Navigating the Sabine River: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the Sabine River: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Sabine River: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Sabine River: A Comprehensive Exploration
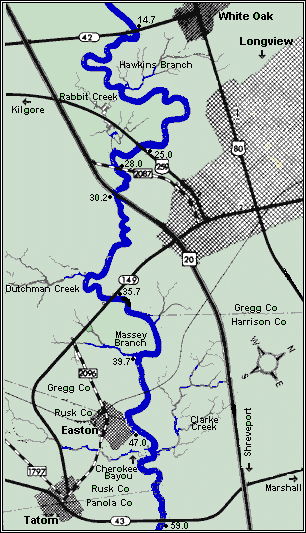
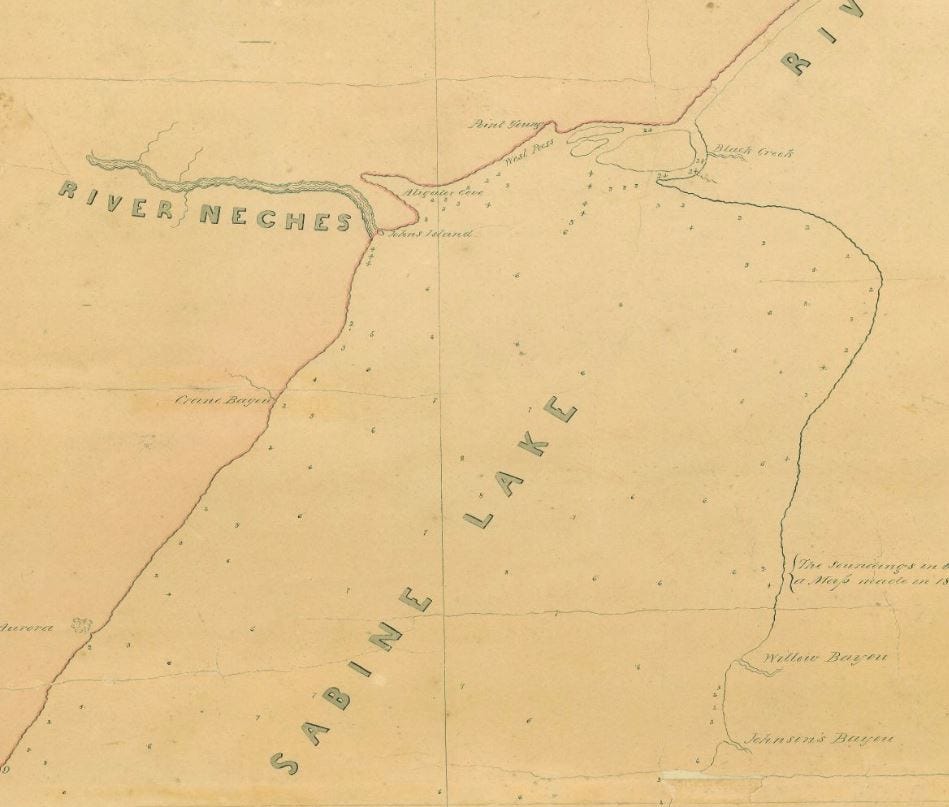
The Sabine River, a meandering waterway tracing a path across the southeastern United States, serves as a natural boundary between Texas and Louisiana. Its course, stretching over 400 miles, traverses diverse landscapes, from the rolling hills of East Texas to the expansive wetlands of southwestern Louisiana. This article delves into the intricacies of the Sabine River, analyzing its geography, history, ecology, and significance, offering a comprehensive understanding of this vital waterway.
A River of Borders and Boundaries:
The Sabine River’s geographical significance lies in its role as a defining border. It forms the boundary between the states of Texas and Louisiana, carving a natural divide that has shaped the history and development of both regions. This shared waterway has influenced the cultural, economic, and political landscapes of the area, fostering a unique relationship between the two states.
