy. The Parthenon, a majestic temple dedicated to the goddess Athena, stands as a testament to this era’s architectural brilliance.
The Peloponnesian War:
The rivalry between Athens and Sparta, the two most powerful city-states, culminated in the devastating Peloponnesian War (431-404 BCE). The war, which ultimately led to the decline of Athenian power, had profound consequences for the entire Greek world.
Alexander the Great and the Hellenistic Era:
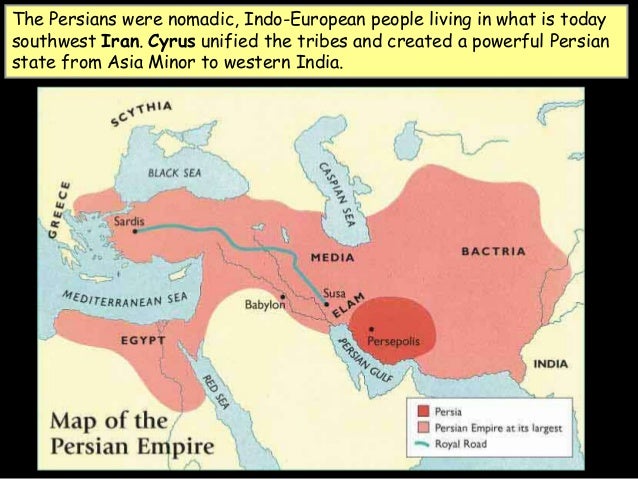
The conquests of Alexander the Great (356-323 BCE) marked a turning point in Greek history. Alexander’s vast empire, stretching from Greece to India, spread Greek culture and language across the ancient world. This era, known as the Hellenistic Period, saw the emergence of new centers of learning and cultural exchange, such as Alexandria in Egypt.
The Roman Conquest:
In 146 BCE, the Roman Republic conquered Greece, bringing an end to its independent existence. However, Greek culture continued to exert a powerful influence on Roman society, contributing to the development of Roman literature, art, and philosophy.
Ancient Greece’s Enduring Legacy:
The influence of Ancient Greece extends far beyond its geographical boundaries. Its contributions to philosophy, literature, art, mathematics, and science continue to shape our world today. The principles of democracy, the pursuit of knowledge, and the ideals of beauty and excellence, all trace their roots back to the ancient Greeks.
FAQs about Ancient Greece on the World Map:
Q: What are the main geographical features of Ancient Greece?
A: Ancient Greece encompassed the southern Balkan Peninsula, the Aegean Islands, and parts of Asia Minor. Its prominent features include the Aegean Sea, numerous islands, and rugged mountainous terrain.
Q: Why were city-states so important in Ancient Greece?
A: The mountainous terrain and the limited resources fostered the development of independent city-states, each with its own government, laws, and culture.
Q: What were the key characteristics of the Golden Age of Athens?
A: The Golden Age of Athens (5th century BCE) was a period of significant cultural and intellectual flourishing. It saw the rise of great philosophers, artists, and playwrights, as well as the development of democracy.
Q: What was the impact of the Peloponnesian War on Ancient Greece?
A: The Peloponnesian War (431-404 BCE) weakened the Greek city-states and ultimately led to the decline of Athenian power.
Q: How did Alexander the Great impact the spread of Greek culture?
A: Alexander’s conquests spread Greek culture and language across a vast empire, leading to the Hellenistic Period, characterized by cultural exchange and the emergence of new centers of learning.
Q: What was the significance of the Roman conquest of Greece?
A: The Roman conquest brought an end to Greek independence but also exposed Greek culture to a wider audience, influencing Roman society and contributing to the development of Roman civilization.
Tips for Understanding Ancient Greece on the World Map:
- Use a world map to trace the geographical boundaries of Ancient Greece.
- Identify the major city-states and their locations.
- Explore the Aegean Sea and its significance for trade and cultural exchange.
- Consider the impact of the mountainous terrain on the development of independent city-states.
- Research the historical events that shaped the Greek world, such as the Persian Wars, the Peloponnesian War, and the conquests of Alexander the Great.
Conclusion:
Ancient Greece, as seen on the world map, was not merely a geographical region but a vibrant civilization that left an indelible mark on human history. Its contributions to philosophy, art, literature, and political thought continue to inspire and shape our world today. By studying Ancient Greece, we gain valuable insights into the complexities of human culture and the enduring power of ideas.
![Ancient Cradles of civilization [1366x786] : r/geography](https://i.redd.it/8qqoksmo12z01.png)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/History_of_Greece_for_High_Schools_and_Academies_1899_14576880059-9b79528371d3443089862b67a1fbc002.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Ancient Greece on the World Map: A Cradle of Civilization. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!