Navigating the Boundaries: A Comprehensive Look at Canada’s Border Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Boundaries: A Comprehensive Look at Canada’s Border Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Boundaries: A Comprehensive Look at Canada’s Border Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Boundaries: A Comprehensive Look at Canada’s Border Map
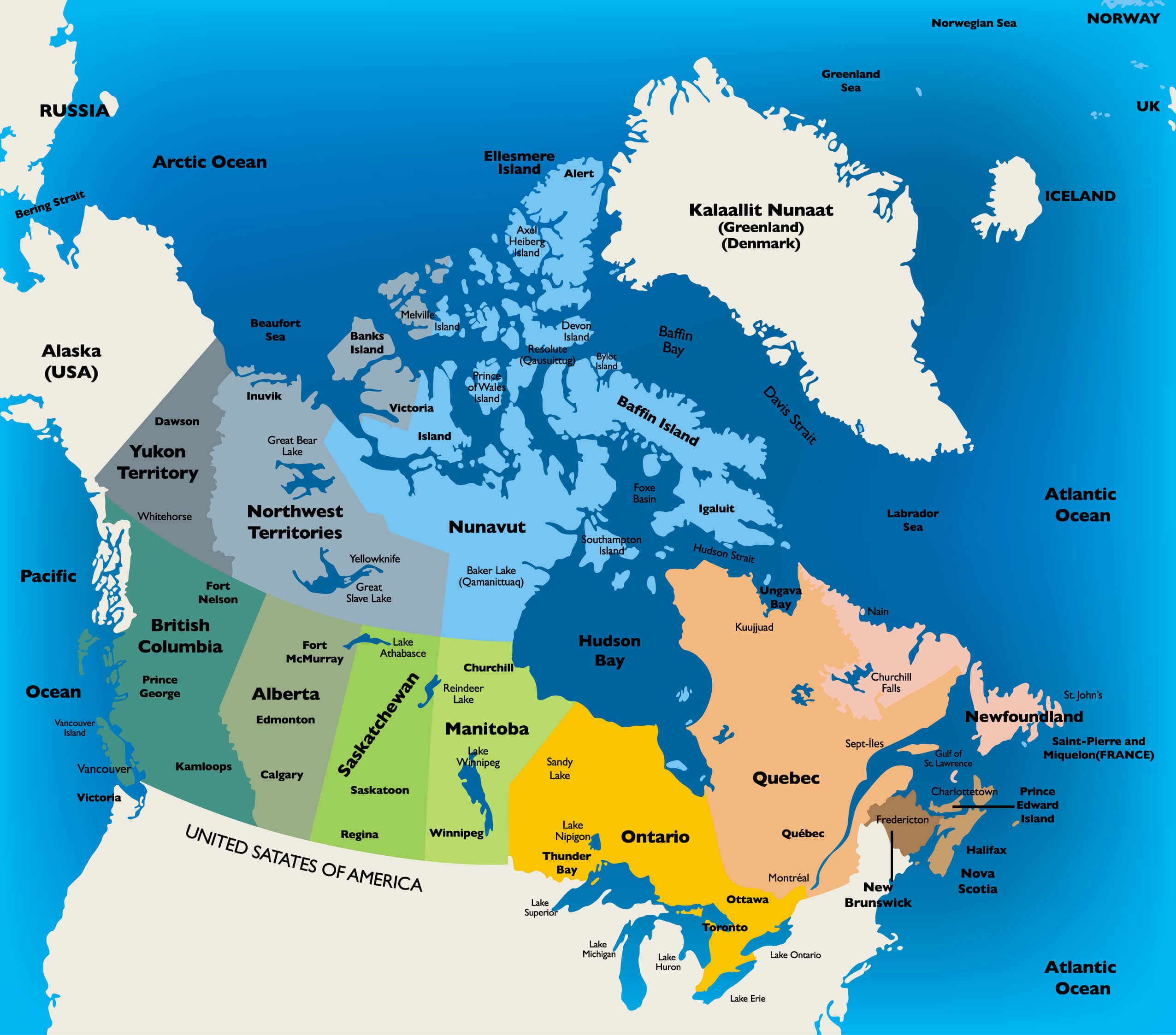
Canada, the second-largest country in the world by land area, shares extensive borders with three nations: the United States to the south, the United Kingdom (via Nunavut) to the northeast, and Denmark (via Greenland) to the north. Understanding the intricacies of these borders is crucial for various reasons, from international relations and trade to environmental management and cultural exchange. This article delves into the complexities of Canada’s border map, exploring its historical evolution, geographical features, and contemporary significance.
