Understanding Heat Domes: A Visual Guide to Extreme Heat Events
Related Articles: Understanding Heat Domes: A Visual Guide to Extreme Heat Events
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Heat Domes: A Visual Guide to Extreme Heat Events. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Heat Domes: A Visual Guide to Extreme Heat Events
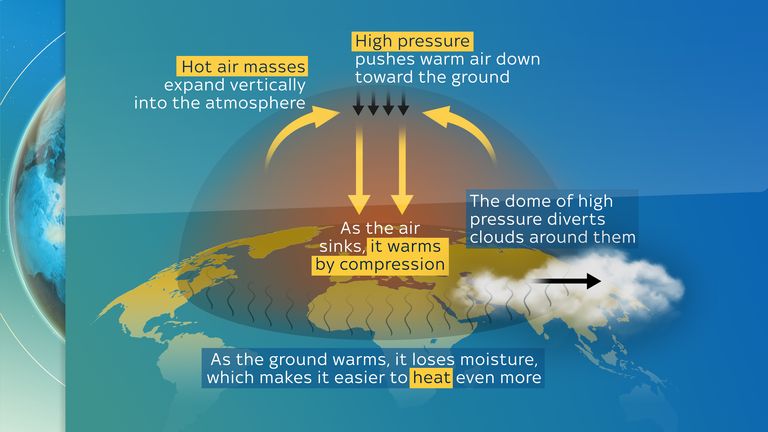
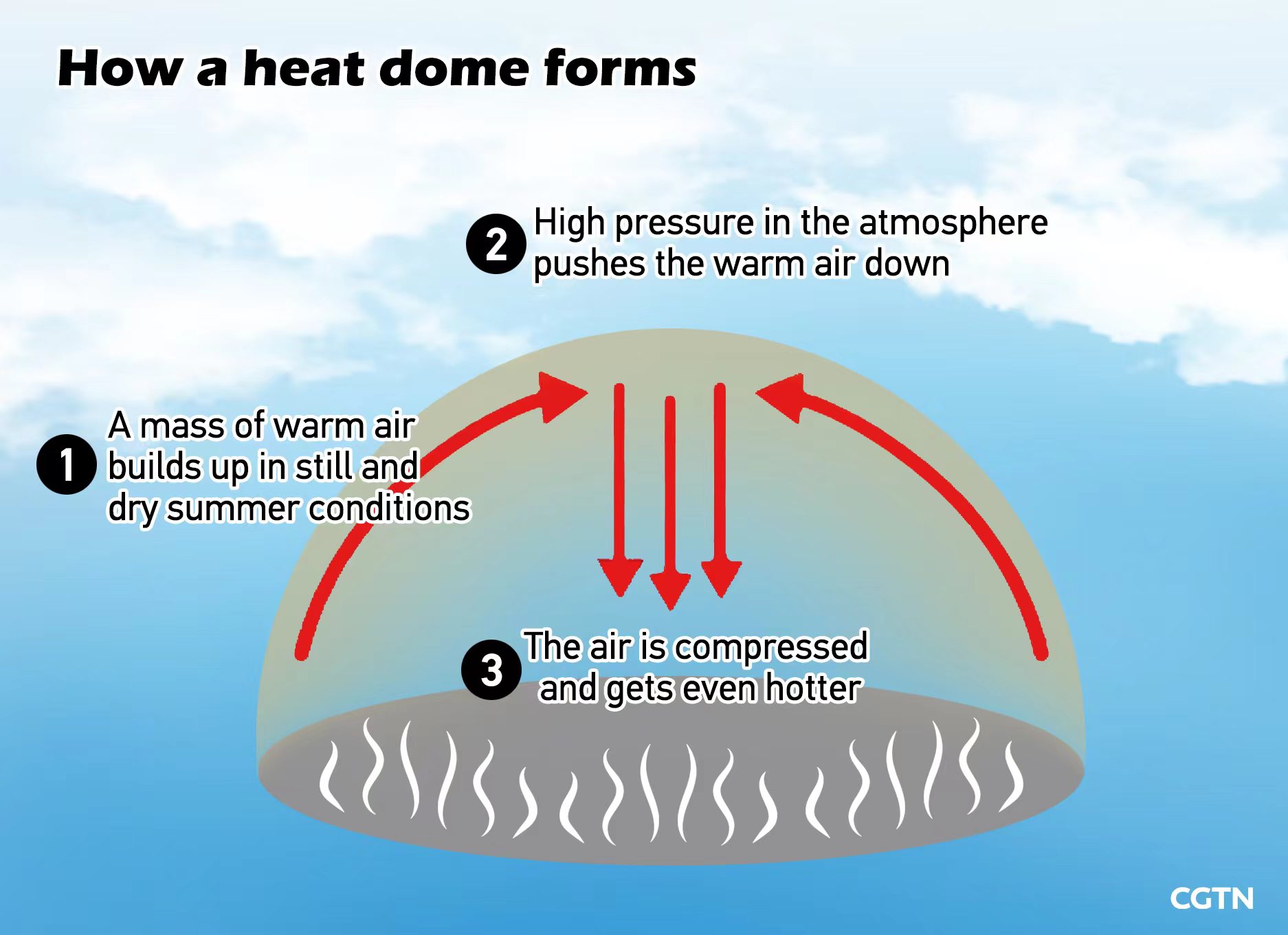
Heat domes, a meteorological phenomenon characterized by an area of high atmospheric pressure trapping hot air close to the ground, have become increasingly prominent in recent years, leading to extreme heat events with potentially devastating consequences. Visualizing these events through heat dome maps offers valuable insights into the spatial extent and intensity of these heat waves, aiding in public preparedness and mitigation efforts.
Unveiling the Invisible: How Heat Dome Maps Work
Heat dome maps are visual representations of air temperature anomalies, showcasing regions experiencing significantly elevated temperatures compared to historical averages. They typically use color gradients to represent the severity of the heat, with warmer colors indicating higher temperatures. These maps are generated using data from various sources, including:
- Weather Satellites: Satellites equipped with infrared sensors measure the temperature of the Earth’s surface, providing a broad overview of heat distribution.
- Weather Stations: Ground-based weather stations collect data on temperature, humidity, and other meteorological variables, offering localized information.
- Numerical Weather Models: Computer models simulate atmospheric conditions, predicting future temperature patterns and generating forecasts for heat dome events.
Navigating the Map: Key Elements and Interpretations
