Charting the Cradle of Civilization: Exploring the Importance of Early Civilization Maps
Related Articles: Charting the Cradle of Civilization: Exploring the Importance of Early Civilization Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Cradle of Civilization: Exploring the Importance of Early Civilization Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Cradle of Civilization: Exploring the Importance of Early Civilization Maps
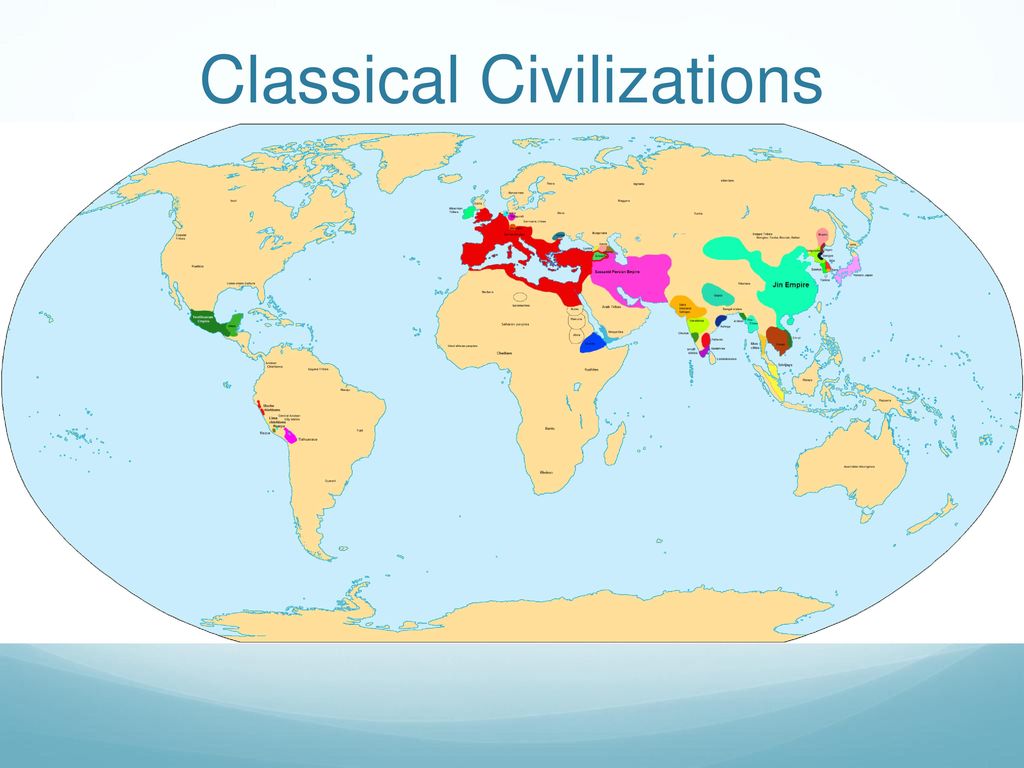
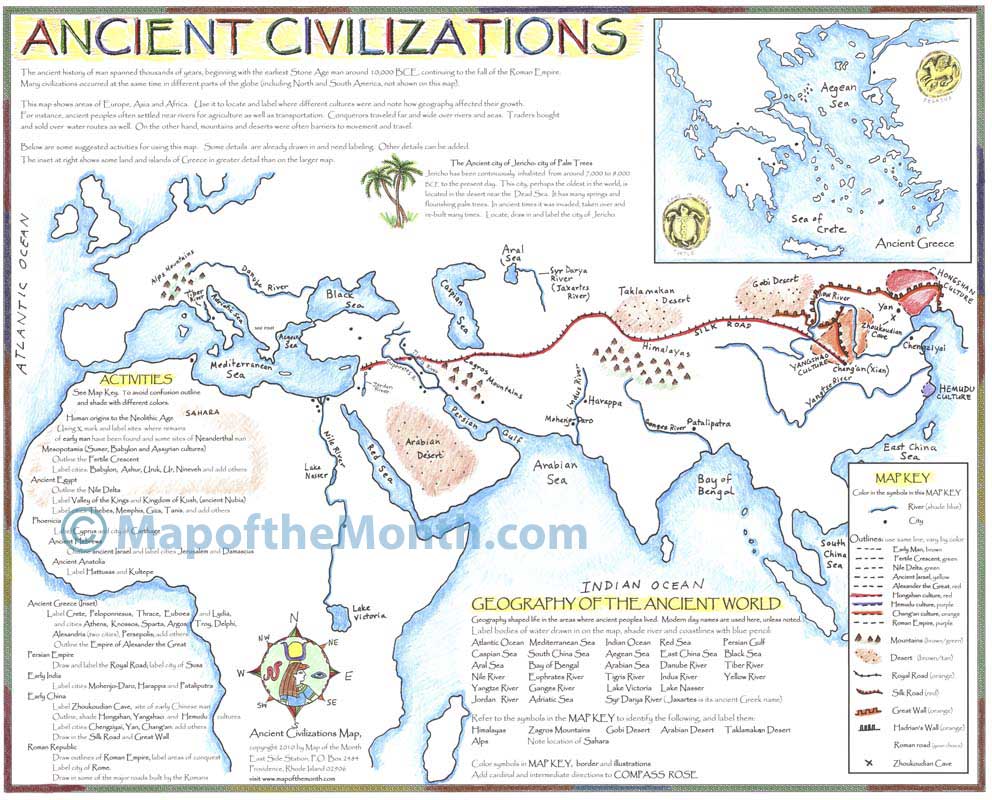
The study of history is fundamentally tied to the understanding of geography. Maps, as visual representations of space, play a crucial role in illuminating the rise and development of early civilizations. These "early civilization maps" serve as powerful tools for understanding the complex interplay of factors that led to the emergence of organized societies, the spread of ideas and technologies, and the interconnectedness of ancient cultures.