A History of Borders: From Exploration to Modernity
Canada’s borders, as we know them today, are the product of centuries of exploration, negotiation, and conflict. The initial European presence in North America stemmed from voyages by explorers like John Cabot and Jacques Cartier, laying the foundation for competing claims by France and England. The Treaty of Paris in 1763, marking the end of the Seven Years’ War, established British control over much of present-day Canada, setting the stage for the eventual formation of the Canadian Confederation in 1867.
The border with the United States was established through a series of treaties, including the Treaty of Ghent in 1814, which ended the War of 1812, and the Webster-Ashburton Treaty of 1842, which resolved several boundary disputes. The Alaska Boundary Dispute of 1903, involving Canada, the United States, and the United Kingdom, further defined the northwestern border.
A Geographical Tapestry: Diverse Landscapes and Shared Resources
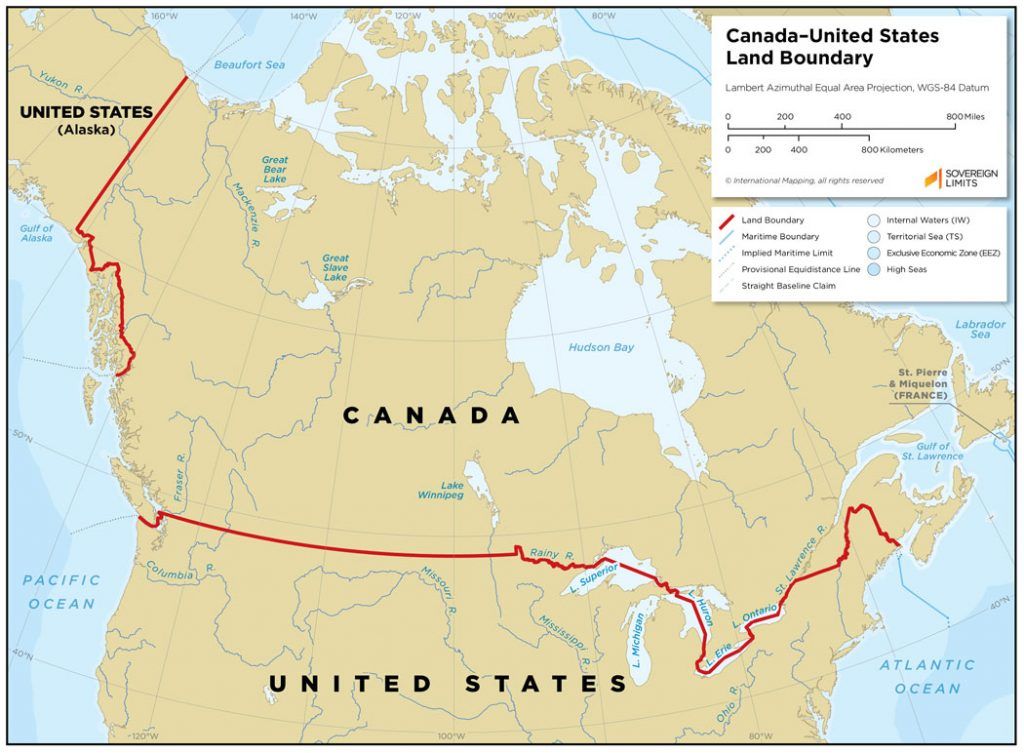
Canada’s borders are not merely lines on a map; they encompass a vast array of geographical features, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges. The border with the United States, stretching over 8,891 kilometers, is the world’s longest undefended border. It traverses diverse landscapes, from the prairies of Manitoba and Saskatchewan to the rugged mountains of British Columbia and the Great Lakes region.
