Europe in the Grip of War: A Geographical Perspective on 1942
Related Articles: Europe in the Grip of War: A Geographical Perspective on 1942
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Europe in the Grip of War: A Geographical Perspective on 1942. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Europe in the Grip of War: A Geographical Perspective on 1942
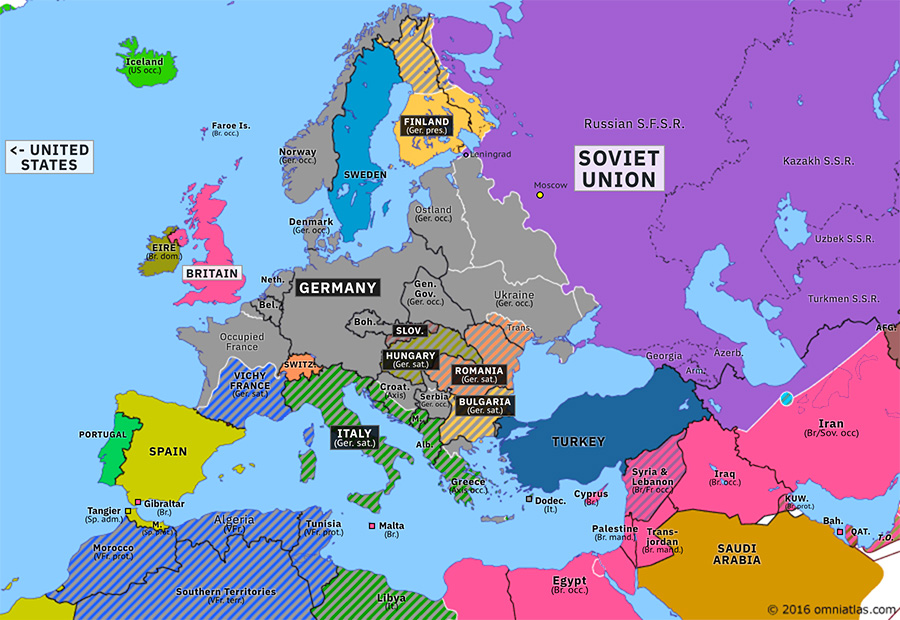