Heat dome maps provide critical information about the geographic extent, intensity, and duration of heat events. Key elements to consider when interpreting these maps include:
- Color Scale: The color gradient indicates the temperature anomaly relative to historical averages. Red and orange hues usually represent the most severe heat, while green and blue indicate cooler temperatures.
- Contour Lines: Lines connecting points of equal temperature highlight areas with similar heat levels. This helps identify the boundaries of the heat dome and its spatial extent.
- Overlayed Features: Maps often incorporate additional layers, such as population density, vulnerable infrastructure, and geographical features, to understand potential impacts on different communities and environments.
Beyond Visualization: The Importance of Heat Dome Maps
Heat dome maps serve as crucial tools for a range of stakeholders, facilitating informed decision-making and proactive responses to extreme heat events:
- Public Health Officials: Maps help identify areas at highest risk of heat-related illnesses, enabling targeted public health interventions, such as heat advisories, cooling centers, and public awareness campaigns.
- Emergency Managers: By visualizing the spatial extent of heat events, emergency managers can anticipate potential challenges and prioritize resources for vulnerable populations and critical infrastructure.
- Infrastructure Managers: Heat dome maps assist in identifying areas at risk of power outages, transportation disruptions, and other infrastructure failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and mitigation strategies.
- Researchers and Scientists: Maps provide valuable data for studying the dynamics of heat domes, understanding their causes, and predicting future occurrences, contributing to improved climate modeling and adaptation strategies.
