Europe’s Peninsulas: A Geographic Tapestry of Diversity
Related Articles: Europe’s Peninsulas: A Geographic Tapestry of Diversity
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Europe’s Peninsulas: A Geographic Tapestry of Diversity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Europe’s Peninsulas: A Geographic Tapestry of Diversity

Europe’s physical geography is defined by its intricate coastline, characterized by numerous peninsulas, each a unique tapestry of land and water. These protrusions of land into the surrounding seas have played a pivotal role in shaping Europe’s history, culture, and environment.
The Significance of Peninsulas
Peninsulas, by their very nature, offer distinct advantages and challenges. Their coastal location fosters maritime trade and cultural exchange, while the surrounding waters provide access to fishing and natural resources. However, peninsulas often face challenges in terms of transportation and communication, as they are geographically isolated from the mainland.
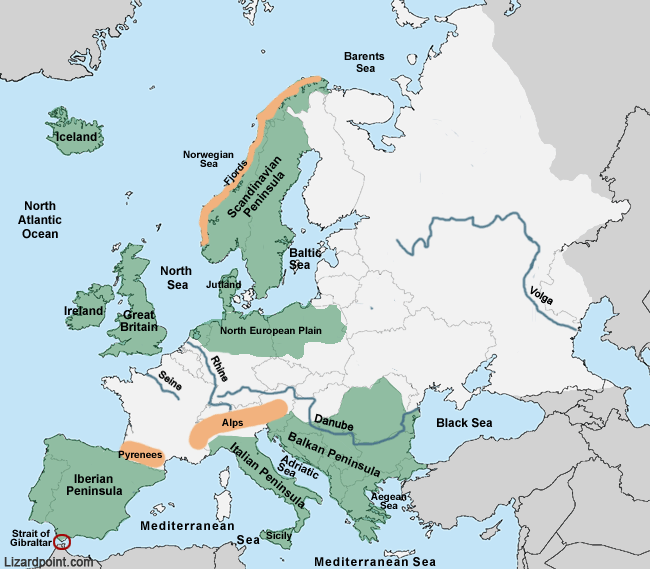
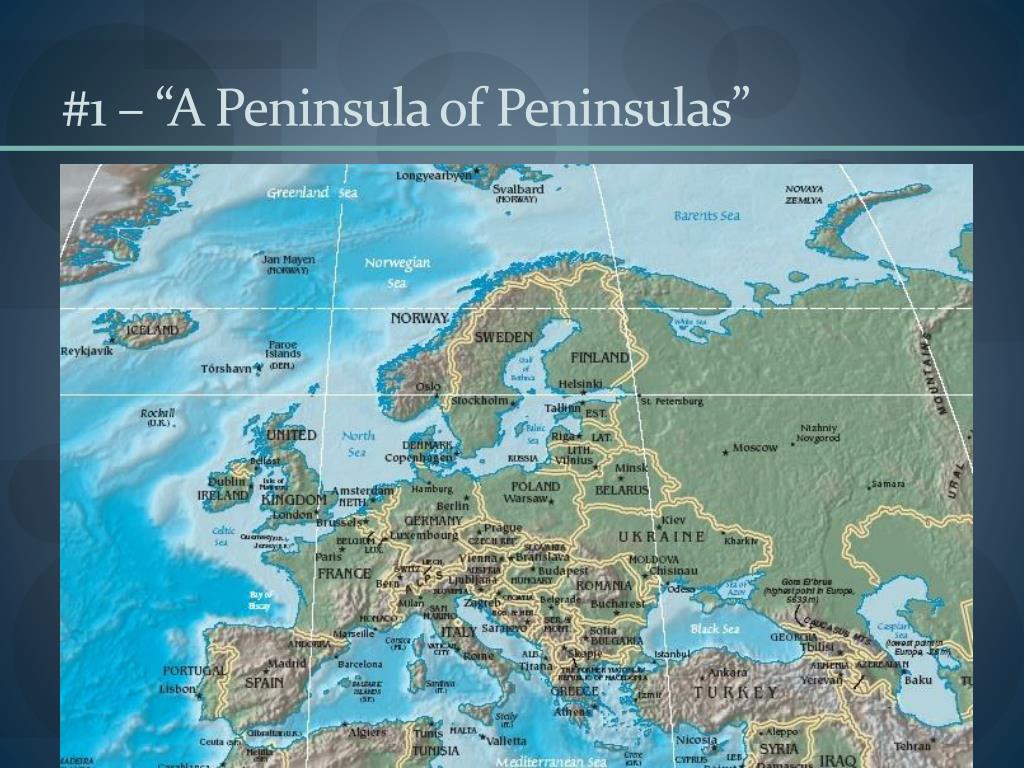
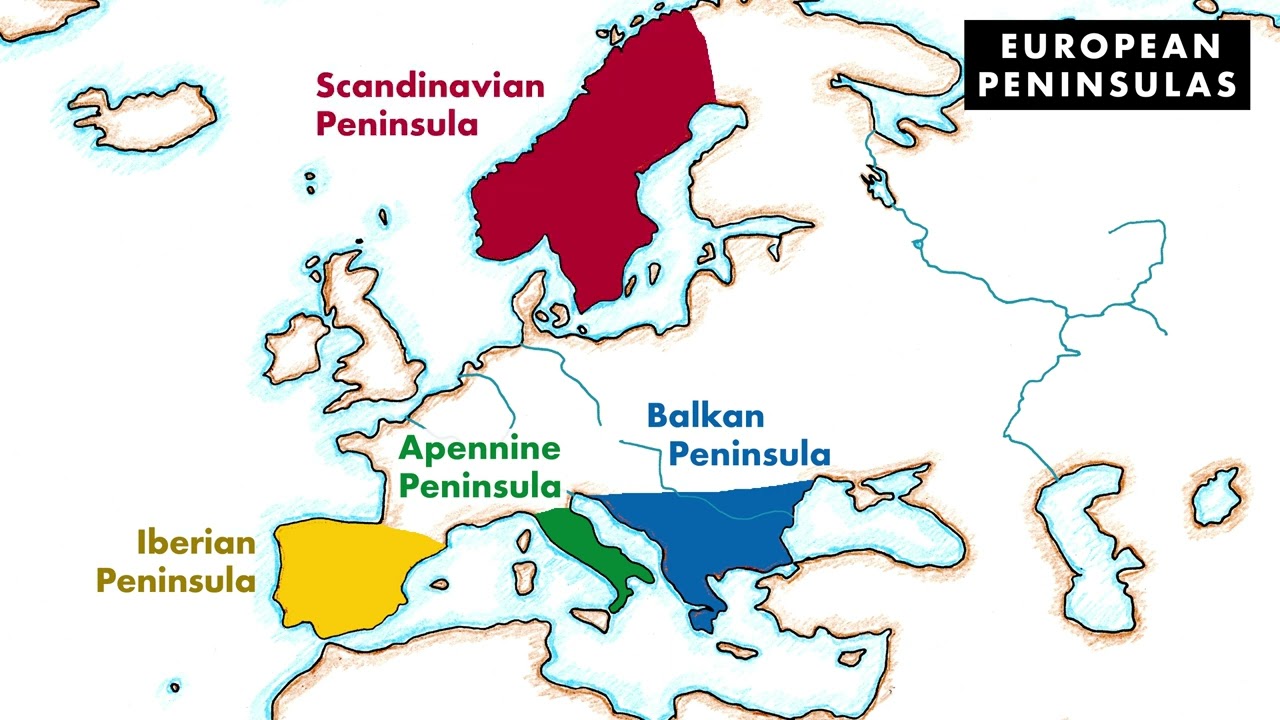
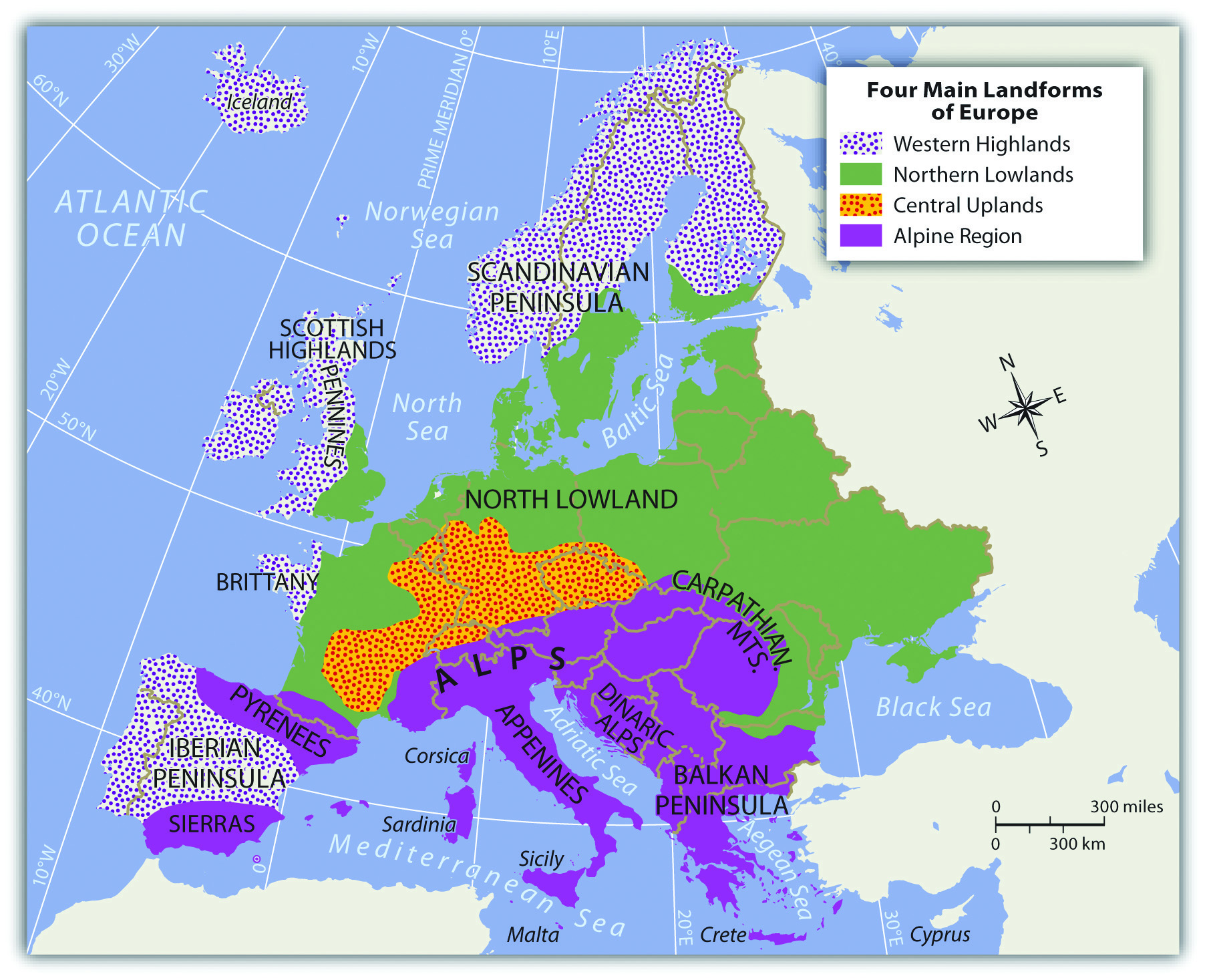
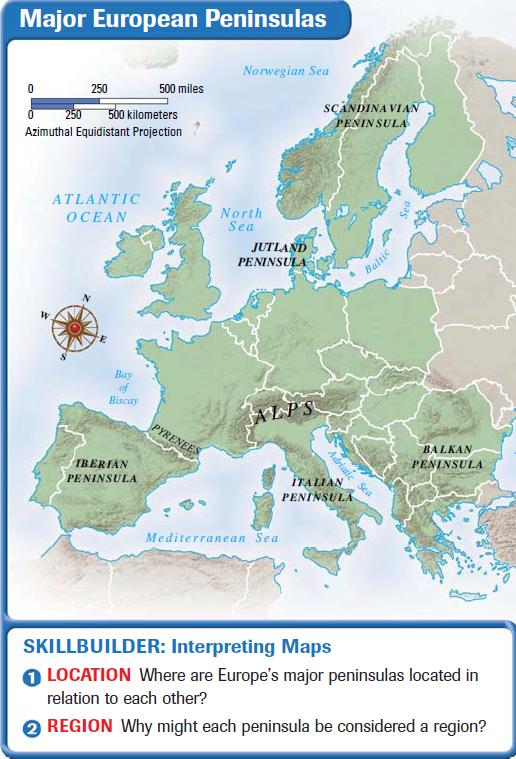
A Geographic Overview of Europe’s Peninsulas
Europe boasts a remarkable array of peninsulas, each with its own distinct characteristics:
- Iberian Peninsula: Situated in southwestern Europe, the Iberian Peninsula is home to Spain and Portugal. It is separated from mainland Europe by the Pyrenees Mountains and bordered by the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Bay of Biscay. This peninsula is characterized by its diverse landscape, including mountains, plains, and coastal areas. Its strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Africa has made it a focal point of historical and cultural interaction.
- Italian Peninsula: Extending into the Mediterranean Sea, the Italian Peninsula is defined by its boot-shaped outline. It encompasses Italy, San Marino, and Vatican City. The peninsula’s mountainous terrain and fertile plains have fostered a rich agricultural tradition, while its coastal location has facilitated maritime trade and cultural exchange.
