Navigating the Complex Tapestry of Middle Eastern Ethnicity: A Geographic Perspective
Related Articles: Navigating the Complex Tapestry of Middle Eastern Ethnicity: A Geographic Perspective
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complex Tapestry of Middle Eastern Ethnicity: A Geographic Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complex Tapestry of Middle Eastern Ethnicity: A Geographic Perspective
The Middle East, a region often defined by its geopolitical significance, is also a fascinating mosaic of diverse ethnicities and cultural identities. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Middle East’s ethnic landscape, exploring the complexities of its formation and the significance of its diverse composition.
Defining the Middle East: A Geographic and Cultural Challenge
Before delving into the intricacies of Middle Eastern ethnicity, it is crucial to acknowledge the ambiguity surrounding the definition of the "Middle East" itself. While often associated with the Arab world, the region encompasses a vast expanse of land stretching from North Africa to Central Asia, encompassing diverse cultural and linguistic groups.
For this analysis, the Middle East is defined as a geographical region encompassing the following countries:
- North Africa: Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia.
- The Levant: Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Palestine, Israel.
- The Arabian Peninsula: Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait.
- Mesopotamia: Iraq.
- The Caucasus: Azerbaijan, Armenia, Georgia.
- Cyprus.
This definition encompasses the geographical and cultural characteristics that contribute to the region’s unique identity. However, it is important to remember that these borders are fluid and contested, and the region’s ethnic composition is constantly evolving.
A Spectrum of Ethnicities: Tracing the Roots of Diversity
The Middle East’s ethnic landscape is characterized by a complex interplay of historical migrations, conquests, and intermingling of cultures. This has resulted in a diverse array of ethnic groups, each with its own unique cultural heritage and traditions.
Arab Ethnicity: The Dominant Force
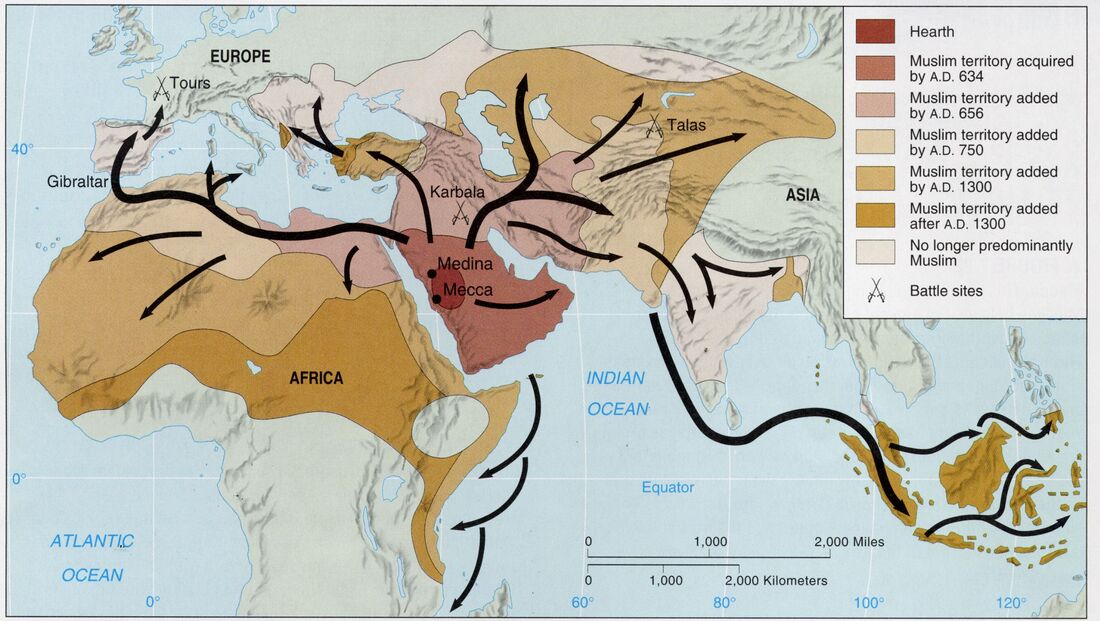
Arab ethnicity constitutes the largest and most dominant ethnic group in the Middle East. The Arabs are primarily associated with the Arabic language and Islamic faith, with their origins tracing back to the Arabian Peninsula. The spread of Islam in the 7th century CE led to the expansion of Arab culture and language throughout the region, solidifying their influence in the Middle East.
Beyond the Arabs: A Tapestry of Other Ethnicities
While Arabs dominate the Middle Eastern population, the region is also home to a vibrant tapestry of other ethnic groups, each contributing to its unique cultural mosaic. These include:
- Turks: Primarily found in Turkey, with significant populations in Cyprus, Syria, and Iraq, Turks are a significant ethnic group in the Middle East. Their influence is visible in language, culture, and history.
