The Sahel: A Band of Transition in Africa
Related Articles: The Sahel: A Band of Transition in Africa
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Sahel: A Band of Transition in Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Sahel: A Band of Transition in Africa
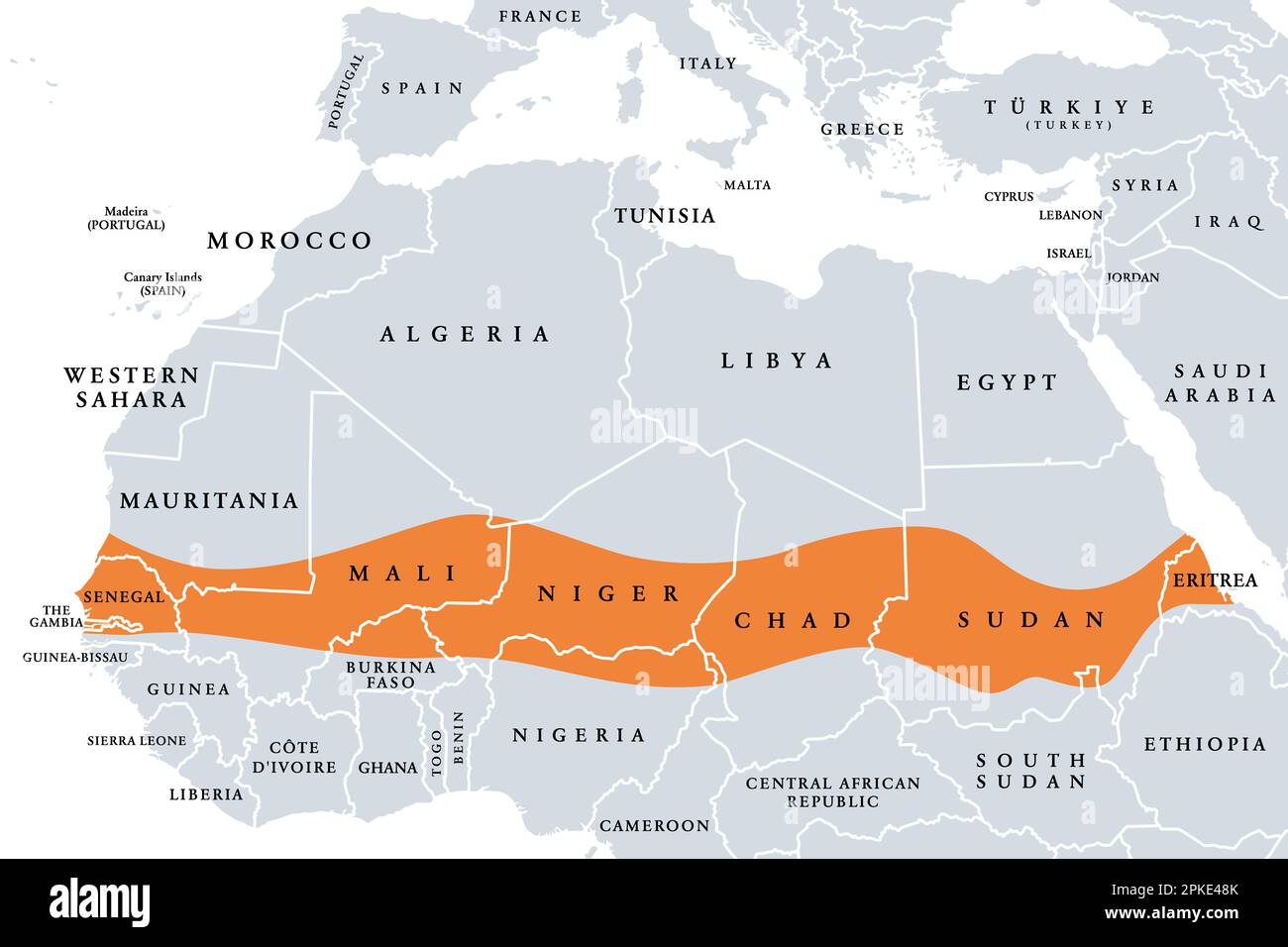
The Sahel, a vast semi-arid region spanning across Africa, is a vital geographical zone that plays a crucial role in the continent’s ecological, social, and economic landscape. This transition zone, situated between the Sahara Desert to the north and the savannas to the south, is characterized by its unique climate, diverse ecosystems, and rich cultural heritage. Understanding the Sahel’s geography, challenges, and potential is essential for informed decision-making regarding its future.