- Balkan Peninsula: Located in southeastern Europe, the Balkan Peninsula is a complex and diverse region encompassing countries like Greece, Albania, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Romania. The peninsula’s mountainous terrain and numerous rivers have shaped its cultural identity and played a role in its political history.
- Scandinavian Peninsula: Situated in northern Europe, the Scandinavian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in Europe, encompassing Norway and Sweden. The peninsula is dominated by the Scandinavian Mountains, which provide stunning natural beauty and abundant natural resources.
- Jutland Peninsula: Located in northern Europe, the Jutland Peninsula is the southernmost part of Denmark. It is separated from the rest of mainland Europe by the narrow straits of the Little Belt and the Great Belt. The peninsula is characterized by its flat landscape and fertile soil, making it an important agricultural region.
- Crimea Peninsula: Located in southeastern Europe, the Crimean Peninsula extends into the Black Sea. It is a region with a complex and contested history, having been part of Russia, Ukraine, and various empires throughout the centuries. The peninsula is known for its diverse landscape, including mountains, plains, and coastal areas.
- Apennine Peninsula: Situated in southern Europe, the Apennine Peninsula is a sub-peninsula of the Italian Peninsula. It encompasses the regions of Lazio, Abruzzo, Molise, Campania, Puglia, Basilicata, and Calabria. The peninsula is characterized by its mountainous terrain, fertile valleys, and coastal areas.
The Impact of Peninsulas on Europe’s History and Culture
Europe’s peninsulas have played a pivotal role in shaping the continent’s history and culture. Their strategic locations have made them important centers of trade, cultural exchange, and political power.
- Trade and Commerce: The peninsulas of Europe have long been centers of maritime trade. Their coastal locations have facilitated the movement of goods and ideas across the Mediterranean Sea, the Atlantic Ocean, and the Baltic Sea. This trade has contributed to the growth of cities, the development of industries, and the spread of cultural influences.
- Cultural Exchange: The peninsulas of Europe have been crossroads of cultures, where different civilizations have interacted and exchanged ideas. This exchange has enriched the cultural landscape of Europe, contributing to the development of art, literature, music, and philosophy.
- Political Power: The peninsulas of Europe have often played a significant role in political history. Their strategic locations have made them targets for conquest and have influenced the balance of power in Europe.
FAQs by Peninsulas in Europe Map
1. What are the largest peninsulas in Europe?
The largest peninsulas in Europe are the Scandinavian Peninsula and the Iberian Peninsula.
2. What is the significance of the Iberian Peninsula?
The Iberian Peninsula has been a major center of trade, cultural exchange, and political power throughout history. Its strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Africa has made it a focal point of interaction between different civilizations.
3. What are the main geographical features of the Italian Peninsula?
The Italian Peninsula is characterized by its boot-shaped outline, mountainous terrain, fertile plains, and coastal areas.
4. What is the significance of the Balkan Peninsula?
The Balkan Peninsula is a complex and diverse region with a rich history and culture. Its mountainous terrain and numerous rivers have shaped its cultural identity and played a role in its political history.
5. What are the main geographical features of the Scandinavian Peninsula?
The Scandinavian Peninsula is dominated by the Scandinavian Mountains, which provide stunning natural beauty and abundant natural resources.
6. What is the significance of the Jutland Peninsula?
The Jutland Peninsula is an important agricultural region with a flat landscape and fertile soil.
7. What is the significance of the Crimea Peninsula?
The Crimean Peninsula is a region with a complex and contested history, having been part of Russia, Ukraine, and various empires throughout the centuries.
8. What are the main geographical features of the Apennine Peninsula?
The Apennine Peninsula is characterized by its mountainous terrain, fertile valleys, and coastal areas.
Tips by Peninsulas in Europe Map
- Utilize the map to understand the geographical context of each peninsula. This will help you visualize the relative size and location of each peninsula, as well as its relationship to surrounding landmasses and bodies of water.
- Focus on the key geographical features of each peninsula. This includes mountains, rivers, plains, and coastal areas. Understanding these features will help you appreciate the unique characteristics of each peninsula and its role in shaping the surrounding region.
- Consider the historical and cultural significance of each peninsula. The peninsulas of Europe have played a pivotal role in shaping the continent’s history and culture. By understanding their historical and cultural significance, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity of Europe.
Conclusion by Peninsulas in Europe Map
Europe’s peninsulas are not merely geographical features, but rather vital components of the continent’s history, culture, and environment. They are testaments to the intricate interplay of land and water, shaping the diverse landscape and rich cultural tapestry of Europe. Understanding the significance of these peninsulas provides a deeper appreciation for the complexities and richness of Europe’s past, present, and future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Europe’s Peninsulas: A Geographic Tapestry of Diversity. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!