The Ural River: A Lifeline Across the Eurasian Steppe
Related Articles: The Ural River: A Lifeline Across the Eurasian Steppe
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Ural River: A Lifeline Across the Eurasian Steppe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ural River: A Lifeline Across the Eurasian Steppe
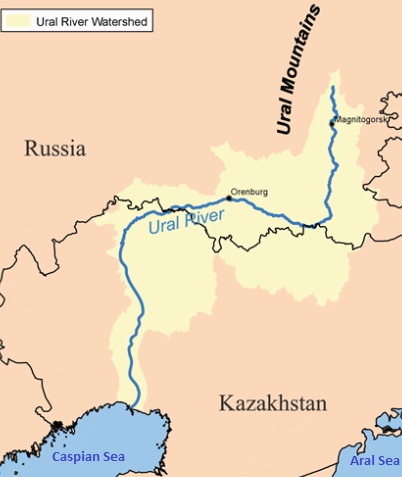
The Ural River, a vital artery traversing the vast expanse of the Eurasian Steppe, holds a significant place in both the physical and historical landscape of the region. This article delves into the geographical, historical, and ecological significance of this remarkable waterway, exploring its role in shaping the surrounding environment and the lives of those who inhabit its banks.
A River of Boundaries and Connections
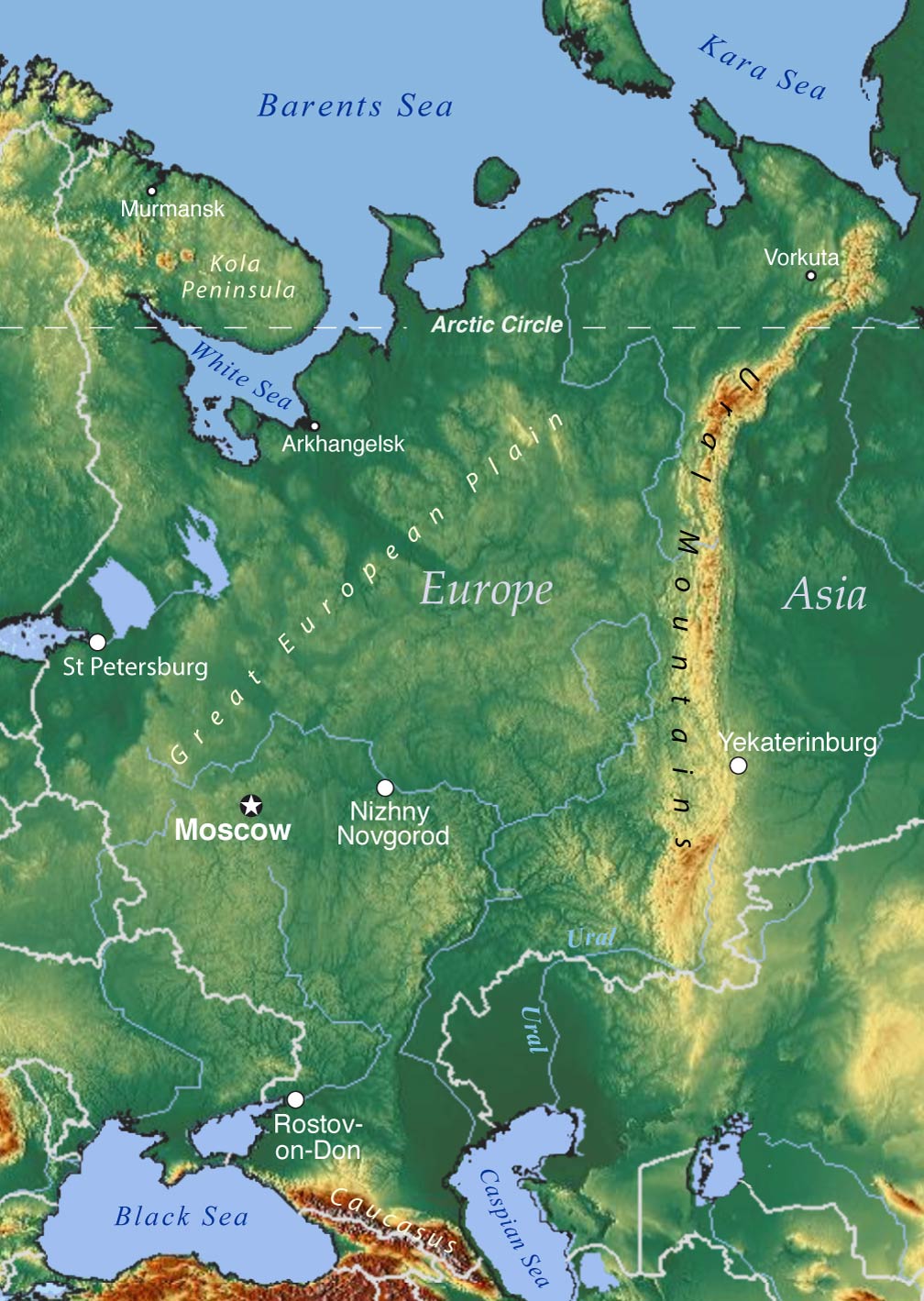
Flowing for over 2,428 kilometers (1,509 miles) from its source in the Ural Mountains, the Ural River carves a path through the southern fringes of the Ural Mountains, meandering westward across the Russian steppes before emptying into the Caspian Sea. This journey places the river at the heart of a complex geopolitical and ecological network.