- Kurds: A distinct ethnic group primarily concentrated in Kurdistan, a region spanning parts of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Syria. Kurds have their own language, culture, and traditions, and their struggle for autonomy has been a defining aspect of Middle Eastern politics.
- Persians: With origins in ancient Persia, now Iran, Persians have a rich cultural heritage, distinguished by their language, art, and literature. They are a significant minority in Iraq and Afghanistan.
- Berbers: Native to North Africa, Berbers are a diverse group with their own distinct language and cultural traditions. They are particularly prominent in Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia.
- Armenians: A Christian ethnic group with historical ties to the region, Armenians have a long and complex history in the Middle East, facing persecution and displacement. They have significant communities in Armenia, Lebanon, Syria, and Turkey.
- Assyrians: An ancient Mesopotamian people with a distinct cultural and religious heritage, Assyrians are a small but significant minority group in Iraq, Syria, and Turkey.
- Jews: With a long and complex history in the Middle East, Jews have faced both persecution and prosperity throughout the region. Today, they are a significant minority in Israel, with smaller communities scattered throughout the Middle East.
- Other Ethnicities: The Middle East is also home to a diverse array of other ethnic groups, including the Circassians, the Chechens, the Arameans, and the Druze, each contributing to the region’s cultural richness.
The Interplay of Ethnicity and Identity: A Complex Landscape
It is crucial to acknowledge that ethnicity is not a fixed or static identity. Individuals can identify with multiple ethnicities, and their sense of belonging can be influenced by factors such as religion, language, and cultural practices. This complex interplay of factors contributes to the dynamic nature of ethnic identity in the Middle East.
The Importance of Understanding Middle Eastern Ethnicity
Understanding the ethnic diversity of the Middle East is crucial for a number of reasons:
- Promoting Intercultural Dialogue: Acknowledging the region’s diverse ethnic composition is essential for fostering dialogue and understanding between different communities.
- Addressing Ethnic Conflicts: Many conflicts in the Middle East have ethnic dimensions. Recognizing these complexities is crucial for finding peaceful solutions.
- Preserving Cultural Heritage: The Middle East’s ethnic diversity is a rich source of cultural heritage. Recognizing and celebrating this diversity is essential for its preservation.
- Promoting Social Cohesion: Understanding the ethnic landscape of the Middle East can contribute to building social cohesion and fostering a sense of shared identity.
FAQs about Middle Eastern Ethnicity
Q: What are the major ethnic groups in the Middle East?
A: The major ethnic groups in the Middle East include Arabs, Turks, Kurds, Persians, Berbers, Armenians, Assyrians, and Jews.
Q: How has the Middle East’s ethnic landscape evolved over time?
A: The Middle East’s ethnic landscape has been shaped by historical migrations, conquests, and cultural intermingling. The region has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the spread of religions, and the movement of people across its borders.
Q: What are the challenges associated with understanding Middle Eastern ethnicity?
A: Understanding Middle Eastern ethnicity is a complex endeavor due to the fluidity of ethnic identities, the historical complexities of the region, and the ongoing political and social conflicts.
Q: How can we promote understanding and tolerance of ethnic diversity in the Middle East?
A: Promoting understanding and tolerance of ethnic diversity in the Middle East requires a multi-faceted approach, including education, dialogue, cultural exchange, and promoting media representation that reflects the region’s diversity.
Tips for Understanding Middle Eastern Ethnicity
- Engage with Diverse Sources: Seek information from a variety of sources, including academic journals, news articles, documentaries, and books written by individuals from diverse backgrounds.
- Learn about History: Understanding the historical context of the Middle East’s ethnic landscape is crucial for appreciating its complexities.
- Respect Cultural Differences: Recognize and respect the cultural practices and beliefs of different ethnic groups.
- Avoid Stereotyping: Resist the temptation to make generalizations about entire ethnic groups.
- Engage in Dialogue: Engage in respectful dialogue with individuals from different ethnic backgrounds to gain a deeper understanding of their perspectives.
Conclusion
The Middle East is a region of remarkable ethnic diversity, a tapestry woven from threads of history, culture, and identity. Understanding this diversity is crucial for fostering intercultural dialogue, addressing conflicts, preserving cultural heritage, and promoting social cohesion. By acknowledging the complex interplay of ethnicity and identity in the Middle East, we can strive to create a more inclusive and harmonious future for the region.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complex Tapestry of Middle Eastern Ethnicity: A Geographic Perspective. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!