The Coronado Map: A Journey Through History and Mystery
Related Articles: The Coronado Map: A Journey Through History and Mystery
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Coronado Map: A Journey Through History and Mystery. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Coronado Map: A Journey Through History and Mystery

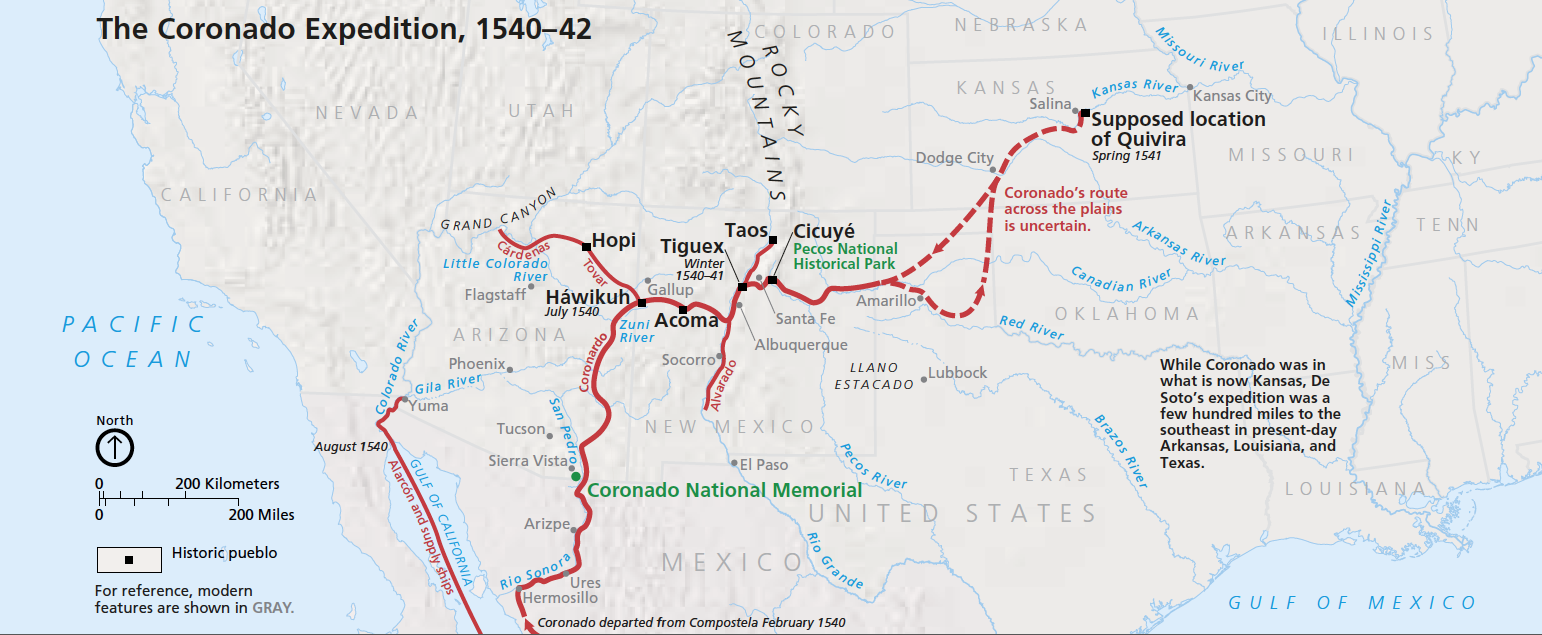
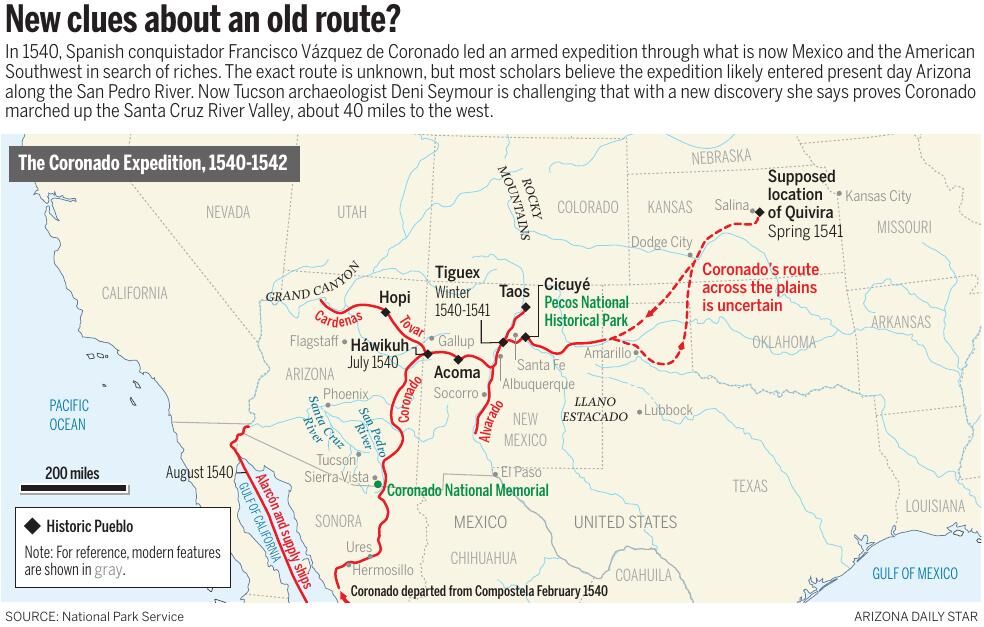
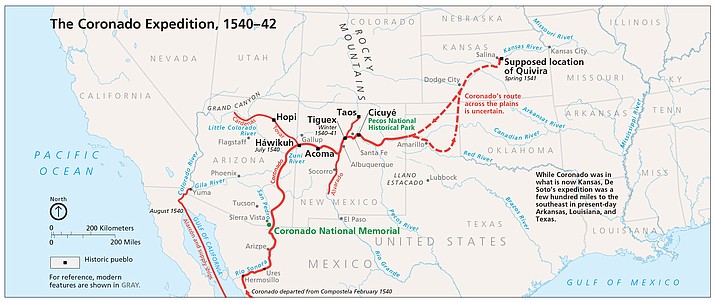
The Coronado Map, also known as the "Mapa de la Provincia de Cibola," is a fascinating artifact that has captivated historians and cartographers for centuries. This enigmatic map, attributed to Pedro de Castañeda de Nájera, a chronicler of the Francisco Vásquez de Coronado expedition, offers a tantalizing glimpse into the exploration of the American Southwest in the 16th century. While its authenticity has been debated for over a century, the Coronado Map remains a crucial piece in the puzzle of early American exploration, offering valuable insights into the geography, culture, and encounters of the time.
A Glimpse into the Coronado Expedition:
The Coronado expedition, led by Francisco Vásquez de Coronado in 1540, was a significant undertaking fueled by the pursuit of the mythical Seven Cities of Cibola, said to be rich in gold and other treasures. The expedition, comprised of hundreds of men and horses, ventured into the vast and unknown territories of present-day Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas, encountering various Native American tribes and landscapes.
The Coronado Map, believed to have been created during or shortly after the expedition, serves as a visual record of this historic journey. It depicts the expedition’s route, highlighting key locations, encounters with indigenous populations, and even the topography of the explored regions.
The Map’s Contents and Significance:
The Coronado Map is a detailed and meticulously crafted document. It showcases the expedition’s path from the starting point in Culiacán, Mexico, through the vast expanse of the Southwest, eventually reaching the Great Plains. The map features various symbols and annotations, providing clues to the expedition’s encounters and discoveries.
Key elements of the map include:
- Route of the expedition: The map traces the journey of the Coronado expedition, highlighting the various stops and encounters along the way.
