EDC Map 2021: A Comprehensive Guide to the Future of Electronic Data Capture
Related Articles: EDC Map 2021: A Comprehensive Guide to the Future of Electronic Data Capture
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to EDC Map 2021: A Comprehensive Guide to the Future of Electronic Data Capture. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
EDC Map 2021: A Comprehensive Guide to the Future of Electronic Data Capture
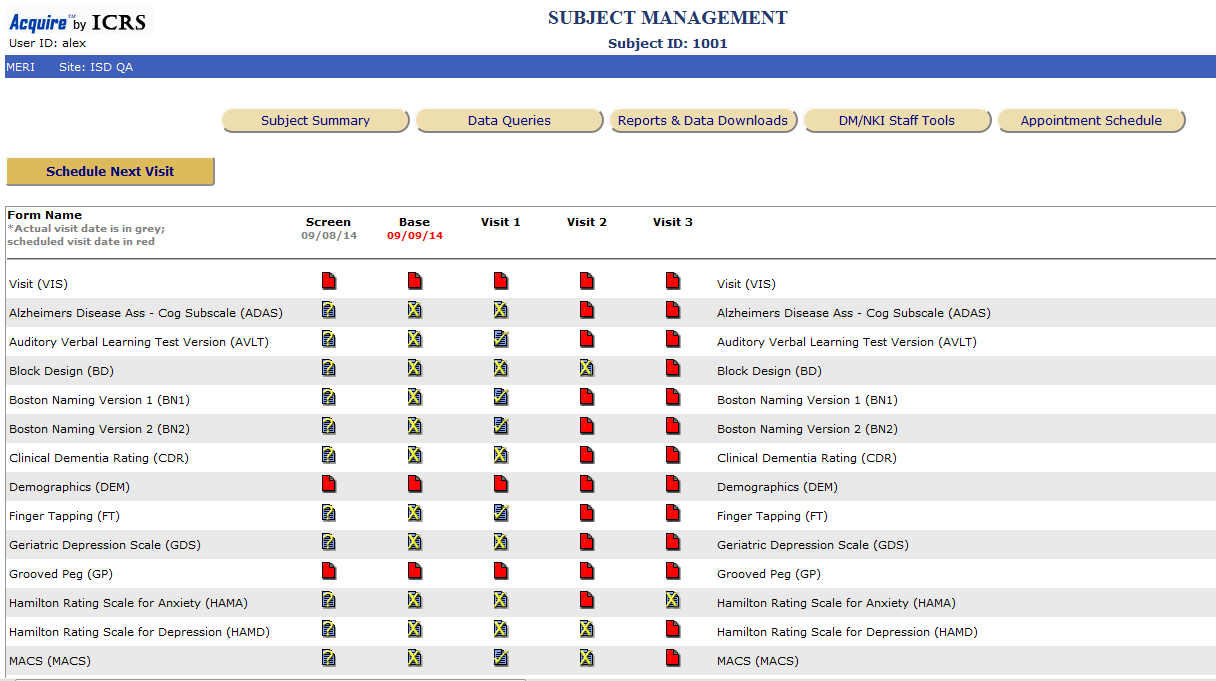
Electronic Data Capture (EDC) has revolutionized clinical research by streamlining data collection, improving accuracy, and accelerating the development of new treatments. EDC maps are crucial tools in this process, providing a visual representation of the data flow and relationships within a clinical trial.
The EDC map for 2021 reflects the evolution of EDC technology, incorporating advancements in data security, interoperability, and user-friendliness. This comprehensive guide explores the key features and benefits of EDC maps in 2021, highlighting their significance in facilitating efficient and effective clinical trials.
Understanding EDC Maps: A Visual Blueprint for Data Management
An EDC map is a graphical representation of the data collection process within a clinical trial. It depicts the flow of data from its origin (e.g., patient records, lab results) to its destination (e.g., data analysis, regulatory submissions). This visual representation offers a clear understanding of:
- Data Sources: The map identifies the various sources from which data is collected, such as patient questionnaires, electronic medical records, or laboratory instruments.
- Data Fields: It outlines the specific data elements collected for each source, ensuring comprehensive data capture.
- Data Relationships: The map illustrates how different data points are interconnected, enabling the identification of potential dependencies and inconsistencies.
- Data Validation Rules: It highlights the rules and checks applied to ensure data accuracy and consistency throughout the collection process.
- Data Flow: The map visualizes the path data takes as it moves through different stages of the trial, from collection to analysis and reporting.
Key Features and Benefits of EDC Maps in 2021
EDC maps in 2021 incorporate several advancements that enhance their functionality and benefit clinical research:
- Enhanced Security: The maps integrate advanced security features, ensuring data integrity and protecting sensitive patient information. This includes encryption, access controls, and audit trails to track all data modifications.
- Improved Interoperability: Modern EDC maps seamlessly integrate with other systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and laboratory information systems (LIS), enabling data exchange and reducing manual data entry.