Understanding the Foundation of Civilization:
Early civilization maps are not mere static representations of landmasses. They are dynamic visualizations of the social, economic, and political landscapes that gave rise to the first cities, states, and empires. By studying these maps, historians and archaeologists gain insights into:
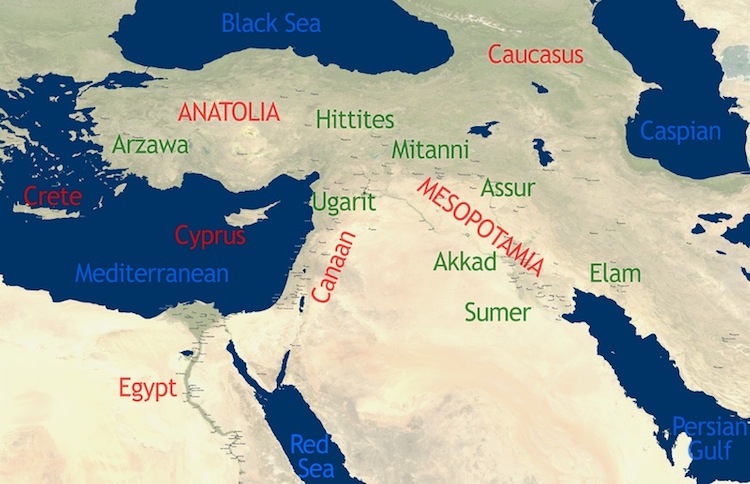
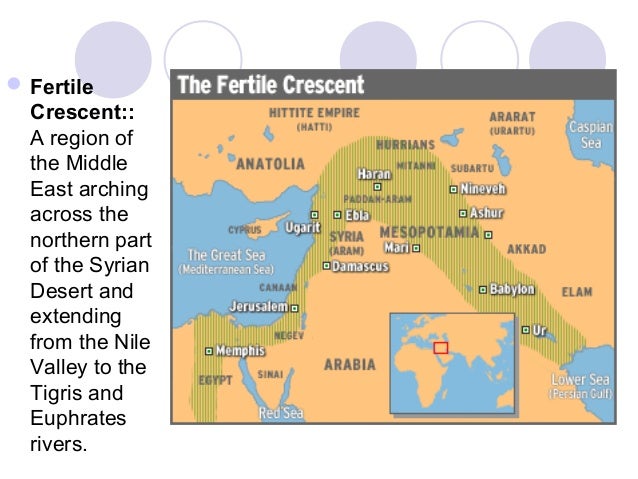
- Resource Distribution: Maps reveal the availability and distribution of essential resources, such as fertile land, water sources, and natural materials. This understanding helps explain the location of early settlements and the development of agricultural practices.
- Trade Networks: Trade routes, depicted on early civilization maps, showcase the interconnectedness of ancient societies. The flow of goods, ideas, and technologies along these routes shaped the cultural and economic development of civilizations.
- Political Boundaries: Maps illustrate the territorial extent of early states and empires, revealing the dynamics of power, conflict, and alliances. They provide crucial information on the rise and fall of empires, the expansion of political influence, and the formation of regional power structures.
- Cultural Diffusion: The spread of cultural practices, religious beliefs, and artistic styles can be traced through the movement of people and goods depicted on maps. These maps reveal the interconnectedness of ancient cultures and the influence of one civilization upon another.