The border with the United Kingdom, via Nunavut, is primarily symbolic, representing a historical and cultural link. The border with Denmark, via Greenland, is a maritime boundary in the Arctic Ocean, encompassing vast stretches of ice and water.
These borders are not merely lines on a map; they represent shared resources, including freshwater, forests, and fisheries. The management of these resources requires collaboration and cooperation between neighboring countries.
The Importance of Borders: From Security to Trade
Canada’s borders play a pivotal role in various aspects of national life, including:
- Security: Borders serve as the first line of defense against external threats, safeguarding national security and ensuring the safety of citizens.
- Trade: Borders facilitate the flow of goods and services between countries, fostering economic growth and prosperity.
- Immigration: Borders regulate the movement of people across national boundaries, contributing to the diversity and dynamism of Canadian society.
- Environment: Borders are crucial for managing shared environmental resources, protecting ecosystems, and mitigating the effects of climate change.
- Cultural Exchange: Borders foster cultural exchange and understanding between nations, promoting diplomacy and international cooperation.
Navigating the Border: A Guide for Travelers
For individuals crossing Canada’s borders, understanding the requirements and procedures is essential. Travelers should be aware of:
- Passport and Visa Requirements: Different nationalities have varying requirements for entry into Canada. It is crucial to check visa regulations and obtain necessary travel documents in advance.
- Customs and Border Protection: All travelers must declare goods and items they are carrying, including food, plants, and animals. Failure to comply can result in penalties.
- Border Crossing Points: Designated border crossing points are available for entry into Canada. Travelers should plan their route and ensure they arrive at a designated crossing.
- Health and Safety: Canada has strict health and safety regulations for imported goods and animals. Travelers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to avoid potential issues.
FAQs on Canada’s Border Map
