Unveiling the Power of Wisconsin’s Geographic Information System (GIS) Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Wisconsin’s Geographic Information System (GIS) Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Wisconsin’s Geographic Information System (GIS) Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Wisconsin’s Geographic Information System (GIS) Map

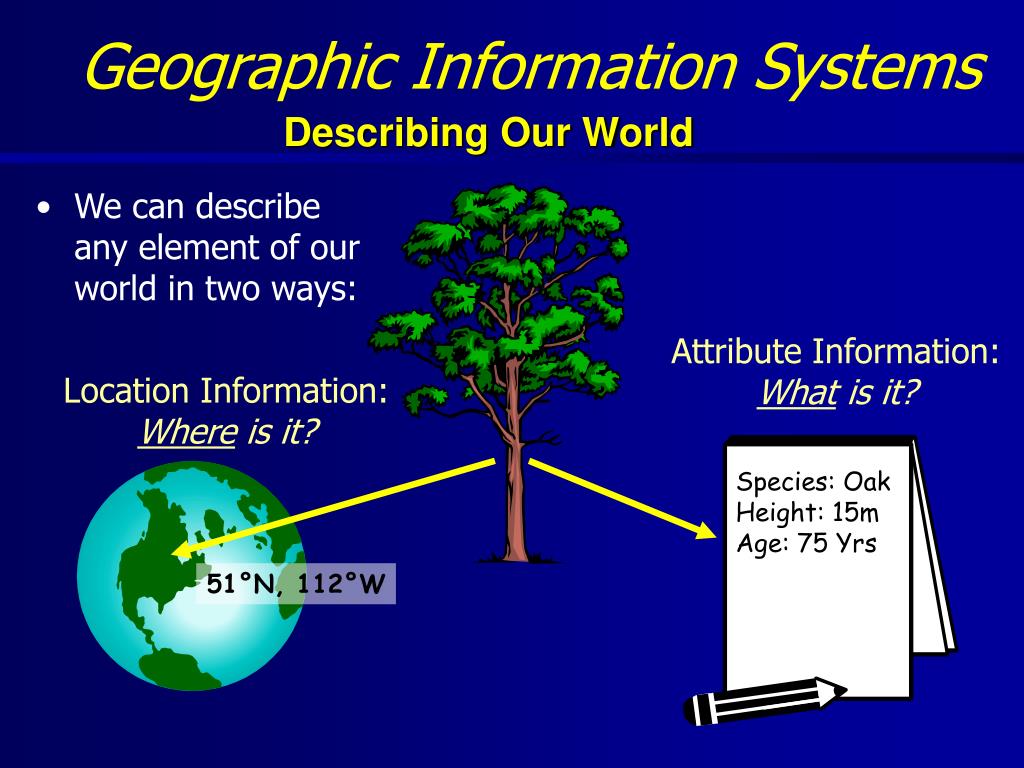
The Wisconsin Geographic Information System (GIS) map, a powerful tool for understanding and managing the state’s diverse landscape, offers a wealth of data and insights. It serves as a comprehensive platform for visualizing, analyzing, and sharing information related to various aspects of the state, from its natural resources and infrastructure to its population distribution and economic activity.
