Understanding the Administrative Landscape of France: A Guide to Its Provinces
Related Articles: Understanding the Administrative Landscape of France: A Guide to Its Provinces
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Administrative Landscape of France: A Guide to Its Provinces. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Administrative Landscape of France: A Guide to Its Provinces
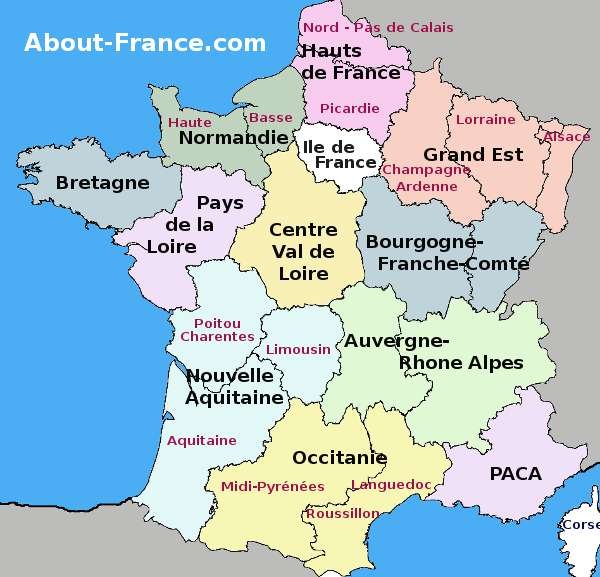
France, a nation steeped in history and cultural richness, boasts a diverse and fascinating administrative landscape. While the country is often perceived as a unified entity, its internal structure is complex and multifaceted. A key element of this structure is the concept of regions, which serve as the primary administrative divisions of France. These regions, often referred to as provinces, play a vital role in the country’s governance, economic development, and cultural identity.
A Historical Perspective on French Provinces
To grasp the significance of French provinces, it is essential to delve into their historical context. Before the French Revolution in 1789, France was divided into a patchwork of provinces, each with its own unique history, traditions, and governance. These provinces, such as Normandy, Brittany, and Provence, were often characterized by strong regional identities and loyalties.
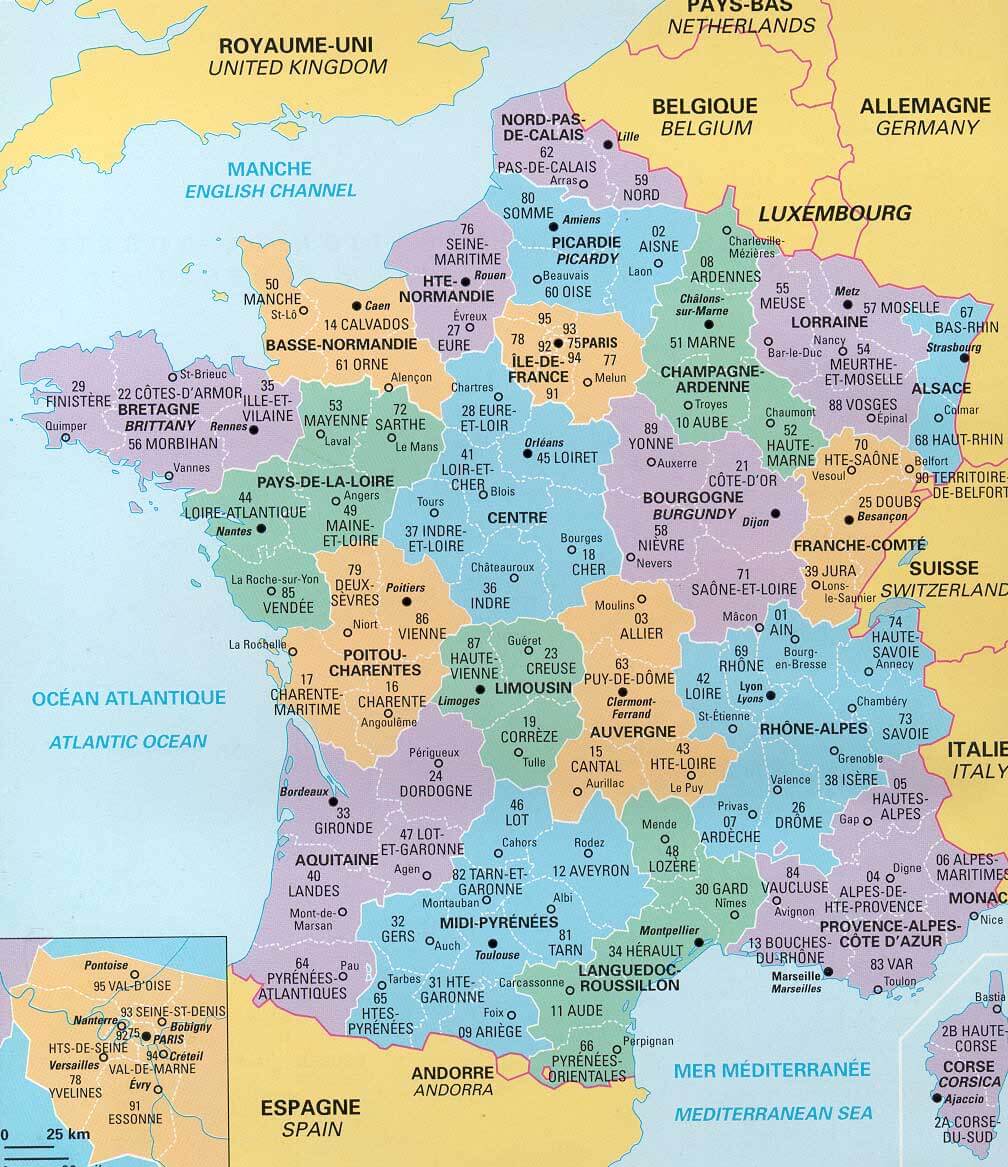
The French Revolution, however, brought about a radical shift in the country’s administrative structure. The monarchy was abolished, and the centralized power of the state was established. The old provincial system was dismantled, and France was divided into 83 departments, each with its own elected council and prefect appointed by the central government.