FAQs about Heat Dome Maps
Q: What are the limitations of heat dome maps?
A: While heat dome maps provide valuable information, they have limitations:
- Data Availability: The accuracy of maps depends on the availability and quality of meteorological data, which can be limited in certain regions.
- Spatial Resolution: Maps may not capture localized variations in temperature within a heat dome, especially at finer scales.
- Dynamic Nature: Heat domes are constantly evolving, and maps may not always reflect the most up-to-date conditions.
Q: How can I access heat dome maps?
A: Heat dome maps are often available through:
- National Weather Services: Agencies like the National Weather Service (NWS) in the United States provide real-time and forecast maps for heat events.
- Climate Data Centers: Institutions like the National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) archive historical and current climate data, including heat dome maps.
- Research Institutions: Universities and research organizations often develop specialized heat dome maps for specific regions or research purposes.
Q: How can heat dome maps be used to mitigate heat-related risks?
A: Heat dome maps can be used for various mitigation strategies:
- Early Warning Systems: Maps can trigger early warnings to communities, allowing individuals to prepare for extreme heat and take necessary precautions.
- Resource Allocation: Maps help allocate resources, such as cooling centers and emergency medical services, to areas most affected by the heat.
- Infrastructure Resilience: Maps can inform decisions about strengthening infrastructure, such as power grids and transportation systems, to withstand extreme temperatures.