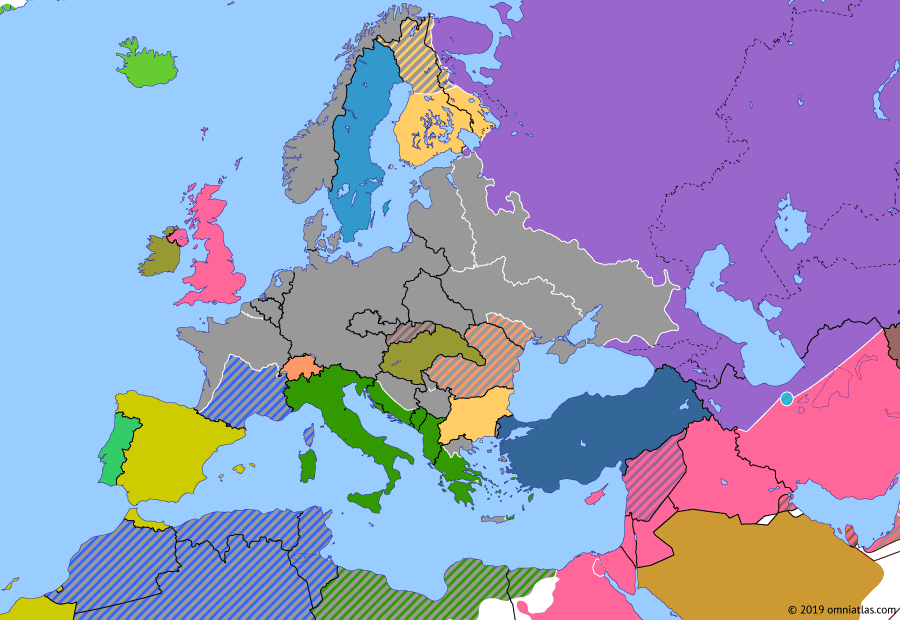
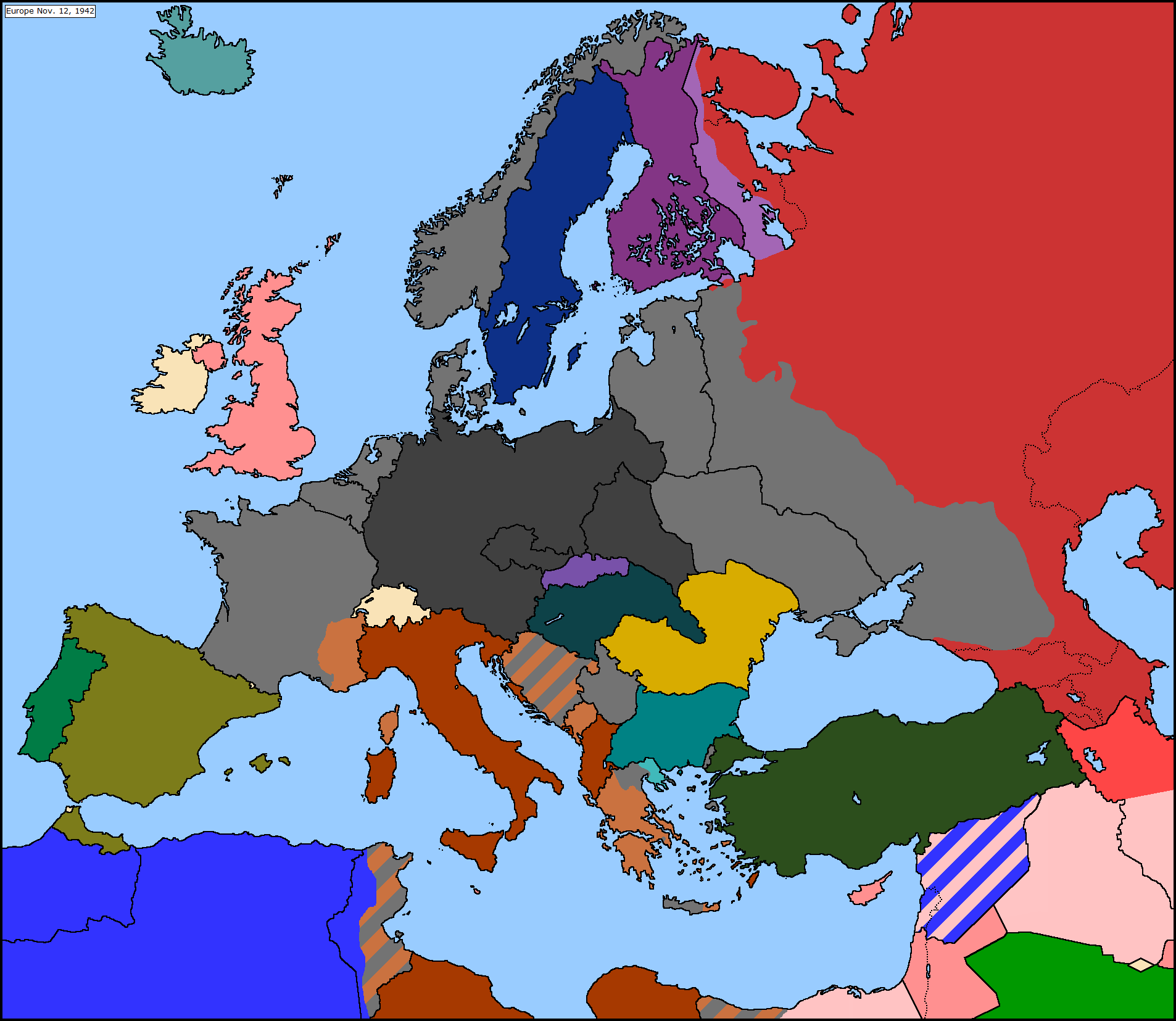
The year 1942 marked a pivotal point in World War II, with the conflict raging across Europe and beyond. Understanding the map of Europe in 1942 provides a crucial lens through which to analyze the strategic landscape of the war, the shifting power dynamics, and the immense human suffering it inflicted.
