The Andes Mountains: A Backbone of South America
Related Articles: The Andes Mountains: A Backbone of South America
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Andes Mountains: A Backbone of South America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Andes Mountains: A Backbone of South America

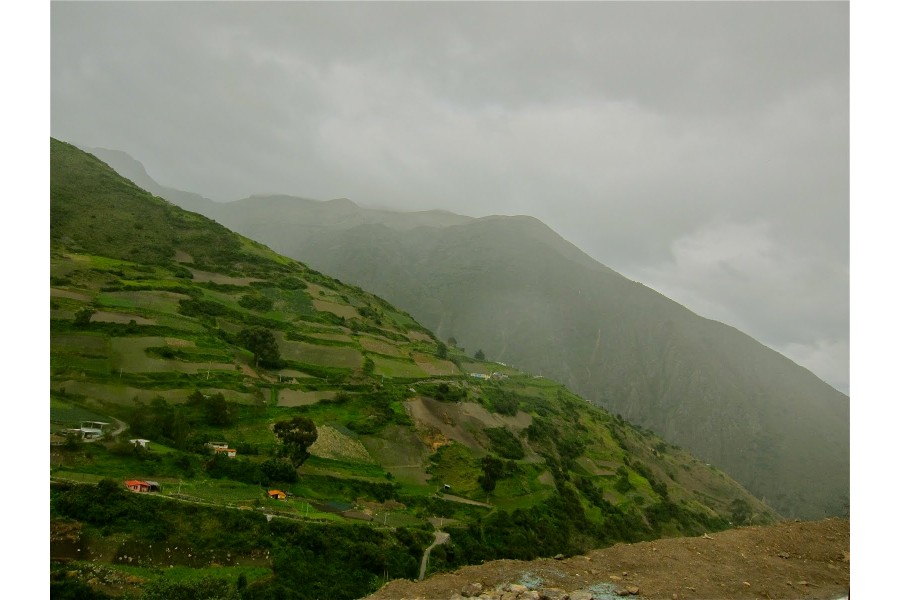
The Andes Mountains, a colossal chain of peaks stretching over 7,000 kilometers along the western edge of South America, are a defining feature of the continent. This majestic mountain range, often referred to as the "spine of the Americas," is not just a geological wonder; it is a vital ecosystem, a cultural tapestry, and a key driver of economic activity. Understanding the Andes Mountains requires an exploration of its geography, its impact on the environment, its rich cultural history, and its significant role in the lives of millions of people.
A Geographic Colossus:
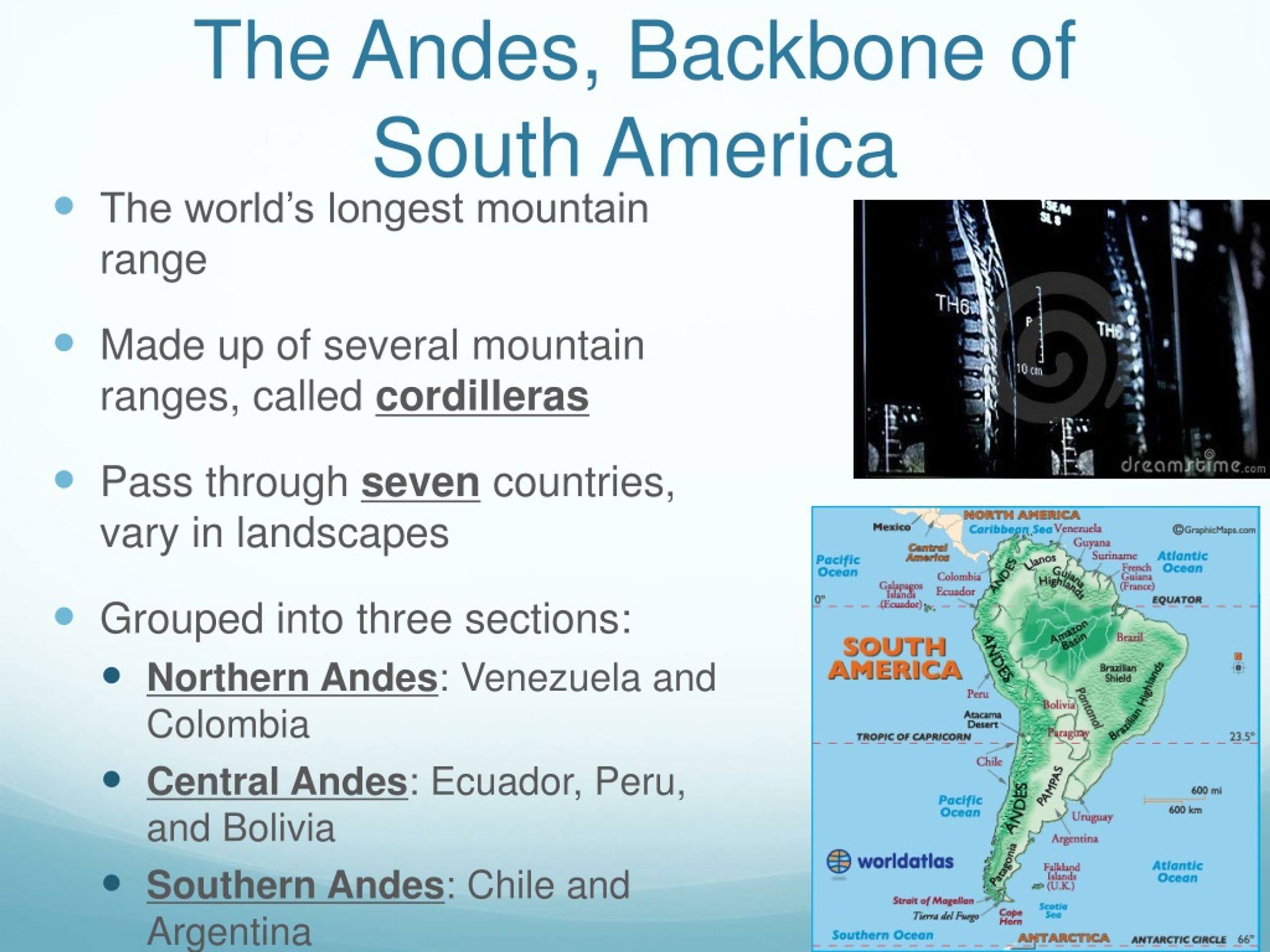
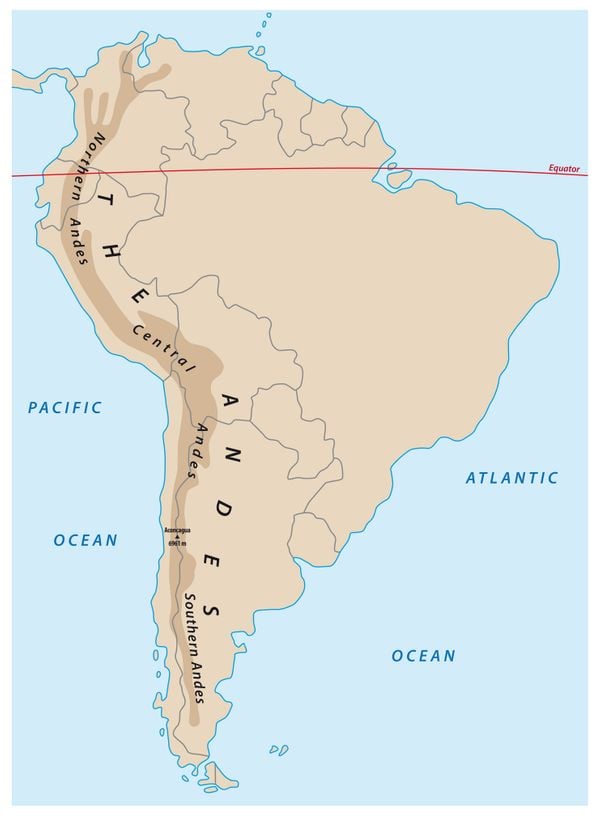
The Andes Mountains, formed by the collision of the Nazca and South American tectonic plates, are the longest mountain range outside of Asia. They traverse seven countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina, encompassing a diverse array of landscapes. From the snow-capped peaks of Aconcagua, the highest mountain outside of Asia, to the arid deserts of Atacama, the Andes display a remarkable range of altitudes, climates, and ecosystems.
A Cradle of Biodiversity:
The Andes are a biodiversity hotspot, harboring a vast array of flora and fauna found nowhere else on Earth. The unique topography and diverse climates have fostered the evolution of countless endemic species. From the vibrant hummingbirds of the cloud forests to the majestic condors soaring over the high peaks, the Andes are a testament to the power of nature to create and sustain life.
