Navigating the Wilderness: A Comprehensive Guide to Trail Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Wilderness: A Comprehensive Guide to Trail Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Wilderness: A Comprehensive Guide to Trail Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Wilderness: A Comprehensive Guide to Trail Maps
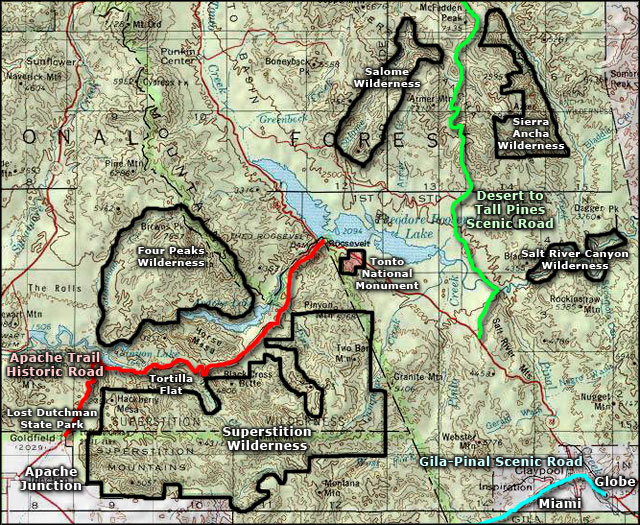
The allure of the wilderness, with its rugged beauty and untamed spirit, draws adventurers seeking solace, challenge, and a connection with nature’s raw power. Yet, venturing into these wild landscapes demands careful planning and meticulous preparation, particularly when it comes to navigating unfamiliar terrain. This is where a crucial tool comes into play: the trail map.
A trail map is not merely a piece of paper; it is a vital guide, a roadmap to safety and success in the wilderness. It provides a visual representation of the landscape, outlining trails, landmarks, elevation changes, and potential hazards. This detailed information empowers hikers and backpackers to make informed decisions, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
Understanding the Importance of Trail Maps
The importance of a trail map cannot be overstated. It serves as a lifeline, offering a tangible connection to the environment and enabling informed decision-making.
- Navigation: Trail maps provide a clear visual representation of the trail network, allowing hikers to identify their location, plan their route, and determine distances between points of interest.
- Safety: A trail map helps identify potential hazards such as steep drop-offs, water crossings, and areas prone to wildlife encounters. This knowledge enables hikers to take necessary precautions and avoid unnecessary risks.
- Emergency Response: In the event of an emergency, a trail map can be crucial for guiding rescue efforts. It provides critical information about the hiker’s location, the terrain, and potential access points for rescue personnel.
- Environmental Awareness: Trail maps often include information about the surrounding ecosystem, such as plant and animal life, historical sites, and designated wilderness areas. This knowledge fosters a deeper understanding and appreciation for the natural environment.
Deciphering the Language of Trail Maps
Trail maps utilize a specific set of symbols and conventions to convey essential information concisely and effectively. Familiarizing oneself with these symbols is crucial for accurate interpretation.
- Trail Types: Different trail types are often represented by distinct colors or line thicknesses. For example, thick black lines might indicate major trails, while thinner blue lines might represent less traveled paths.
- Elevation: Contour lines depict changes in elevation. Closely spaced lines indicate steeper slopes, while widely spaced lines indicate gentler terrain.
- Water Features: Symbols representing rivers, streams, lakes, and springs provide information about water sources and potential obstacles.
- Points of Interest: Landmarks such as campsites, shelters, viewpoints, and trailheads are often marked with specific symbols.
- Cautionary Symbols: Symbols indicating hazards such as steep drop-offs, avalanche zones, or wildlife crossings alert hikers to potential dangers.
Types of Trail Maps
Several types of trail maps cater to different needs and preferences.
- Paper Maps: Traditional paper maps are lightweight, durable, and readily available. They offer a detailed overview of the area and can be used even without electronic devices.
- Digital Maps: Smartphone apps and GPS devices offer interactive maps with real-time location tracking, elevation data, and downloadable offline maps.
- Topographic Maps: These maps provide detailed elevation information, contour lines, and geographic features, making them ideal for planning challenging hikes or backpacking trips.
Choosing the Right Trail Map
Selecting the appropriate trail map is crucial for a successful and safe adventure. Consider the following factors:
- Destination: Choose a map specifically designed for the area you plan to hike.
- Trail Difficulty: Select a map that includes information about the trail’s length, elevation gain, and potential hazards.
- Personal Preferences: Consider your comfort level with different types of maps, such as paper maps, digital maps, or topographic maps.
Using Trail Maps Effectively
Once you have a suitable trail map, it is essential to utilize it effectively to maximize its benefits.
- Pre-Trip Planning: Study the map thoroughly before your hike, identifying the trail route, potential hazards, and key landmarks.
- Mark Your Route: Use a pencil to mark your planned route on the map, making it easier to follow during your hike.
- Carry a Compass: Combine the map with a compass for accurate navigation, especially in areas with limited landmarks.
- Check Your Location: Regularly refer to the map to ensure you are staying on the intended trail.
- Be Prepared for Unexpected Situations: Carry a backup map or download offline maps to your phone in case of unforeseen circumstances.