Geography and Climate:
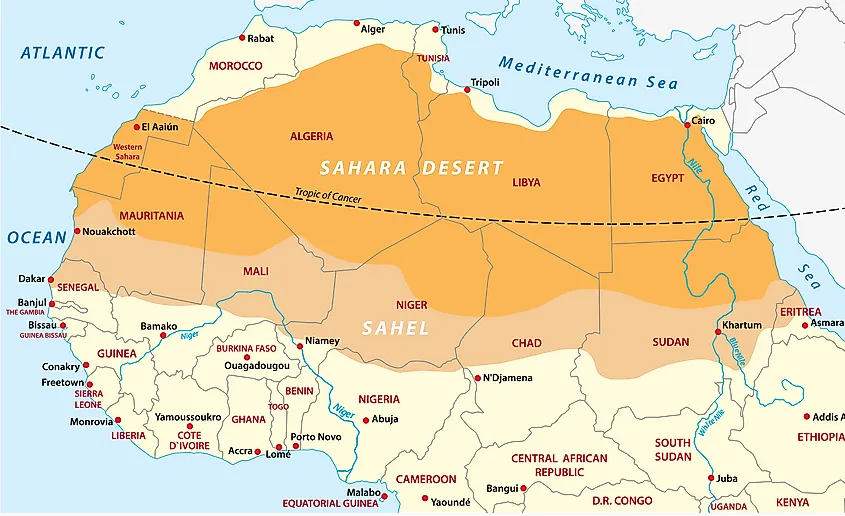
The Sahel stretches across eleven countries in North and West Africa, including Senegal, Mauritania, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, Chad, Sudan, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Djibouti, and Somalia. The region covers an area of approximately 3.3 million square kilometers, encompassing diverse landscapes ranging from dry grasslands and scrubland to rocky plateaus and seasonal wetlands.
The Sahel’s defining characteristic is its semi-arid climate, characterized by low and erratic rainfall. The region experiences a distinct dry season, typically lasting from October to May, during which rainfall is scarce or absent. The rainy season, from June to September, brings much-needed precipitation, but its intensity and duration can vary significantly from year to year. This unpredictable climate makes the Sahel highly vulnerable to droughts, a recurring phenomenon that has devastating consequences for the region’s inhabitants and ecosystems.
Ecosystems and Biodiversity:
Despite its harsh climate, the Sahel boasts a rich and diverse array of ecosystems. The region’s vegetation varies greatly, with grasslands dominated by drought-resistant grasses and shrubs in the northern parts, transitioning to more wooded areas with acacia and baobab trees in the south. This variation in vegetation supports a diverse range of animal life, including gazelles, antelopes, lions, hyenas, and numerous bird species.
The Sahel’s ecosystems are also crucial for the livelihoods of millions of people, providing essential resources such as grazing land for livestock, fuelwood, and medicinal plants. However, these ecosystems are increasingly threatened by human activities, such as overgrazing, deforestation, and land degradation, which exacerbate the effects of climate change and contribute to desertification.
Human Population and Culture:
The Sahel is home to a diverse population of approximately 100 million people, representing various ethnic groups and cultures. The region’s population density is relatively low, but it is growing rapidly, placing immense pressure on resources and leading to increasing competition for land and water.
The Sahel’s cultural heritage is rich and multifaceted, with a long history of nomadic pastoralism, agriculture, and trade. Traditional societies in the region have developed unique adaptations to the harsh environment, including sophisticated knowledge of water management, livestock breeding, and sustainable land use practices. However, these traditional practices are increasingly challenged by globalization, urbanization, and the influx of new technologies.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Sahel faces a complex set of challenges, including:
- Climate Change and Desertification: The Sahel is particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, experiencing rising temperatures, erratic rainfall patterns, and increased drought frequency. These changes exacerbate existing environmental problems, leading to land degradation, desertification, and biodiversity loss.