A Continent Divided:
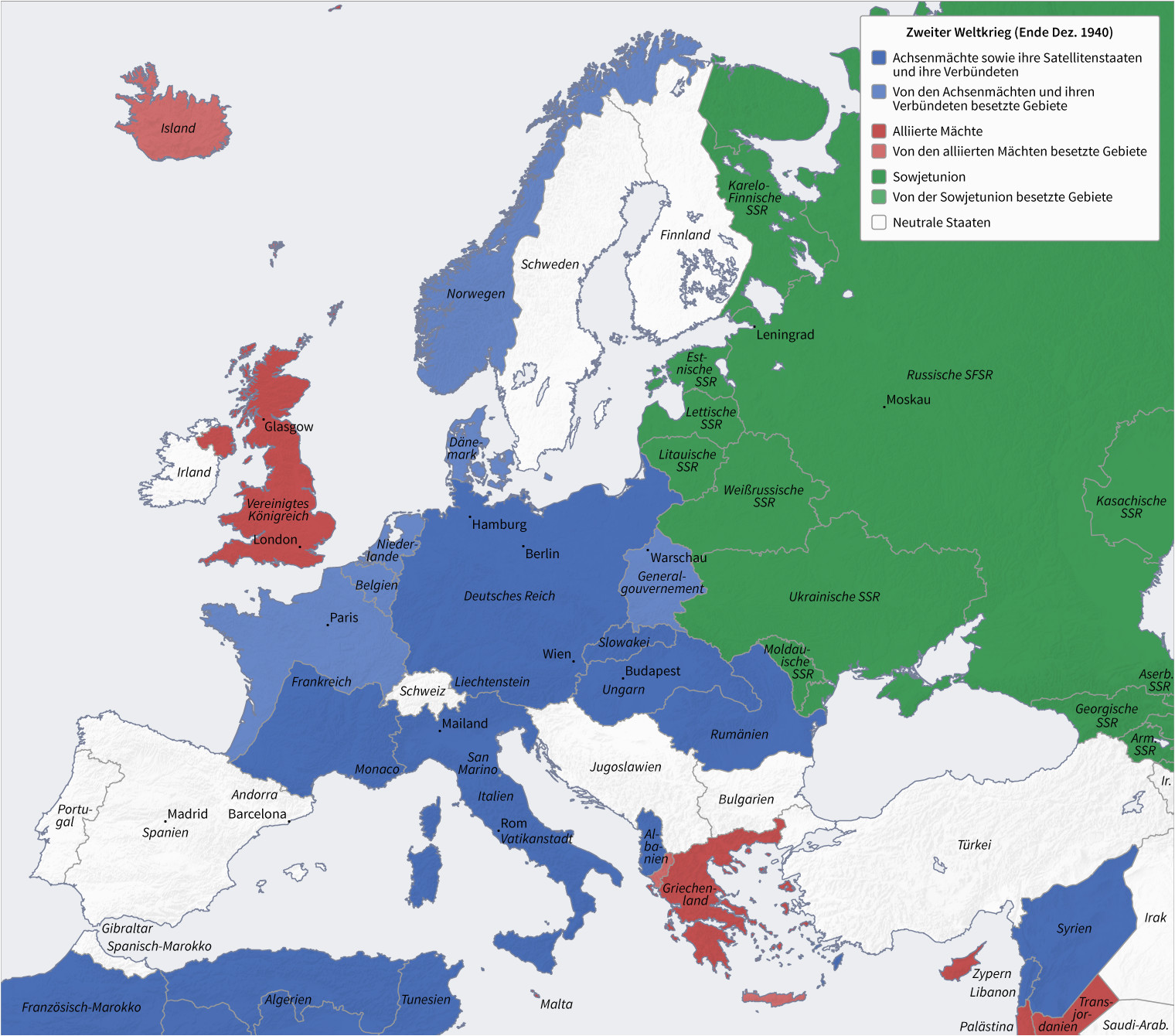
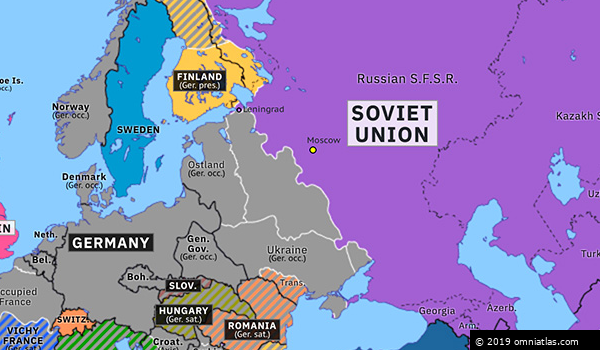
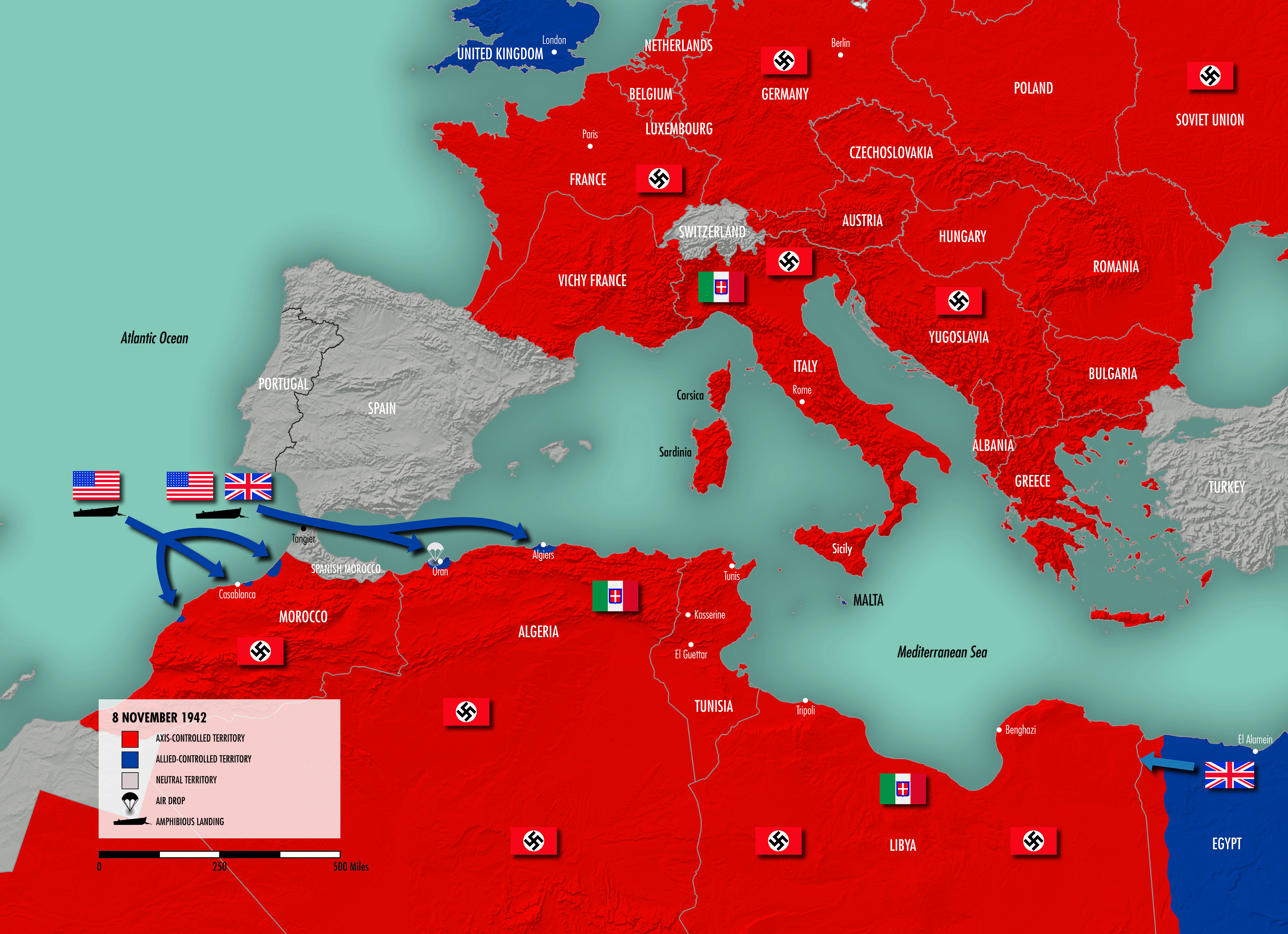
The map of Europe in 1942 reveals a continent deeply divided. The Axis powers, led by Germany, Italy, and Japan, had secured significant territorial gains. Nazi Germany dominated much of mainland Europe, stretching from the Atlantic coast to the eastern borders of the Soviet Union. The German-occupied territories included France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Denmark, Norway, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Austria, and much of the Balkans. Italy controlled Albania, Greece, and parts of Yugoslavia.