- Indigenous settlements: The map depicts numerous Native American villages and settlements, offering insights into the demographics and geographical distribution of these communities.
- Geographic features: The map includes representations of rivers, mountains, deserts, and other topographical features, providing a valuable record of the landscape encountered by the expedition.
- Symbols and annotations: The map utilizes symbols and annotations to represent various aspects of the expedition, such as battles, encounters with indigenous people, and the discovery of resources.
The Authenticity Debate:
While the Coronado Map offers a compelling glimpse into the 16th-century exploration of the American Southwest, its authenticity has been subject to ongoing debate. Skeptics argue that the map’s detail and accuracy are questionable, suggesting it might be a later creation based on existing information.
Proponents of the map’s authenticity point to its intricate details, its correspondence with historical accounts of the Coronado expedition, and the presence of unique symbols and annotations that suggest a firsthand account.
Despite the ongoing debate, the Coronado Map remains a valuable artifact for historians and cartographers, offering insights into the exploration of the American Southwest and the encounters with indigenous populations during this pivotal period.
The Map’s Legacy and Importance:
Regardless of its authenticity, the Coronado Map holds significant historical and cultural value. It serves as a testament to the human spirit of exploration and discovery, highlighting the arduous journey undertaken by the Coronado expedition. The map’s depiction of the Southwest’s landscape, its indigenous peoples, and the expedition’s encounters provides valuable insights into the history of the region.
The Coronado Map also underscores the complexity of early American history, showcasing the intertwining of European exploration, indigenous cultures, and the pursuit of wealth and power. It serves as a reminder of the profound impact of European exploration on the indigenous populations of the Americas, and the lasting consequences of these encounters.
FAQs about the Coronado Map:
Q: What is the Coronado Map?
A: The Coronado Map, also known as the "Mapa de la Provincia de Cibola," is a 16th-century map attributed to Pedro de Castañeda de Nájera, a chronicler of the Francisco Vásquez de Coronado expedition. It is believed to depict the route of the expedition and the landscape, people, and encounters encountered during their journey through the American Southwest.
Q: Is the Coronado Map authentic?
A: The authenticity of the Coronado Map is a subject of ongoing debate. While some scholars believe it to be a genuine artifact from the 16th century, others argue that it is a later creation based on existing information.
Q: What is the significance of the Coronado Map?
A: The Coronado Map, regardless of its authenticity, holds significant historical value. It offers insights into the exploration of the American Southwest, the encounters with indigenous populations, and the geographical features of the region during the 16th century.
Q: What are some of the key features of the Coronado Map?
A: The Coronado Map depicts the route of the Coronado expedition, indigenous settlements, geographic features, and utilizes symbols and annotations to represent various aspects of the expedition.
Q: Where is the Coronado Map located?
A: The Coronado Map is currently housed at the Newberry Library in Chicago, Illinois.
Tips for Studying the Coronado Map:
- Consult historical accounts: Compare the information on the Coronado Map with historical accounts of the expedition, such as Castañeda’s own writings, to gain a better understanding of the context and accuracy of the map.
- Examine the symbols and annotations: Analyze the symbols and annotations used on the map to decipher their meaning and interpret the information they convey.
- Research the indigenous cultures: Learn about the indigenous cultures encountered by the Coronado expedition to gain a deeper understanding of the map’s depiction of these communities.
- Compare the map to other sources: Compare the Coronado Map to other maps and documents from the same period to identify similarities and differences and gain a broader perspective on the exploration of the American Southwest.
Conclusion:
The Coronado Map remains a captivating artifact that offers a glimpse into the exploration of the American Southwest during the 16th century. While its authenticity remains a subject of debate, its historical and cultural significance cannot be denied. The map serves as a reminder of the human spirit of exploration, the complex history of the region, and the enduring impact of European encounters with indigenous populations. Its study continues to offer valuable insights into the past, enriching our understanding of the history and geography of the American Southwest.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Coronado Map: A Journey Through History and Mystery. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!