A Cultural Tapestry:
The Andes have been home to indigenous cultures for millennia. The Inca Empire, a powerful civilization that flourished in the 15th and 16th centuries, left an indelible mark on the region. Their sophisticated agricultural techniques, intricate architecture, and complex social structures continue to inspire and influence the lives of Andean communities today. From the vibrant textiles of the Quechua people to the traditional music of the Aymara, the cultural heritage of the Andes is a living legacy that enriches the lives of millions.
A Vital Resource:
The Andes Mountains are a vital resource for the surrounding regions. The vast reserves of minerals, including copper, silver, and gold, have fueled economic development throughout the region. The Andean highlands also play a crucial role in water management, providing water resources for agriculture, industry, and human consumption. Furthermore, the Andean slopes are home to diverse agricultural systems, supporting a wide range of crops from coffee and coca to quinoa and potatoes.
Navigating the Andes: A Map’s Importance
An Andes Mountains South America map is essential for comprehending the region’s geography, its cultural diversity, and its economic significance. The map provides a visual representation of the mountain range’s vastness, its interconnectedness with surrounding regions, and its impact on the lives of millions. It allows for a deeper understanding of:
- Spatial Relationships: The map reveals the geographic distribution of different Andean ecosystems, from the lush Amazonian foothills to the arid Atacama Desert. It highlights the relationship between the Andes and the Pacific Ocean, the Amazon basin, and the vast plains of Argentina.
- Cultural Diversity: The map showcases the diverse indigenous cultures that have thrived in the Andes for centuries. It illustrates the geographic distribution of different ethnic groups and their unique traditions, languages, and artistic expressions.
- Economic Activities: The map reveals the location of key mining operations, agricultural zones, and transportation routes that underpin the region’s economy. It highlights the importance of the Andes in resource extraction, agricultural production, and trade.
- Environmental Concerns: The map illustrates the impact of climate change on the Andean glaciers, which are vital sources of water for millions of people. It reveals the challenges faced by Andean communities in adapting to changing environmental conditions.
FAQs about the Andes Mountains South America Map:
1. What is the highest peak in the Andes Mountains?
The highest peak in the Andes Mountains is Aconcagua, located in Argentina. It stands at 6,961 meters (22,838 feet) above sea level, making it the highest mountain outside of Asia.
2. What countries does the Andes Mountain range traverse?
The Andes Mountains stretch through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina.
3. What are the main environmental challenges facing the Andes Mountains?
The Andes Mountains face several environmental challenges, including:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures are causing glaciers to melt at an alarming rate, threatening water supplies for millions of people.
- Deforestation: The clearing of forests for agriculture and logging is leading to soil erosion, habitat loss, and increased vulnerability to climate change.
- Mining: Mining activities can cause pollution and damage to ecosystems, particularly in sensitive high-altitude areas.
4. What are some of the key cultural features of the Andes Mountains?
The Andes Mountains are home to a rich tapestry of indigenous cultures, characterized by:
- Traditional Textiles: Andean communities are renowned for their vibrant textiles, often incorporating intricate designs and symbolic motifs.
- Music and Dance: Traditional Andean music and dance are characterized by their rhythmic melodies, expressive movements, and cultural significance.
- Languages: A variety of indigenous languages, including Quechua, Aymara, and Mapudungun, are spoken in the Andes, reflecting the region’s rich cultural heritage.
5. How does the Andes Mountains South America map contribute to our understanding of the region?
The Andes Mountains South America map provides a visual representation of the region’s geography, its cultural diversity, and its economic significance. It helps us understand the complex relationships between the mountains, the environment, and the people who live there.
Tips for Using the Andes Mountains South America Map:
- Focus on Key Features: Pay attention to the location of major mountain ranges, rivers, cities, and cultural sites.
- Explore Different Perspectives: Consider the map’s representation of altitude, climate, and cultural diversity.
- Connect the Dots: Use the map to understand the relationship between the Andes and the surrounding regions, including the Pacific Ocean, the Amazon Basin, and the plains of Argentina.
- Think Critically: Consider the limitations of the map and the potential biases it may contain.
Conclusion:
The Andes Mountains South America map is an indispensable tool for understanding the complexities of this remarkable region. It provides a visual representation of the mountain range’s geography, its cultural diversity, and its economic significance, allowing for a deeper appreciation of the Andes’ role in shaping the history, culture, and environment of South America. By exploring the map, we gain insights into the region’s unique challenges and opportunities, fostering a deeper understanding of the vital connection between the Andes and the lives of millions of people.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Andes Mountains: A Backbone of South America. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!