1. What is the longest border shared by Canada?
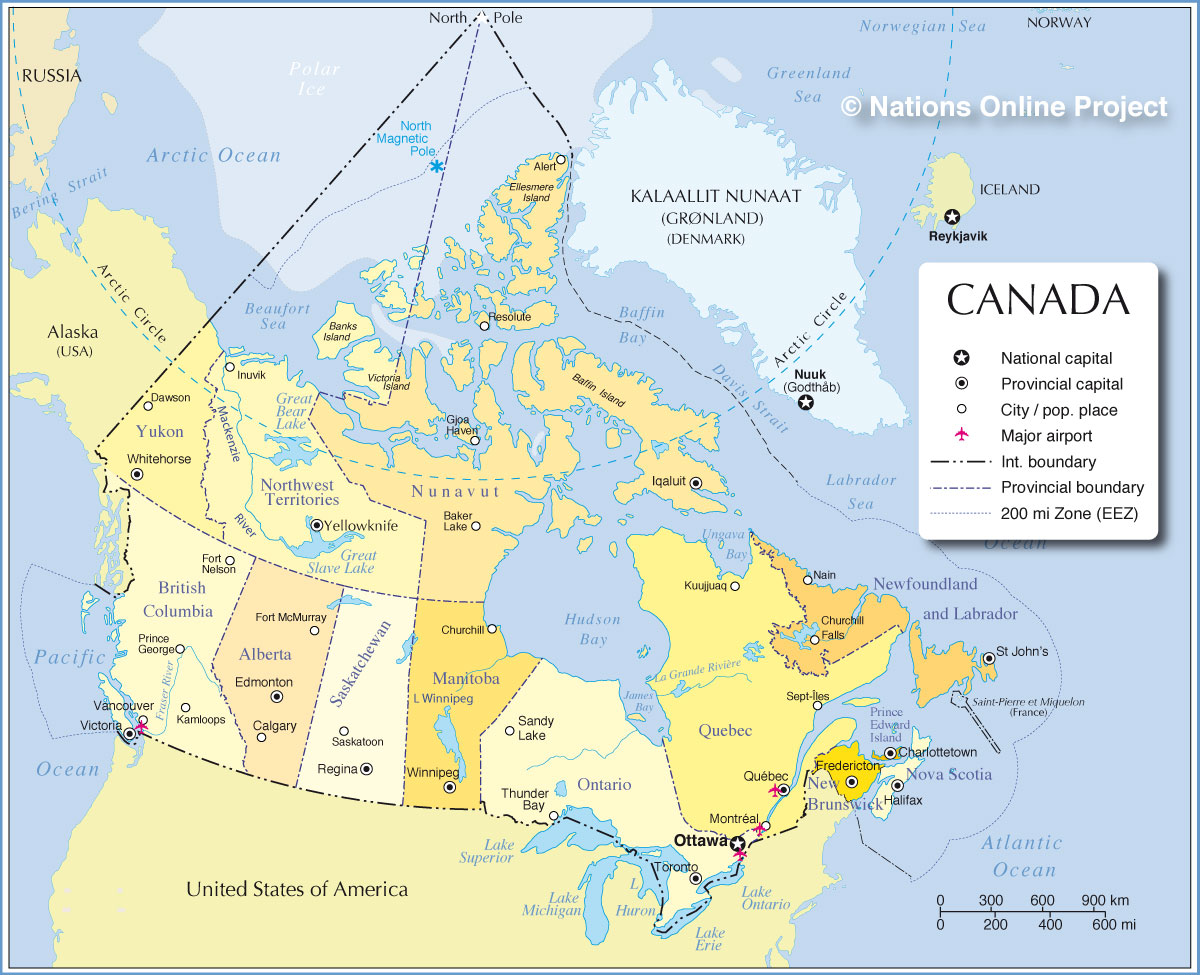
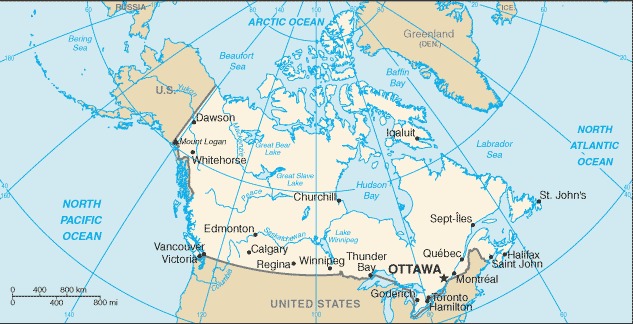
Canada’s longest border is with the United States, spanning over 8,891 kilometers.
2. What are the major border crossings between Canada and the United States?
Major border crossings include:
- Land: Niagara Falls, Detroit-Windsor, Peace Arch (Vancouver-Blaine), Emerson-Pembina, Sault Ste. Marie, Prescott-Ogdensburg, St. Stephen-Calais
- Air: Toronto Pearson International Airport, Montreal Pierre Elliott Trudeau International Airport, Vancouver International Airport, Calgary International Airport
3. What are the key differences between the Canadian and American border security measures?
Both countries have robust border security measures, but there are some differences. Canada has a focus on low-level border security, relying on trust and cooperation, while the United States has a more stringent approach due to its history of terrorism and illegal immigration.
4. What are the major challenges facing Canada’s border management?
Challenges include:
- Illegal Immigration: Managing the flow of undocumented migrants and asylum seekers.
- Cross-Border Crime: Combating drug trafficking, human trafficking, and other criminal activities.
- Environmental Protection: Balancing economic development with environmental sustainability.
- Climate Change: Adapting to the impacts of climate change on border infrastructure and ecosystems.
Tips for Understanding Canada’s Border Map
- Use Interactive Maps: Online resources, such as Google Maps and the Government of Canada’s website, offer interactive maps with detailed information on border crossings, customs regulations, and travel advisories.
- Consult Travel Guides: Travel guides often provide comprehensive information on border procedures, visa requirements, and essential tips for travelers.
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on any changes to border regulations, travel advisories, and security measures through official government sources.
- Plan Ahead: Plan your travel route in advance, including border crossing points and estimated wait times.
- Be Prepared: Carry all necessary travel documents, including passports, visas, and proof of citizenship.
