Understanding the Key to Map Interpretation: The Map Bar Scale
Related Articles: Understanding the Key to Map Interpretation: The Map Bar Scale
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Key to Map Interpretation: The Map Bar Scale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Key to Map Interpretation: The Map Bar Scale

Maps are powerful tools for navigating the world, whether it’s a local neighborhood or the vast expanse of a continent. However, their utility hinges on our ability to accurately interpret the distances they represent. This is where the map bar scale, a vital component of map design, comes into play.
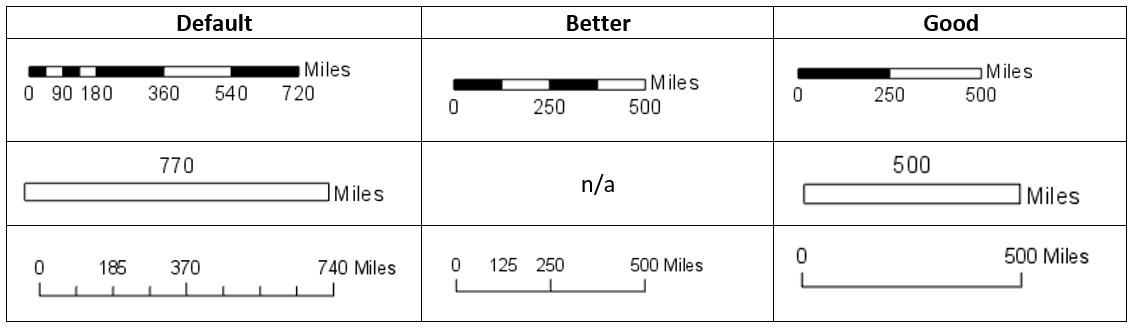
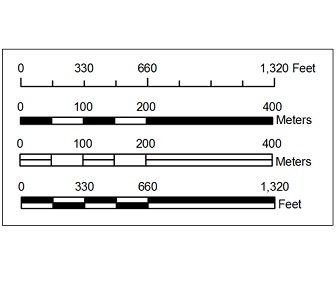
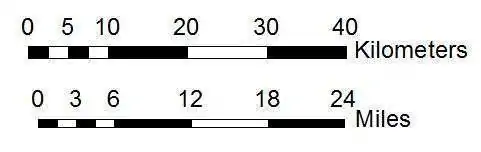
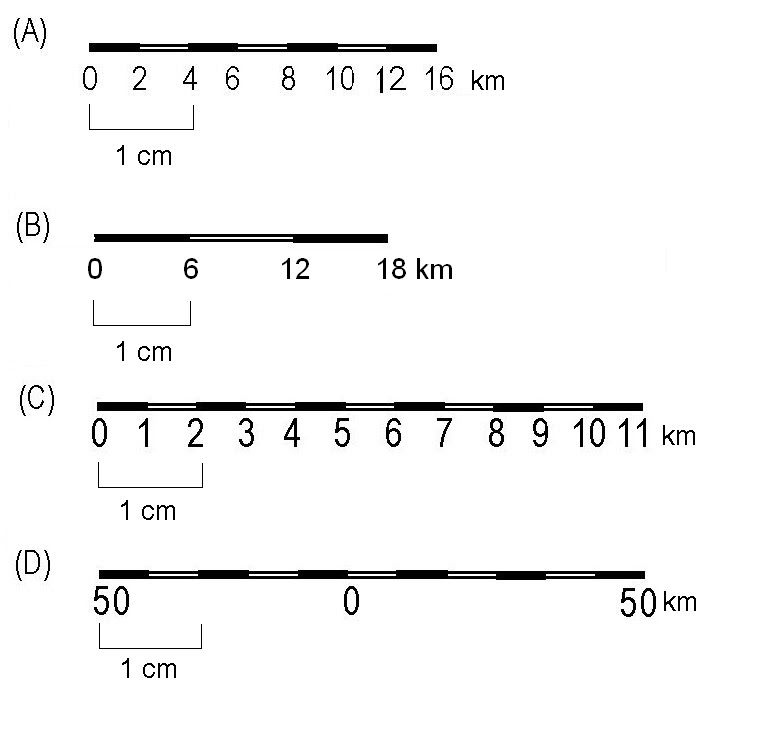
A map bar scale, also known as a graphic scale, provides a visual representation of distances on a map. It consists of a graduated line, typically divided into segments, with corresponding numerical values indicating the actual distance represented by each segment. This simple yet effective tool allows users to directly measure distances on the map and translate them into real-world measurements.