- Urban Planning: Maps can guide urban planning decisions, such as creating green spaces, reducing heat island effects, and promoting sustainable building practices.
Tips for Using Heat Dome Maps Effectively
- Understand the Map’s Purpose: Consider the intended audience and specific applications of the map before interpreting its data.
- Consult Multiple Sources: Cross-reference information from different maps and data sources to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the heat event.
- Consider Context: Analyze the map in the context of local geography, population density, and existing vulnerabilities to assess potential impacts.
- Stay Informed: Regularly monitor updates and forecasts as heat domes are dynamic events that can change rapidly.
Conclusion: Visualizing Heat Events for a Safer Future
Heat dome maps offer a powerful tool for understanding, preparing for, and mitigating the impacts of extreme heat events. By visualizing the spatial extent and intensity of these heat waves, they enable informed decision-making, resource allocation, and public awareness efforts. As climate change intensifies the frequency and severity of heat domes, these maps will become increasingly critical for safeguarding communities and ensuring a resilient future.
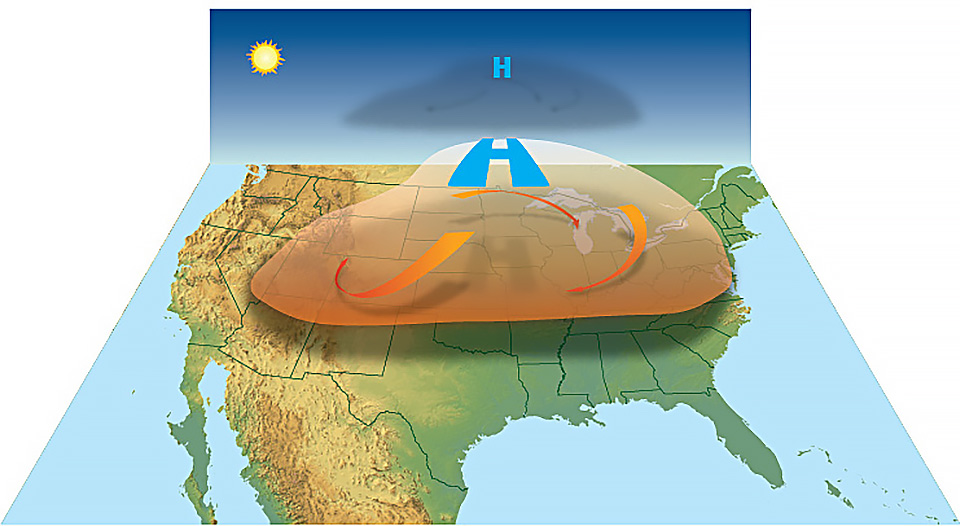

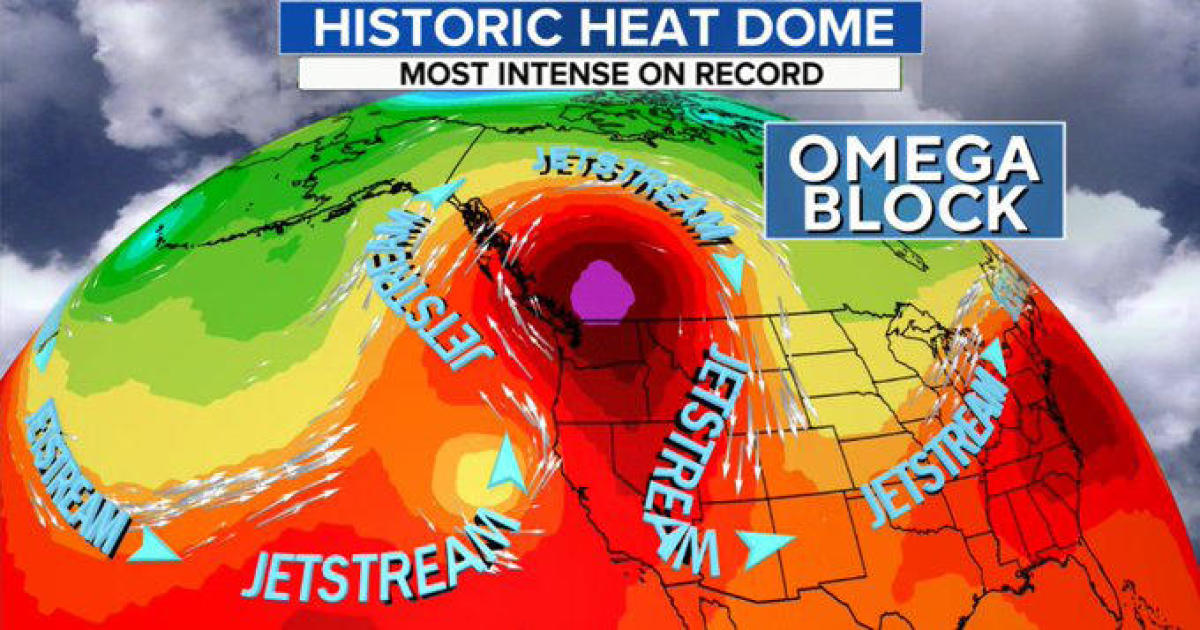

![Heat Domes Explained [UPSC Geography Notes]](https://cdn1.byjus.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/heat-dome-1536x866.jpeg)

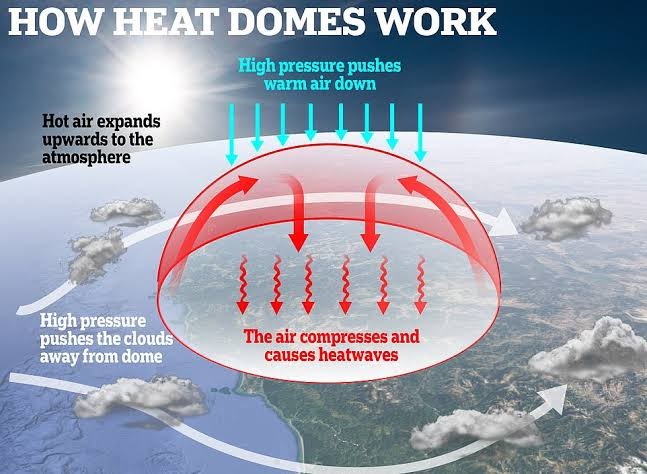
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Heat Domes: A Visual Guide to Extreme Heat Events. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!