Conclusion
Canada’s border map is not just a collection of lines on a map but a dynamic representation of the country’s history, geography, and relationships with its neighbors. Understanding these borders is crucial for navigating international relations, fostering economic growth, safeguarding national security, and managing shared resources. By embracing a collaborative approach, Canada can continue to strengthen its border management systems and ensure the well-being of its citizens and the environment.
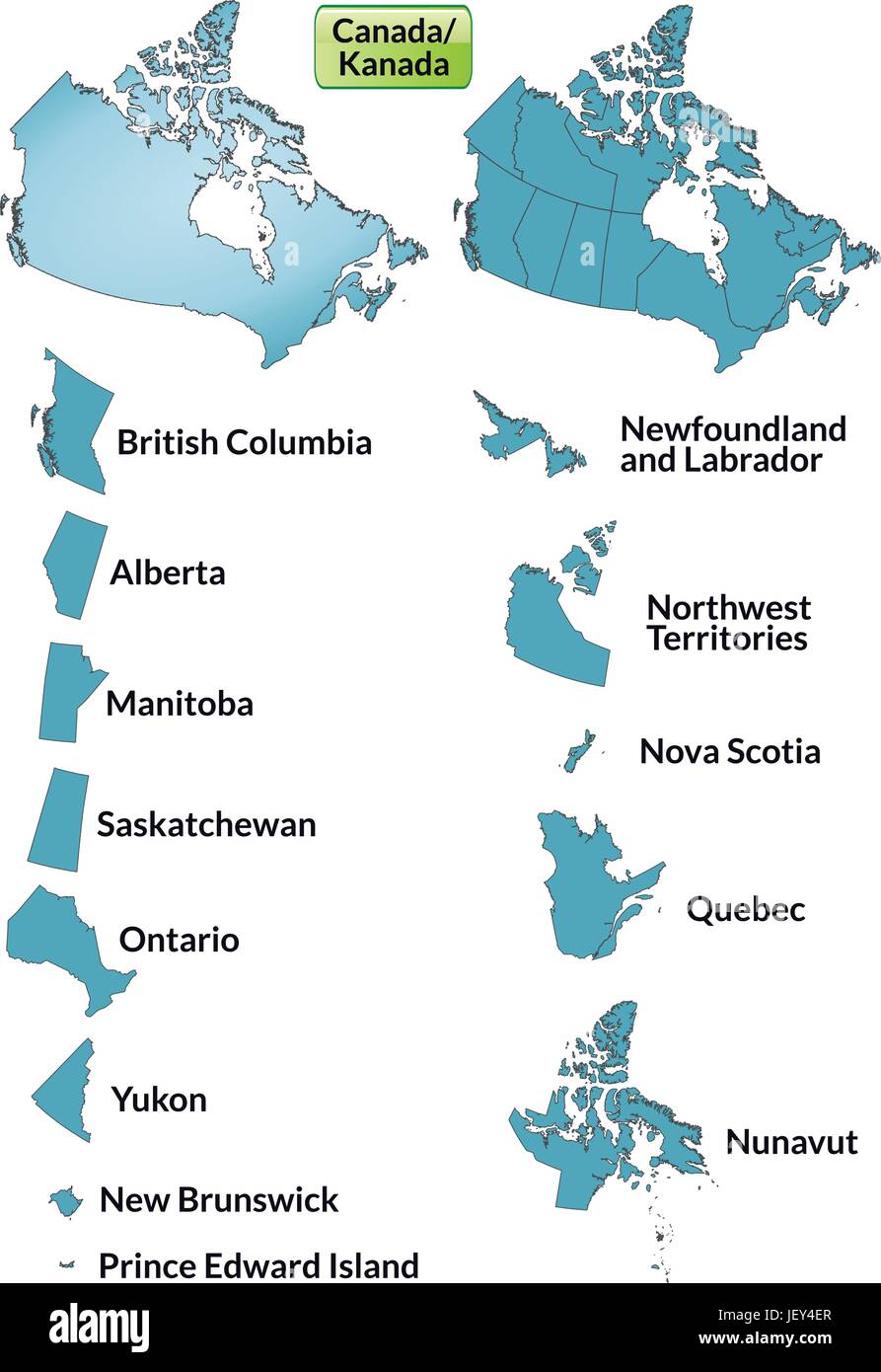

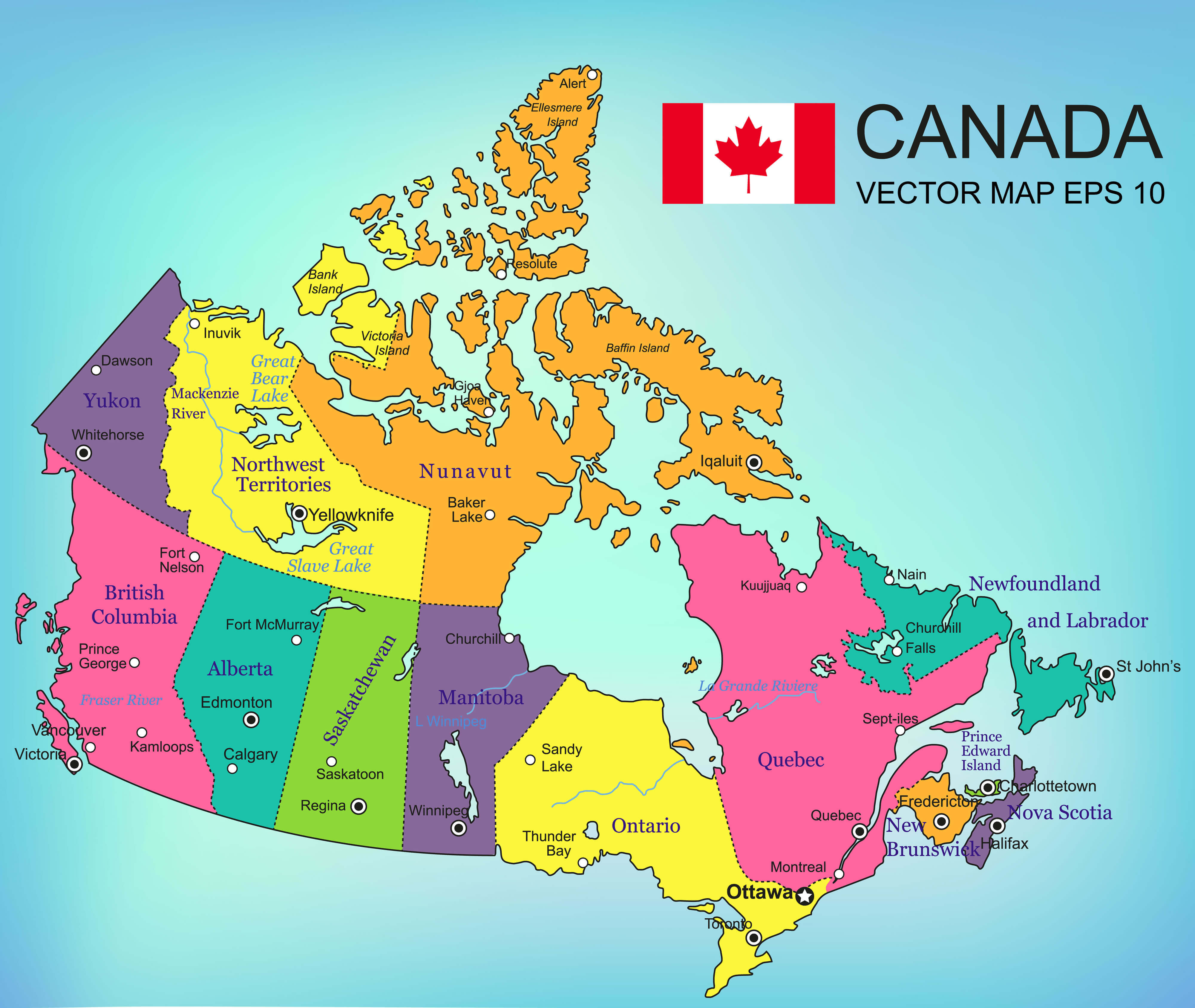

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Boundaries: A Comprehensive Look at Canada’s Border Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!