The Significance of the Map Bar Scale
The map bar scale plays a crucial role in ensuring map accuracy and user comprehension. It serves as a fundamental reference point, enabling users to:
- Determine actual distances: By measuring the distance between two points on a map using the bar scale, users can calculate the real-world distance between those points.
- Compare distances: The bar scale allows for easy comparison of distances between different locations on the map.
- Maintain consistency: The bar scale ensures that all distances on the map are represented accurately and consistently, regardless of the map’s size or orientation.
- Overcome limitations of verbal scales: Verbal scales, which express the ratio between map distance and real-world distance, can be difficult to interpret, particularly for users unfamiliar with map conventions. The map bar scale offers a more intuitive and visually accessible alternative.
Types of Map Bar Scales
Map bar scales can be presented in various forms, each offering unique advantages:
- Linear Scale: The most common type, a linear scale consists of a straight line divided into segments, each representing a specific real-world distance. The segments are typically labeled with numerical values, making distance measurement straightforward.
- Verbal Scale: A verbal scale expresses the ratio between map distance and real-world distance. For example, "1:100,000" indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units in the real world. While verbal scales provide a numerical representation of the scale, they can be less intuitive than graphic scales for visual interpretation.
- Representative Fraction (RF): The RF is a mathematical expression of the scale, written as a fraction. For example, an RF of 1:100,000 means that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units in the real world. RFs are commonly used in cartographic applications and are particularly useful for calculating precise distances.
Choosing the Appropriate Map Bar Scale
The choice of map bar scale depends on the purpose of the map and the intended audience. For maps intended for general use, a linear scale with clear labeling is often preferred. For maps intended for specialized applications, such as engineering or surveying, a verbal scale or RF may be more appropriate.
The Importance of Accuracy
The accuracy of the map bar scale is paramount to ensuring the map’s reliability. Any inaccuracies in the scale can lead to significant errors in distance measurement and interpretation. Therefore, it is essential to use reliable and accurate map sources and to verify the bar scale’s accuracy before relying on the map for critical applications.
Frequently Asked Questions about Map Bar Scales
Q: How do I use a map bar scale to measure distances?
A: To measure distances using a map bar scale, simply place a ruler or straight edge along the desired distance on the map. Then, align the ruler with the bar scale and count the number of segments that correspond to the measured distance on the map. Multiply this number by the distance represented by each segment on the bar scale to determine the actual distance.
Q: What is the difference between a map bar scale and a verbal scale?
A: A map bar scale provides a visual representation of distances, while a verbal scale expresses the scale ratio numerically. The map bar scale is more intuitive for visual interpretation, while the verbal scale offers a precise mathematical representation of the scale.
Q: Can I use a map bar scale to measure distances on a map from a different source?
A: It is generally not recommended to use a map bar scale from one map to measure distances on another map, even if they are from the same source. Different maps may have different scales, and using an incorrect bar scale can lead to inaccurate distance measurements.
Q: How do I determine the accuracy of a map bar scale?
A: The accuracy of a map bar scale can be assessed by comparing distances measured using the scale to known distances on the ground. If the measurements are consistent, the bar scale is likely accurate. However, it is important to note that the accuracy of a map bar scale can be affected by factors such as the map’s age, the method used to create the map, and the accuracy of the underlying geographic data.
Tips for Using Map Bar Scales Effectively
- Always check the map bar scale before using the map. Ensure that the bar scale is appropriate for the purpose of the map and that it is accurate.
- Use a ruler or straight edge to measure distances on the map. This will ensure more accurate measurements than using a finger or other less precise tools.
- Be mindful of the units of measurement used on the map bar scale. Make sure that the units are consistent with the units you are using to measure distances.
- Consider the limitations of the map bar scale. The bar scale represents a simplified representation of distances, and it may not be perfectly accurate for all measurements.
Conclusion
The map bar scale is an essential element of map design, providing a visual representation of distances that is crucial for accurate map interpretation. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it an invaluable tool for navigating the world, whether it’s for personal travel, research, or professional applications. By understanding the map bar scale and its principles, users can unlock the full potential of maps and confidently navigate the world around them.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Key to Map Interpretation: The Map Bar Scale. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!