The Modern Era of French Regions
While the departmental structure remains in place, France introduced a new layer of administrative division in 1982 with the creation of regions. These regions, initially 22 in number, were designed to decentralize power and give local communities greater autonomy in decision-making. Each region has its own elected regional council and a president, who is responsible for overseeing the region’s affairs.
The Restructuring of French Regions
In 2014, a major administrative reform took place, reducing the number of regions from 22 to 13. This restructuring aimed to streamline governance, enhance efficiency, and promote economic cooperation between neighboring regions. The new regions, while retaining their historical identities, often encompass several former departments.
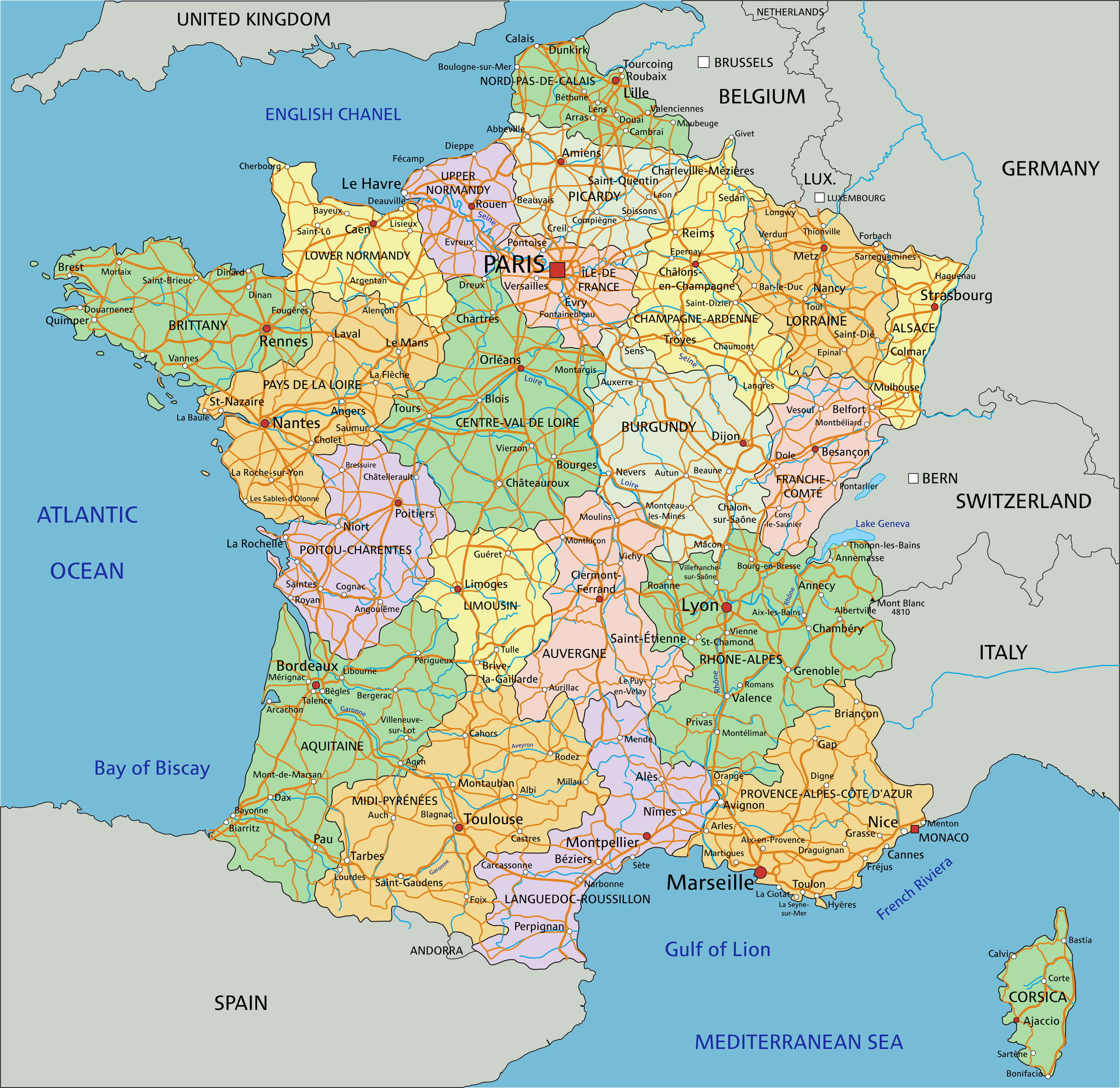
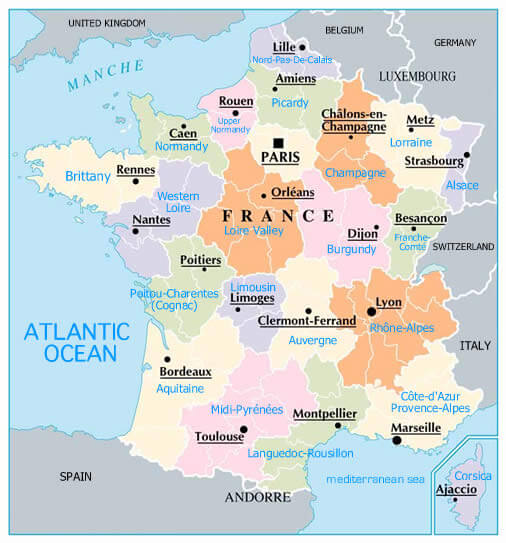
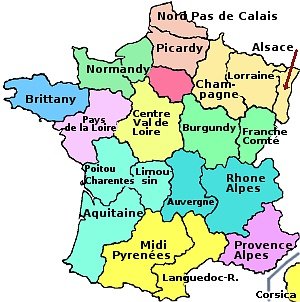
Exploring the French Provinces Map
Understanding the administrative structure of France is best accomplished through a visual representation – the French provinces map. This map depicts the 13 regions of France, highlighting their boundaries and names. It also often includes details such as major cities, rivers, and geographical features, providing a comprehensive overview of the country’s spatial organization.
The Importance of the French Provinces Map
The French provinces map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the country’s geography, history, and administration. It helps to:
- Visualize the administrative structure of France: The map clearly illustrates the boundaries of the 13 regions and their respective departments.
- Gain insight into regional identities: Each region possesses its own distinct cultural heritage, traditions, and dialect, which can be explored through the map.
- Understand regional economic development: The map can reveal the economic strengths and weaknesses of different regions, facilitating targeted investment and development initiatives.
- Support tourism planning: The map helps travelers identify regions of interest based on their preferences for cultural experiences, natural landscapes, or historical sites.
- Facilitate communication and collaboration: The map serves as a common reference point for communication and collaboration between regional governments, businesses, and individuals.
FAQs about French Provinces Map
1. What are the 13 regions of France?
The 13 regions of France are:
- Île-de-France
- Grand Est
- Hauts-de-France
- Normandie
- Centre-Val de Loire
- Pays de la Loire
- Bretagne
- Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Occitanie
- Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
- Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
- Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
- Corse
2. How are the regions of France different from the departments?
Regions are larger administrative units that encompass several departments. Departments are smaller subdivisions within regions, responsible for local governance.
3. What are the major cities located in each region?
Each region has its own major cities, which serve as economic and cultural centers. For example, Paris is the capital of Île-de-France, Lyon is the major city in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, and Marseille is a key city in Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur.
4. Are the regions of France truly independent?
While regions have significant autonomy in decision-making, they are still subject to the authority of the central government in Paris. The French government retains ultimate control over national policies and legislation.
5. How can I access a French provinces map?
French provinces maps are readily available online through various sources, including government websites, mapping services like Google Maps, and educational resources.
Tips for Using the French Provinces Map
- Explore the map in detail: Pay attention to the boundaries of each region, its major cities, and geographical features.
- Compare regions: Examine the differences and similarities between regions in terms of their size, population density, economic activity, and cultural heritage.
- Focus on specific interests: If you are interested in a particular aspect of France, such as history, gastronomy, or wine production, use the map to identify regions that align with your interests.
- Combine the map with other resources: Use the map in conjunction with travel guides, historical accounts, and cultural descriptions to gain a deeper understanding of each region.
Conclusion
The French provinces map serves as a crucial tool for understanding the intricate administrative structure of France. It provides a visual representation of the country’s regions, highlighting their historical significance, cultural diversity, and economic development. By navigating the map, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and fascinating landscape of France, both geographically and administratively. The map offers a valuable window into the country’s rich history, diverse cultures, and dynamic regional identities.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Administrative Landscape of France: A Guide to Its Provinces. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!