A Journey Through Diverse Landscapes:
The Sabine River’s journey begins in the rolling hills of East Texas, where its headwaters originate in the Sabine National Forest. As it flows southward, the river meanders through a tapestry of diverse landscapes. Its course traverses through forests, prairies, swamps, and bayous, each environment contributing to its unique ecological character. The river’s journey is punctuated by numerous tributaries, each adding its own contribution to the river’s flow and ecosystem.
A Historical Tapestry:
The Sabine River has witnessed centuries of human activity, its banks bearing witness to the passage of time. Native American tribes, such as the Caddo and the Atakapa, inhabited the river’s valley for millennia, utilizing its resources for sustenance and transportation. European exploration and settlement followed, with Spanish explorers charting the river in the 16th century and French and American settlers establishing communities along its banks. The river’s strategic location contributed to its role in various historical events, including the Louisiana Purchase and the Texas Revolution.
An Ecosystem of Significance:
The Sabine River is a vital ecological corridor, supporting a diverse array of plant and animal life. Its waters provide habitat for numerous fish species, including bass, catfish, and crappie, attracting anglers from across the region. The river’s banks and surrounding wetlands are home to a variety of bird species, including migratory waterfowl, herons, and egrets. The river’s rich biodiversity underscores its importance as a crucial component of the regional ecosystem.
Navigating the Sabine:
The Sabine River has long been a significant waterway for transportation, with its waters facilitating trade and movement throughout its history. Today, the river remains a popular destination for recreational boating, fishing, and kayaking. Its meandering course offers scenic beauty and opportunities for exploration, attracting enthusiasts seeking to experience the natural wonders of the region.
Challenges and Conservation:
The Sabine River, like many waterways, faces challenges related to pollution, habitat degradation, and water management. Agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and urban development contribute to water quality issues, impacting the river’s ecosystem and its inhabitants. Conservation efforts are underway to address these challenges, focusing on water quality improvement, habitat restoration, and sustainable management practices.
FAQs:
1. What is the source of the Sabine River?
The Sabine River originates in the Sabine National Forest in East Texas.
2. What is the length of the Sabine River?
The Sabine River is approximately 400 miles long.
3. What states does the Sabine River flow through?
The Sabine River flows through the states of Texas and Louisiana.
4. What are some of the major cities located along the Sabine River?
Major cities located along the Sabine River include Orange, Beaumont, and Port Arthur in Texas, and Lake Charles in Louisiana.
5. What are some of the key ecological features of the Sabine River?
The Sabine River supports a diverse ecosystem, including a variety of fish species, birds, and other wildlife. Its wetlands and surrounding forests are important habitats for numerous species.
6. What are some of the challenges facing the Sabine River?
The Sabine River faces challenges related to pollution, habitat degradation, and water management. These issues stem from agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and urban development.
7. What are some of the conservation efforts underway to protect the Sabine River?
Conservation efforts are underway to address water quality issues, restore habitats, and promote sustainable management practices along the Sabine River.
Tips:
1. Plan your visit: Research the best time to visit the Sabine River based on your interests, such as fishing, boating, or wildlife viewing.
2. Be prepared: Pack appropriate clothing, sunscreen, insect repellent, and any necessary boating equipment.
3. Respect the environment: Dispose of trash properly, avoid disturbing wildlife, and follow all local regulations.
4. Explore different areas: The Sabine River offers a variety of landscapes and activities, from scenic boat tours to hiking trails.
5. Learn about the history and culture: Visit local museums and historical sites to learn more about the river’s rich history and cultural heritage.
Conclusion:
The Sabine River, a vital waterway traversing the border of Texas and Louisiana, is a testament to the interconnectedness of nature and human activity. Its journey through diverse landscapes, its historical significance, and its ecological importance highlight the river’s enduring role in the region’s development. By understanding the Sabine River’s geography, history, ecology, and challenges, we can appreciate its value and contribute to its conservation, ensuring its continued health and vibrancy for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Sabine River: A Comprehensive Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
