Mapping the Great War: Germany’s Territorial Ambitions and Strategic Challenges in World War I
Related Articles: Mapping the Great War: Germany’s Territorial Ambitions and Strategic Challenges in World War I
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Great War: Germany’s Territorial Ambitions and Strategic Challenges in World War I. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Great War: Germany’s Territorial Ambitions and Strategic Challenges in World War I

World War I, a conflict of unprecedented scale and devastation, reshaped the geopolitical landscape of Europe. At its heart lay Germany, a nation driven by expansionist ambitions and a desire to assert its dominance on the continent. Understanding the war’s unfolding through the lens of maps provides a crucial insight into the strategic complexities and territorial shifts that defined the conflict.
Germany’s Geographic Position and Initial Objectives:
Germany, situated in the heart of Europe, possessed a strategic location that facilitated both expansion and vulnerability. Its borders with France, Russia, and Austria-Hungary made it a potential flashpoint for conflict. Germany’s initial war aims were driven by a desire to secure its position as a dominant power. These objectives included:
- Expansion into Eastern Europe: Germany sought to establish control over territories in Poland, Lithuania, and Ukraine, hoping to secure access to raw materials and create a buffer zone against Russia.
- Domination of the North Sea: Control over the North Sea was crucial for Germany’s economic and military ambitions. This included securing access to vital shipping lanes and establishing naval superiority.
- Elimination of French threat: Germany aimed to weaken France, its traditional rival, by seizing territories in Alsace-Lorraine and potentially pushing further into French territory.
The Western Front: A Stalemate of Trenches and Attrition:
Germany’s initial offensive strategy, aimed at a swift victory through a decisive breakthrough, ultimately failed. The Western Front, characterized by elaborate trench systems and brutal artillery bombardments, evolved into a stalemate. The Schlieffen Plan, Germany’s military strategy, aimed to swiftly defeat France before Russia could mobilize. However, the plan faltered due to logistical challenges and the unexpected resistance of the French and British forces.
The Eastern Front: A Shifting Battlefield:
The Eastern Front, characterized by its vast expanse and fluidity, witnessed a constant ebb and flow of battles. Germany, allied with Austria-Hungary, initially achieved significant victories against Russia. However, the Russian Empire, despite its logistical and strategic shortcomings, possessed a vast manpower reserve. The Eastern Front ultimately became a drain on Germany’s resources, leading to a gradual decline in its military strength.
The Importance of Maps in Understanding the War:
Maps are essential tools for understanding the complexities of World War I. They provide visual representations of:
- Battlefronts and troop movements: Maps illustrate the shifting lines of battle, highlighting areas of intense fighting and strategic maneuvers.
- Strategic objectives and territorial gains: Maps depict the territorial ambitions of warring nations, showcasing their expansionist goals and the areas they sought to control.
- Logistical challenges and supply lines: Maps reveal the logistical difficulties faced by armies, highlighting the importance of transportation routes and supply networks.
- Impact of geography on warfare: Maps demonstrate how geographical features, such as rivers, mountains, and forests, influenced military operations and strategic decisions.
Key Maps of World War I:
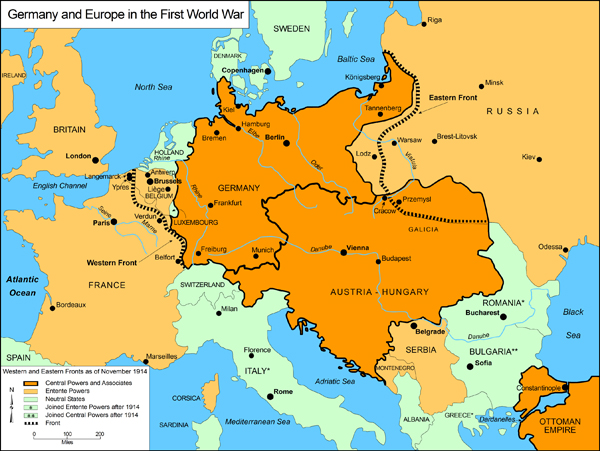
- Map of Europe in 1914: This map illustrates the pre-war political landscape of Europe, highlighting the alliances and tensions that led to the outbreak of war.
- Map of the Western Front: This map depicts the intricate network of trenches, fortifications, and battlefields that characterized the Western Front.
- Map of the Eastern Front: This map shows the vast expanse of the Eastern Front, the shifting battle lines, and the key cities and territories contested.
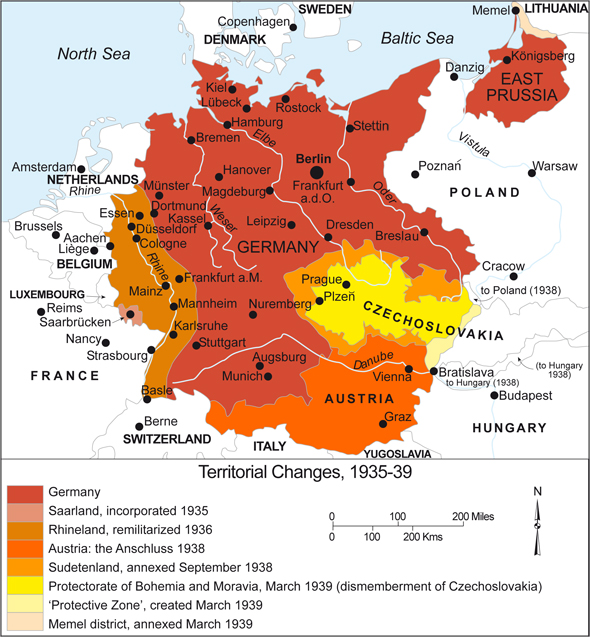
- Map of the German Empire: This map illustrates the territorial extent of the German Empire in 1914, highlighting its strategic position and its ambitions for expansion.