- Poverty and Inequality: Poverty and inequality are widespread in the Sahel, with a large proportion of the population living below the poverty line. This poverty is often linked to limited access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
- Conflict and Instability: The Sahel is prone to conflict and instability, driven by factors such as poverty, inequality, climate change, and competition for resources. Armed groups, ethnic tensions, and political instability have created a volatile environment, hindering development and humanitarian efforts.
- Food Insecurity: The Sahel is highly susceptible to food insecurity, with recurrent droughts and other climatic shocks leading to crop failures and livestock losses. This vulnerability is exacerbated by poverty, conflict, and limited access to markets and infrastructure.
- Migration and Displacement: Climate change, conflict, and poverty are driving increasing migration and displacement in the Sahel. People are forced to leave their homes in search of better opportunities, leading to overcrowding in urban areas and putting pressure on resources and social services.
Despite these challenges, the Sahel also presents significant opportunities for sustainable development and regional cooperation. These opportunities include:
- Harnessing Renewable Energy: The Sahel has vast potential for renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and biomass. Investing in renewable energy infrastructure can help address the region’s energy needs while reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
- Promoting Sustainable Land Management: Implementing sustainable land management practices, such as agroforestry, rainwater harvesting, and soil conservation, can help restore degraded lands, improve food security, and enhance resilience to climate change.
- Developing Human Capital: Investing in education, healthcare, and skills development is crucial for empowering communities and creating a more resilient and prosperous Sahel.
- Strengthening Regional Cooperation: Collaborative efforts between Sahelian countries are essential for addressing transboundary challenges, such as climate change, conflict, and migration. Regional cooperation can facilitate knowledge sharing, resource mobilization, and coordinated action.
FAQs about the Sahel:
1. Why is the Sahel important?
The Sahel is important for its unique geographical location, diverse ecosystems, and significant role in Africa’s ecological and social landscape. It provides essential resources, supports a rich cultural heritage, and influences regional and global climate patterns.
2. What are the main challenges facing the Sahel?
The Sahel faces numerous challenges, including climate change, desertification, poverty, conflict, food insecurity, and migration. These challenges are interconnected and pose significant threats to the region’s environment, people, and future development.
3. What can be done to address the challenges in the Sahel?
Addressing the challenges in the Sahel requires a multi-faceted approach that combines sustainable development, conflict resolution, humanitarian assistance, and regional cooperation. Investing in renewable energy, promoting sustainable land management, developing human capital, and strengthening regional partnerships are crucial steps towards a more resilient and prosperous Sahel.
4. How does climate change impact the Sahel?
Climate change is exacerbating existing challenges in the Sahel, leading to more frequent and severe droughts, rising temperatures, and increased desertification. These changes are disrupting livelihoods, driving migration, and posing significant threats to the region’s ecosystems and human well-being.
5. What is the role of international organizations in the Sahel?
International organizations play a vital role in supporting development efforts in the Sahel, providing humanitarian assistance, promoting peacebuilding, and facilitating regional cooperation. They also play a crucial role in raising awareness of the challenges facing the region and advocating for increased investment in sustainable development initiatives.
Tips for Engaging with the Sahel:
- Stay informed about the region’s challenges and opportunities: Regularly consult reputable sources, such as international organizations, research institutions, and news outlets, to stay updated on the latest developments in the Sahel.
- Support organizations working to address the region’s challenges: Consider donating to or volunteering with organizations working on sustainable development, conflict resolution, humanitarian assistance, and climate change mitigation in the Sahel.
- Advocate for policies that promote sustainable development and peace in the Sahel: Engage with your elected officials and policymakers to advocate for policies that support the region’s development and address the challenges it faces.
- Learn about the Sahel’s rich cultural heritage: Explore the region’s art, music, literature, and traditions to gain a deeper understanding of its diversity and resilience.
Conclusion:
The Sahel is a vital region facing complex challenges and presenting significant opportunities. Understanding its geography, climate, ecosystems, and human population is crucial for informed decision-making regarding its future. Addressing the challenges of climate change, poverty, conflict, and food insecurity requires a comprehensive and collaborative approach that combines sustainable development, peacebuilding, and regional cooperation. By investing in renewable energy, promoting sustainable land management, developing human capital, and strengthening regional partnerships, we can help create a more resilient and prosperous Sahel for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Sahel: A Band of Transition in Africa. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!