Unraveling the Earth’s Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Longitude
Related Articles: Unraveling the Earth’s Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Longitude
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Earth’s Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Earth’s Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Longitude
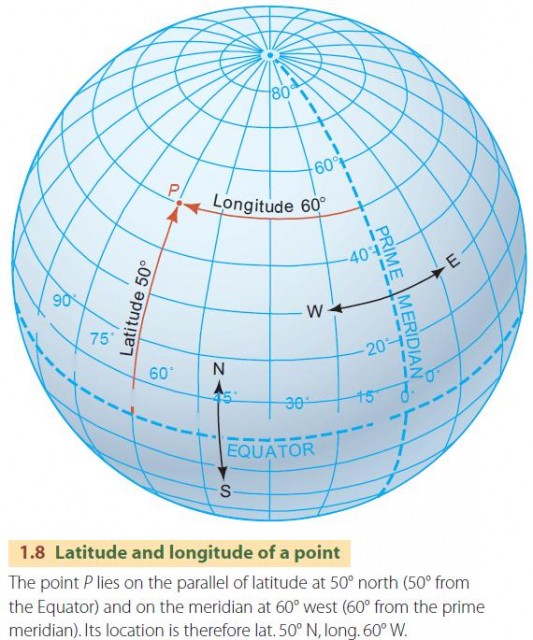
The Earth, a vast and complex sphere, is a tapestry woven with lines of latitude and longitude, invisible threads that map its surface and guide our understanding of its geography. While latitude lines run horizontally, encircling the globe like belts, longitude lines, also known as meridians, extend vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, resembling slices of an orange. These lines are crucial for pinpointing locations on our planet, enabling navigation, understanding time zones, and facilitating global communication.
Understanding Longitude: A Deep Dive
Imagine a hypothetical line drawn from the North Pole to the South Pole, passing through Greenwich, England. This line, known as the Prime Meridian, serves as the zero-degree reference point for longitude. Every other meridian is measured in degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian, with a maximum of 180 degrees in each direction.
The Significance of Longitude
Longitude’s importance is deeply rooted in its ability to provide a precise measure of east-west position. This has revolutionized navigation, making it possible to determine a ship’s or plane’s exact location on the open sea or in the vast expanse of the sky.
- Navigation: Before the development of accurate longitude measurement, seafaring was fraught with danger. Sailors relied on celestial navigation, which was imprecise and susceptible to weather conditions. The invention of the marine chronometer, a device for keeping accurate time at sea, enabled sailors to calculate their longitude and navigate safely across oceans.
- Time Zones: The Earth’s rotation, combined with longitude, defines time zones. Each time zone covers 15 degrees of longitude, allowing for a consistent system of timekeeping across the globe. This standardization is essential for international communication, transportation, and commerce.
- Mapping and Surveying: Longitude is fundamental to creating accurate maps and conducting geographical surveys. It provides a framework for defining locations and understanding the spatial relationships between various points on Earth.
- Scientific Research: Longitude plays a vital role in scientific research, particularly in fields like geology, meteorology, and oceanography. It allows scientists to track the movement of tectonic plates, analyze weather patterns, and study ocean currents.
Delving Deeper: The History of Longitude
The quest for a reliable method to determine longitude has captivated scientists and explorers for centuries. Early attempts involved observing celestial bodies, but these methods were unreliable and prone to error. The invention of the marine chronometer by John Harrison in the 18th century marked a significant breakthrough, paving the way for accurate longitude measurement and revolutionizing navigation.
The Evolution of Longitude Measurement
- Early Methods: Ancient civilizations employed various methods, including observing the stars and using compass readings, to estimate longitude. However, these methods were imprecise and limited in their application.
- The Marine Chronometer: John Harrison’s invention of the marine chronometer in the 18th century was a pivotal moment in the history of navigation. This precise timekeeping device enabled sailors to calculate their longitude by comparing the time at their current location with the time at a known location, such as Greenwich.
- Modern Techniques: Today, longitude is determined using advanced technologies, including GPS (Global Positioning System) and satellite navigation. These systems rely on a network of satellites orbiting Earth to provide precise location data, making it possible to determine longitude with remarkable accuracy.
Navigating the World of Longitude: FAQs
1. How is longitude measured?
Longitude is measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds, with the Prime Meridian serving as the zero-degree reference point. Degrees are measured eastward or westward from the Prime Meridian, with a maximum of 180 degrees in each direction.
2. What is the difference between longitude and latitude?
Longitude lines run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, while latitude lines run horizontally around the Earth. Longitude measures east-west position, while latitude measures north-south position.
3. How does longitude affect time zones?
The Earth’s rotation and longitude determine time zones. Each time zone covers 15 degrees of longitude, with a one-hour difference between adjacent zones. This system ensures consistent timekeeping across the globe.
4. How is longitude used in navigation?
Longitude is crucial for navigation, as it allows sailors and pilots to determine their east-west position. By combining longitude with latitude, a precise location can be determined.
5. What are some examples of how longitude is used in everyday life?
Longitude is used in countless ways in our daily lives, including:
- Navigation: GPS systems, maps, and online navigation apps rely on longitude to provide accurate location data.
- Timekeeping: Our understanding of time zones and the setting of clocks is based on longitude.
- Communication: Longitudinal coordinates are used to route calls and data across the globe.
- Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists use longitude to track weather patterns and predict storms.
Tips for Understanding Longitude
- Visualize the Earth: Imagine a globe and visualize longitude lines running vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole.
- Use a map: Study a world map and identify the Prime Meridian and other longitude lines.
- Explore online resources: Numerous websites and apps provide interactive maps and explanations of longitude.
- Connect with real-world applications: Think about how longitude is used in navigation, timekeeping, and other aspects of our lives.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Longitude
Longitude, a fundamental concept in geography and navigation, has transformed our understanding of the Earth and its complexities. Its ability to pinpoint locations, define time zones, and facilitate global communication has profoundly shaped our world. As we continue to explore and innovate, the importance of longitude will only grow, enabling us to navigate the vastness of our planet with ever-increasing precision and understanding.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Earth’s Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to Longitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!