FAQs About the Map of Germany in World War I:
Q: What are the key features of the map of Germany in World War I?
A: The map of Germany in World War I showcases its strategic location at the heart of Europe, its borders with key adversaries like France and Russia, and its territorial ambitions for expansion in both the east and west.
Q: How did the map of Germany change during the war?
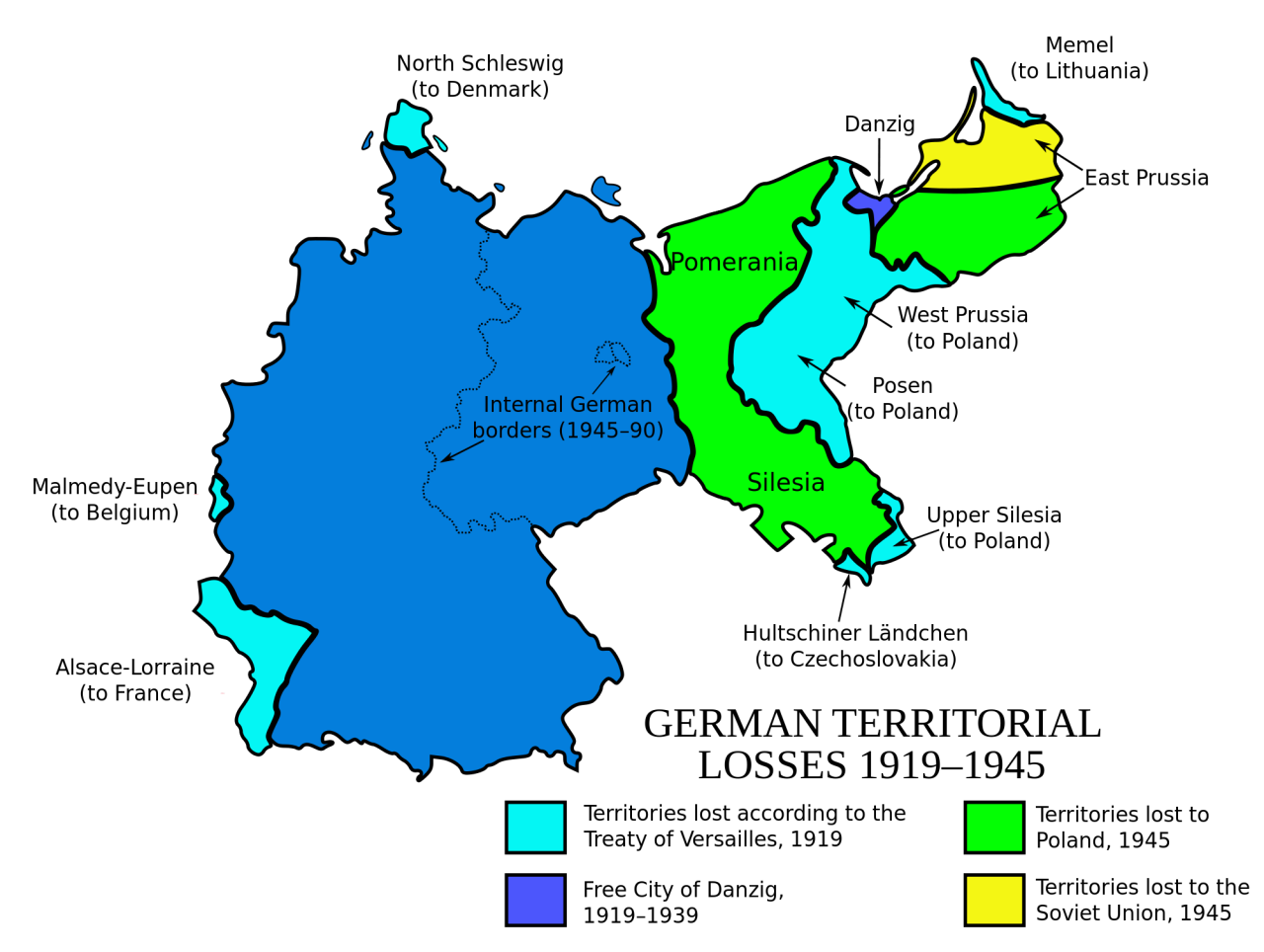
A: The map of Germany changed significantly during the war as its territorial ambitions clashed with the realities of the battlefield. Germany experienced both territorial gains and losses, particularly in the east where it faced resistance from Russia and its allies.
Q: What role did maps play in the strategic decisions of the German military?
A: Maps were indispensable tools for the German military, providing crucial information for planning offensives, deploying troops, and managing logistical operations. They helped commanders assess terrain, identify strategic locations, and anticipate enemy movements.
Tips for Analyzing Maps of Germany in World War I:
- Pay attention to scale: Maps should be examined carefully to understand the relative distances between locations and the scale of military operations.
- Consider the context: Maps should be interpreted in the context of the broader historical narrative, taking into account political alliances, military strategies, and the social and economic conditions of the time.
- Analyze symbols and legends: Maps utilize various symbols and legends to represent different features, such as troop movements, fortifications, and supply lines.
- Compare and contrast maps: Comparing maps from different time periods can reveal the evolution of battlefronts, territorial changes, and strategic shifts throughout the war.
Conclusion:
The map of Germany in World War I serves as a powerful visual representation of the conflict’s strategic complexities and territorial ambitions. It highlights Germany’s central role in the war, its initial aims for expansion, and the challenges it faced in achieving its objectives. Understanding the map’s nuances offers a deeper insight into the war’s course, the motivations of its key players, and the enduring consequences of its devastating impact on the world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Great War: Germany’s Territorial Ambitions and Strategic Challenges in World War I. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!