The Eastern Front: A Brutal Struggle:
The Eastern Front, the theatre of war between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union, was the most brutal and devastating front of the war. In 1942, the German Wehrmacht launched Operation Barbarossa, aiming to capture the Soviet capital of Moscow and cripple the Soviet war machine. While the initial advance was successful, the German forces faced fierce resistance from the Red Army and were ultimately defeated in the Battle of Moscow. The Eastern Front became a bloody stalemate, with millions of casualties on both sides.
The Western Front: A Defensive Stance:
The Western Front, characterized by a stalemate between the Axis and Allied forces, remained relatively quiet in 1942. While Germany occupied France, the British and their allies were preparing for a counteroffensive. The Allied forces launched raids on German-occupied territories and conducted air warfare, but major land battles were limited.
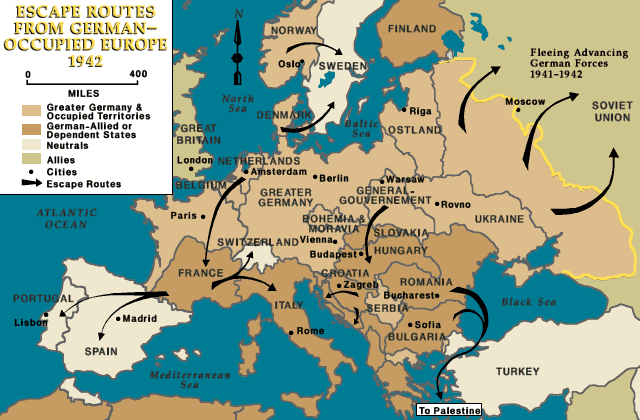
The Rise of Resistance:
Despite the overwhelming power of the Axis, resistance movements emerged across occupied Europe. These groups, often operating in secret, engaged in sabotage, espionage, and propaganda, undermining the Axis occupation and providing vital support to the Allied cause.
The Global Reach of War:
The war in Europe was not confined to the continent. The Axis powers, particularly Japan, had expanded their reach into Asia and the Pacific. Japan’s conquests in Southeast Asia and the Pacific islands had a significant impact on the global balance of power.
The Impact of the War:
The map of Europe in 1942 reflects the devastating impact of the war on the continent. Millions of people were displaced from their homes, forced to flee the violence, and subjected to persecution and brutality. The war also led to the destruction of infrastructure, economies, and cultural heritage.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What were the key strategic objectives of Germany in 1942?
A: Germany’s strategic objectives in 1942 were to secure control over the Soviet Union’s resources, defeat the Soviet Union, and establish a dominant position in Europe.
Q: How did the war affect the lives of ordinary Europeans?
A: The war had a profound impact on the lives of ordinary Europeans. Many were forced to live under occupation, facing restrictions on their freedoms, food shortages, and the threat of violence.
Q: What role did the United States play in the war in 1942?
A: The United States entered the war in 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. In 1942, the US provided crucial military and economic support to the Allies, particularly in the Pacific theater.
Q: What were the main factors contributing to the Allied victory in the war?
A: The Allied victory was the result of a combination of factors, including the resilience of the Soviet Union, the strategic brilliance of Allied leaders, the increasing industrial capacity of the Allies, and the growing strength of the resistance movements.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Europe in 1942:
- Focus on the key battlefronts: The Eastern Front and the Western Front were the most significant theaters of war in 1942.
- Pay attention to the shifting borders: The map of Europe in 1942 was constantly changing as the Axis forces advanced and retreated.
- Consider the impact of occupation: The German occupation had a profound impact on the lives of people living in occupied territories.
- Recognize the role of resistance movements: Resistance movements played a crucial role in undermining the Axis occupation.
Conclusion:
The map of Europe in 1942 provides a powerful reminder of the devastating impact of World War II on the continent. It highlights the strategic complexities of the war, the shifting power dynamics, and the immense human cost. Understanding this map is essential for grasping the historical context of the war and its enduring legacy.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Europe in the Grip of War: A Geographical Perspective on 1942. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!