Defining Borders: The Ural River has long served as a natural boundary, dividing the Eurasian continent into Europe and Asia. This geographic distinction, while not universally accepted, has profoundly influenced the historical development of the region, shaping cultural identities and political boundaries.
Connecting Continents: Despite its role as a dividing line, the Ural River also serves as a crucial link between the two continents. It has facilitated trade and cultural exchange for centuries, acting as a conduit for the movement of goods, people, and ideas. This interconnectedness is evident in the diverse cultures and languages that have flourished along its banks.
A Source of Life: The Ural River is a vital source of water for the surrounding region, supporting a rich ecosystem and providing sustenance for both humans and wildlife. Its fertile floodplains have long been home to agricultural communities, while its waters sustain a diverse array of flora and fauna.
Historical Significance
The Ural River has played a central role in the history of the region, witnessing the rise and fall of empires, the development of trade routes, and the evolution of human settlements.
Ancient Civilizations: Archaeological evidence suggests that the banks of the Ural River were inhabited by nomadic tribes as far back as the Bronze Age. These early settlements thrived on the river’s resources, utilizing its waters for agriculture, fishing, and transportation.
The Silk Road: The Ural River played a crucial role in the development of the Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting East Asia with Europe. The river provided a vital passage for goods and travelers, contributing to the economic and cultural exchange between the East and West.
Russian Expansion: During the Tsarist era, the Ural River became a key component in Russia’s eastward expansion. The river served as a natural border, facilitating military campaigns and the establishment of settlements in the vast Siberian territories.
Industrialization and Modernity: The 20th century witnessed the rise of heavy industries along the Ural River, particularly in the cities of Orenburg and Magnitogorsk. These industries relied on the river for water and transportation, contributing to the region’s economic development.
Ecological Importance
The Ural River is a critical component of the Eurasian Steppe ecosystem, supporting a diverse range of flora and fauna. Its waters provide habitat for numerous fish species, including sturgeon, pike, and carp, while its floodplains sustain a variety of birds, mammals, and reptiles.
Biodiversity Hotspot: The Ural River is home to a rich biodiversity, including several endangered species. The river’s ecological significance has led to efforts to conserve its natural resources and protect its fragile ecosystem.
Water Management Challenges: The Ural River faces significant water management challenges, including pollution from industrial waste and agricultural runoff. These challenges threaten the river’s ecological health and the livelihoods of those who depend on its resources.
The Future of the Ural River
The Ural River faces a complex future, marked by the need to balance its ecological importance with the demands of economic development. Sustainable water management practices, pollution control measures, and conservation efforts are crucial for ensuring the river’s long-term health and the prosperity of the surrounding communities.
FAQs about the Ural River
1. Why is the Ural River considered a boundary between Europe and Asia?
While not universally accepted, the Ural River is often considered a natural boundary between Europe and Asia due to its geographic position and the distinct geological and cultural characteristics of the surrounding regions.
2. What are the main economic activities along the Ural River?
The Ural River supports a variety of economic activities, including agriculture, fishing, transportation, and industry. The region is known for its oil and gas reserves, as well as its mining and manufacturing industries.
3. What are the environmental challenges facing the Ural River?
The Ural River faces significant environmental challenges, including pollution from industrial waste and agricultural runoff, as well as the impact of climate change on water availability.
4. What are the efforts being made to conserve the Ural River?
Efforts to conserve the Ural River include pollution control measures, habitat restoration projects, and the promotion of sustainable water management practices.
5. What is the cultural significance of the Ural River?
The Ural River has played a significant role in the development of local cultures and traditions. Its banks have been home to diverse ethnic groups, each with their own unique customs and beliefs.
Tips for Exploring the Ural River
1. Visit the Ural Mountains: The source of the Ural River lies in the majestic Ural Mountains, offering opportunities for hiking, skiing, and exploring the region’s natural beauty.
2. Explore the cities of Orenburg and Magnitogorsk: These cities offer a glimpse into the region’s industrial history and cultural heritage, with museums, theaters, and historical landmarks.
3. Take a river cruise: Several companies offer river cruises along the Ural River, providing a unique perspective on the surrounding landscape and its cultural significance.
4. Visit the Orenburg State Nature Reserve: This reserve protects a diverse range of flora and fauna, offering opportunities for wildlife viewing and nature photography.
5. Learn about the region’s history and culture: The Ural River region is rich in history and culture, with museums, historical sites, and local festivals offering insights into the region’s past and present.
Conclusion
The Ural River stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of nature and human society. Its role as a source of life, a facilitator of trade, and a defining boundary has shaped the region’s physical and cultural landscape. As the world faces the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, the need to protect and manage the Ural River sustainably becomes increasingly critical. By understanding the river’s significance and implementing responsible practices, we can ensure that this vital waterway continues to nourish the surrounding environment and the lives of those who depend on it.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ural River: A Lifeline Across the Eurasian Steppe. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!