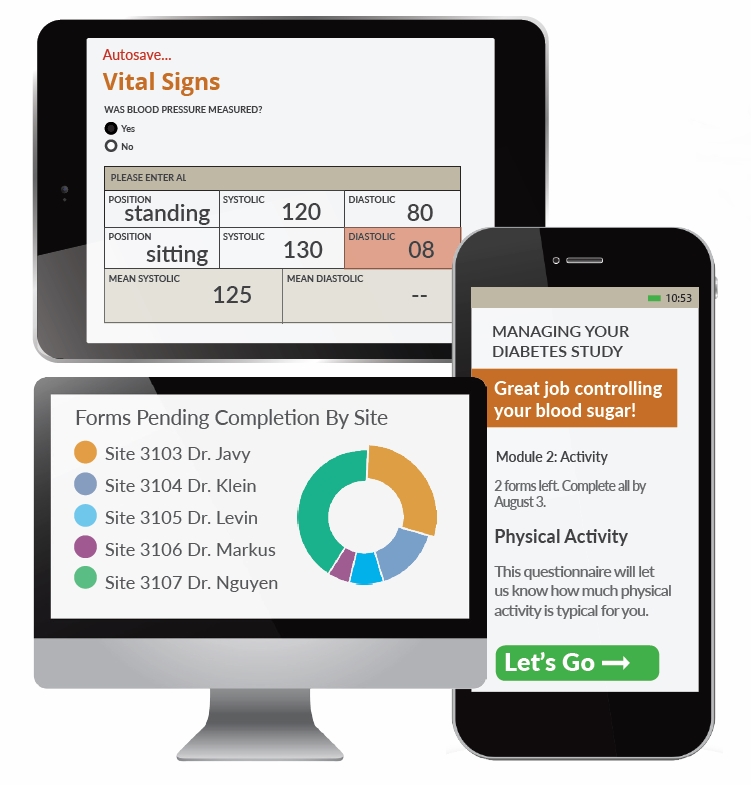
- User-Friendly Interfaces: The maps are designed with user-friendliness in mind, offering intuitive navigation and clear visual representations. This facilitates easy data access and comprehension for both researchers and data managers.
- Real-time Data Monitoring: EDC maps enable real-time monitoring of data collection progress, allowing researchers to identify potential issues and take corrective measures promptly. This reduces delays and improves overall trial efficiency.
- Data Standardization and Consistency: The maps promote data standardization and consistency across different sites and studies, ensuring that data is collected in a uniform and accurate manner.
The Importance of EDC Maps in Clinical Research
EDC maps play a pivotal role in clinical research, offering numerous benefits that contribute to the success of trials:
- Improved Data Quality: By streamlining data collection and implementing validation rules, EDC maps contribute to data accuracy and minimize errors.
- Increased Efficiency: Automated data capture and processing reduce manual tasks, freeing up researchers to focus on data analysis and interpretation.
- Reduced Costs: By improving efficiency and minimizing errors, EDC maps contribute to cost savings in clinical research.
- Faster Trial Completion: Efficient data management and real-time monitoring accelerate the trial process, leading to faster completion and timelier results.
- Enhanced Compliance: EDC maps ensure data integrity and compliance with regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of audit findings.
FAQs Regarding EDC Maps
Q: What are the different types of EDC maps available?
A: There are various types of EDC maps, each tailored to specific needs. Some common types include:
- Data Flow Maps: These maps illustrate the movement of data from its source to its destination.
- Data Dictionary Maps: These maps define the data elements collected in a trial, including their names, data types, and validation rules.
- System Integration Maps: These maps depict the integration of EDC systems with other applications, such as EHRs and LIS.
Q: How are EDC maps created?
A: EDC maps are typically created using specialized software tools that allow users to visually design and configure the data flow and relationships. These tools often provide templates and pre-defined elements to streamline the map creation process.
Q: Who benefits from using EDC maps?
A: EDC maps benefit various stakeholders involved in clinical research, including:
- Researchers: They provide a clear understanding of the data collection process, enabling efficient data analysis and interpretation.
- Data Managers: They offer a comprehensive overview of data flow and relationships, facilitating data management and quality control.
- Sponsors: They provide a visual representation of the trial’s data infrastructure, ensuring data integrity and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Regulators: They offer transparency into the data collection process, facilitating review and approval of clinical trials.
Tips for Effective EDC Map Implementation
- Involve all stakeholders: Ensure that researchers, data managers, and sponsors are actively involved in the EDC map creation process.
- Define clear objectives: Clearly define the goals of the EDC map to ensure it meets the specific needs of the clinical trial.
- Use standardized terminology: Employ consistent naming conventions and data definitions throughout the map.
- Regularly review and update: Periodically review the EDC map to ensure it remains accurate and reflects any changes in the trial design or data collection procedures.
- Provide training: Offer comprehensive training to all users on the EDC map and its functionalities.
Conclusion
EDC maps are indispensable tools in modern clinical research, facilitating efficient data management, enhancing data quality, and accelerating the development of new treatments. By embracing the advancements in EDC technology, researchers and data managers can leverage the power of EDC maps to streamline their operations, improve trial outcomes, and ultimately contribute to the advancement of medical science.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into EDC Map 2021: A Comprehensive Guide to the Future of Electronic Data Capture. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!