FAQs about Trail Maps
Q: What is the best way to carry a trail map?
A: Securely store the map in a waterproof container or map case. Consider using a map holder that allows easy access while keeping the map protected from the elements.
Q: How do I determine the scale of a trail map?
A: The scale is usually indicated in the map legend or on the map’s margin. It shows the ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground.
Q: What is the difference between a trail map and a topographic map?
A: A trail map focuses on trails and landmarks, while a topographic map provides detailed elevation information, contour lines, and geographic features.
Q: Can I rely solely on GPS for navigation?
A: While GPS devices are helpful, it is crucial to have a backup navigation system, such as a paper map and compass. GPS devices can malfunction or lose signal in remote areas.
Tips for Using Trail Maps
- Practice using a compass and map before your hike.
- Familiarize yourself with the symbols and conventions used on the map.
- Take regular breaks to reorient yourself and check your location.
- Inform someone about your planned route and expected return time.
- Carry a first-aid kit and emergency supplies.
Conclusion
A trail map is an indispensable tool for anyone venturing into the wilderness. It provides a comprehensive guide to the terrain, enabling safe navigation, informed decision-making, and a deeper understanding of the surrounding environment. By utilizing trail maps effectively, hikers can minimize risks, maximize enjoyment, and foster a profound connection with nature’s untamed beauty.


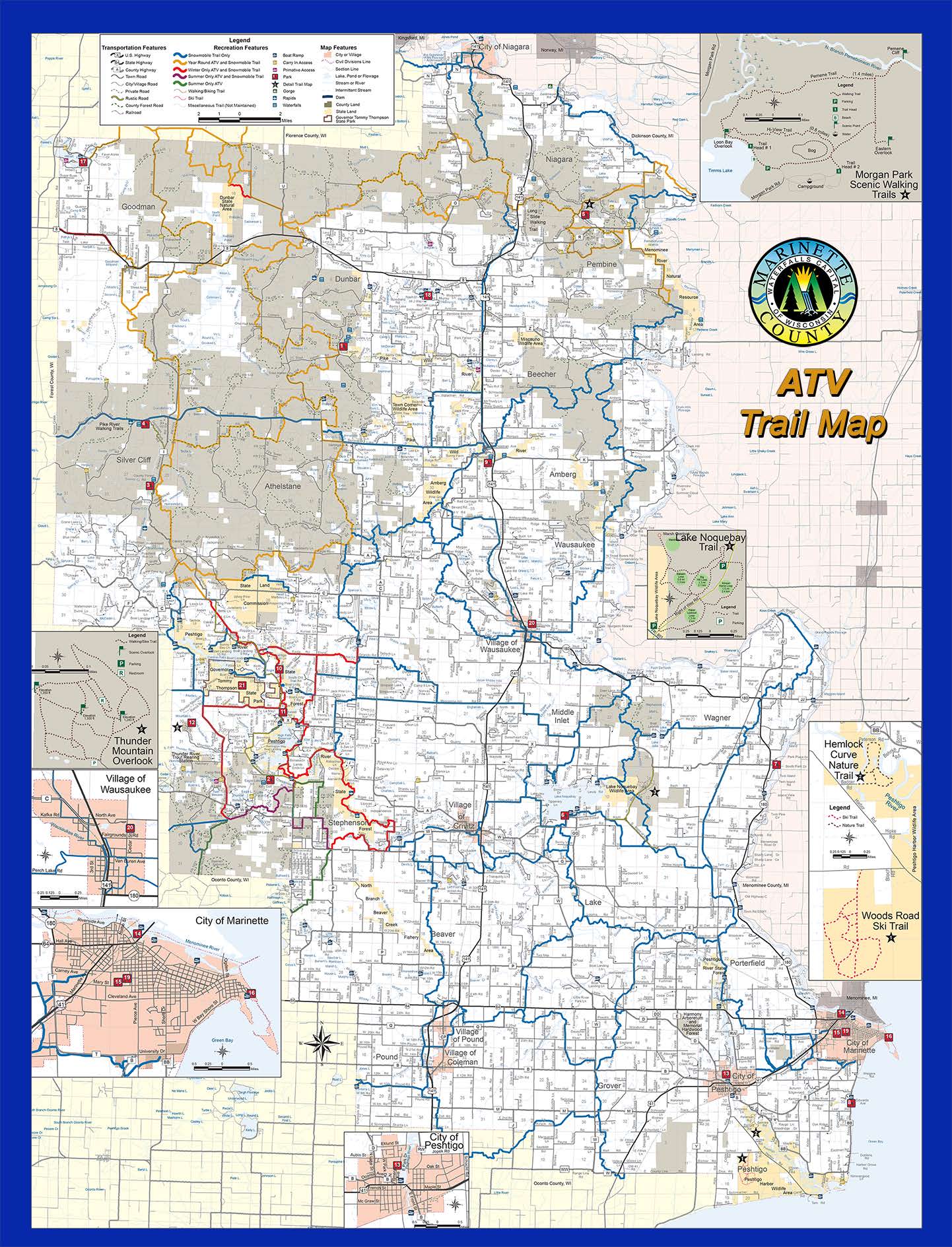





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Wilderness: A Comprehensive Guide to Trail Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!