Beyond the Physical Landscape:
Early civilization maps transcend the mere depiction of physical features. They offer a window into the intangible aspects of early societies, such as:
- Social Organization: Maps can reveal the distribution of population, the location of urban centers, and the organization of social classes, providing valuable insights into the social structures of ancient civilizations.
- Religious Beliefs: The location of sacred sites, temples, and pilgrimage routes on early civilization maps offers clues to the religious practices and beliefs of ancient societies.
- Technological Advancements: Maps can document the development and spread of key technologies, such as irrigation systems, writing, and metalworking, showcasing the ingenuity and innovation of early civilizations.
The Value of Early Civilization Maps:
The study of early civilization maps offers numerous benefits for understanding the past:
- Contextualization of Historical Events: Maps provide a spatial framework for understanding the context of historical events. They help to visualize the geographical factors that influenced political decisions, military campaigns, and cultural interactions.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Early civilization maps serve as a bridge between different academic disciplines, such as history, archaeology, geography, and anthropology. They foster collaboration and a holistic approach to understanding the past.
- Educational Value: Maps are powerful tools for teaching and learning. They provide a visual and engaging way to introduce students to the complexities of ancient civilizations and the interconnectedness of human history.
- Preservation and Conservation: The mapping of ancient sites and landscapes plays a crucial role in their preservation and conservation. By documenting these areas, we can better understand their historical significance and protect them for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: What are the earliest known civilization maps?
A: The earliest known maps depicting civilization are from ancient Mesopotamia, dating back to the 3rd millennium BCE. These maps, often inscribed on clay tablets, show city layouts, irrigation systems, and land ownership.
Q: How accurate are early civilization maps?
A: The accuracy of early civilization maps varies depending on the period and culture. Some maps are highly detailed and accurate, while others are more symbolic or schematic. Archaeological evidence and modern surveying techniques help to verify the accuracy of these maps.
Q: What are the challenges of interpreting early civilization maps?
A: Interpreting early civilization maps can be challenging due to:
- Lack of Standardized Symbols: Ancient mapmakers used different symbols and conventions, making interpretation difficult.
- Limited Data: Maps often represent a snapshot of a particular time period, making it difficult to fully understand the historical context.
- Cultural Bias: Maps may reflect the biases and perspectives of the mapmakers, influencing their representation of the world.
Tips for Studying Early Civilization Maps:
- Consider the Map’s Purpose: Understanding the intended audience and purpose of a map can help interpret its meaning.
- Analyze Symbols and Conventions: Pay attention to the symbols and conventions used on the map, as they provide clues to the mapmaker’s intent.
- Compare with Other Sources: Compare the map with other historical sources, such as texts and archaeological evidence, to gain a more complete understanding.
- Recognize Limitations: Be aware of the limitations of early civilization maps, such as their accuracy and potential biases.
Conclusion:
Early civilization maps are indispensable tools for understanding the rise and development of ancient societies. They provide a visual and spatial framework for understanding the interconnectedness of human history, the dynamics of power, and the complex interplay of factors that shaped the world we live in today. By studying these maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the ingenuity, resilience, and interconnectedness of ancient civilizations, offering invaluable insights into the human story.

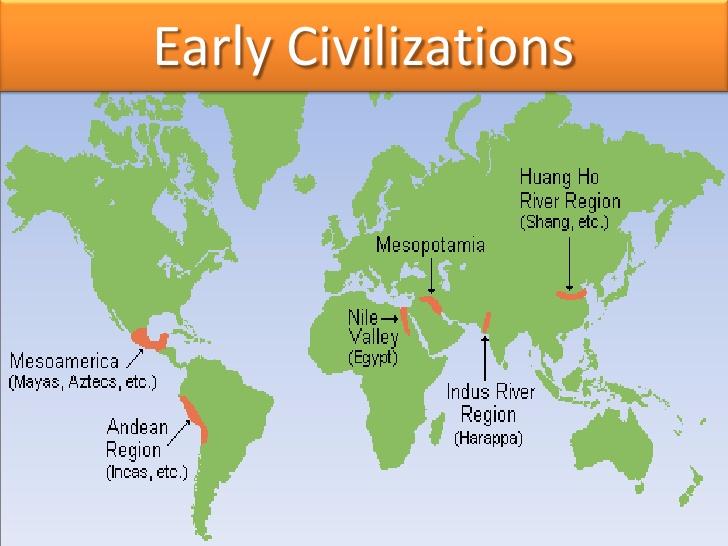
.png/390px-Indus_Valley_Civilization%2C_Mature_Phase_(2600-1900_BCE).png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Cradle of Civilization: Exploring the Importance of Early Civilization Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!