A Digital Canvas for Understanding Wisconsin:
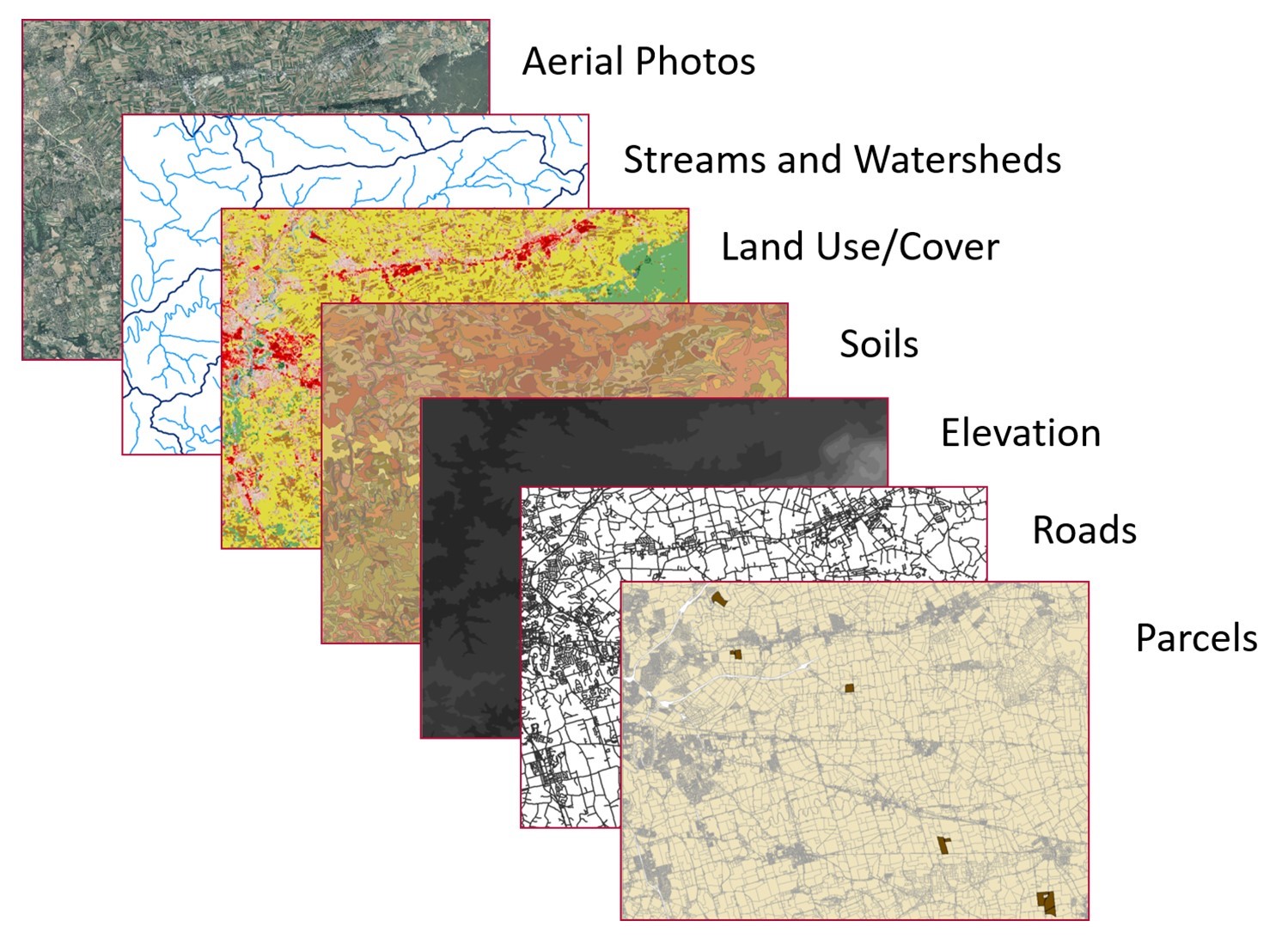
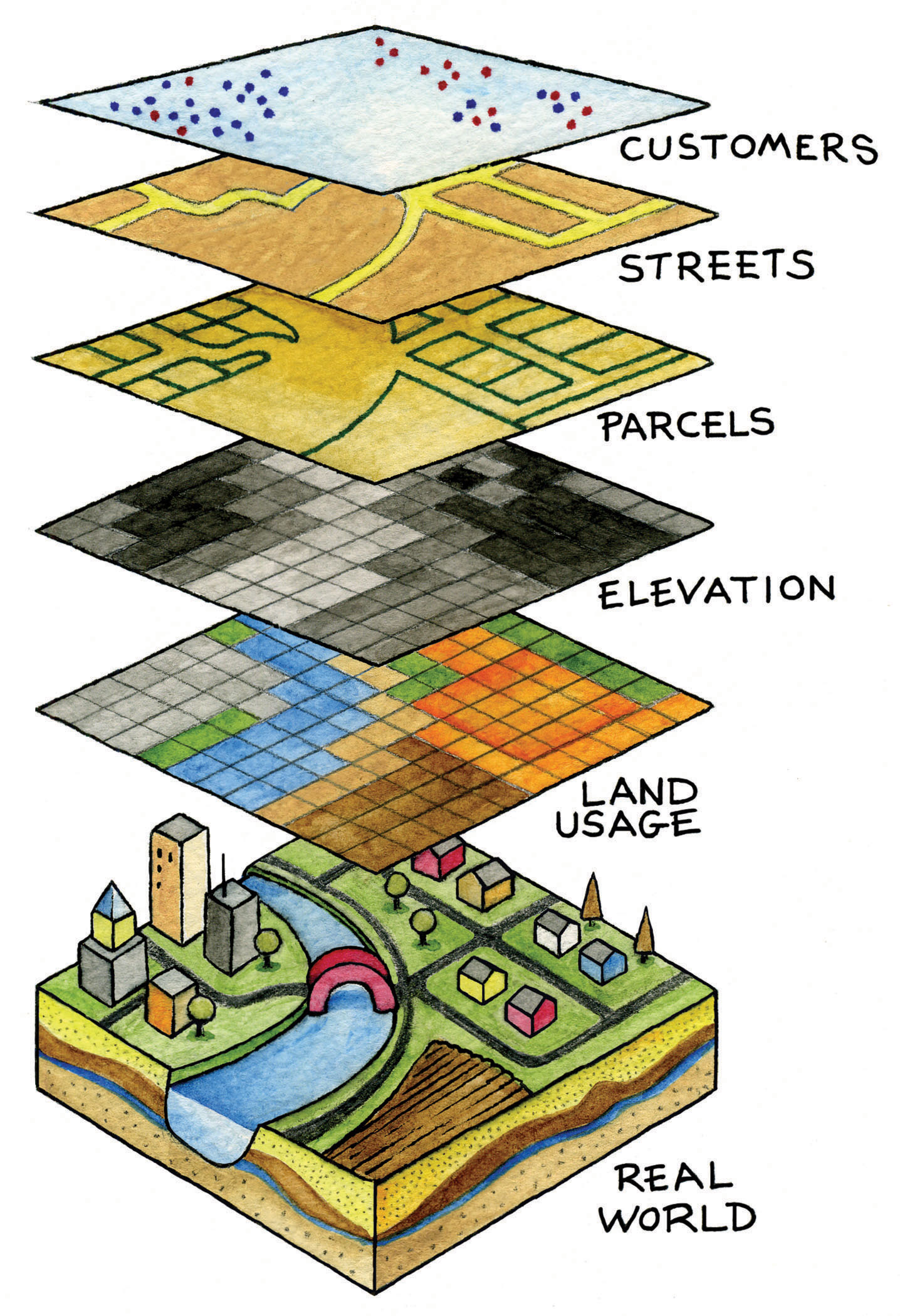
The GIS map operates on a foundation of geographic data, which is then structured and organized into layers. These layers represent different aspects of the state, allowing users to explore and analyze relationships between various geographical features. For instance, one layer might depict the distribution of forests, while another might highlight the location of roads and highways. By overlaying these layers, users can gain valuable insights into how different elements interact within the state’s landscape.
Unveiling the Benefits:
The Wisconsin GIS map offers numerous benefits, making it an indispensable tool for various stakeholders:
1. Enhanced Decision-Making: By providing a comprehensive and interactive view of the state’s geography, the GIS map empowers decision-makers in various sectors. From government agencies planning infrastructure projects to businesses choosing locations for new facilities, the map offers valuable insights to inform strategic choices.
2. Effective Resource Management: The GIS map plays a crucial role in managing the state’s natural resources. By providing detailed information on land cover, water bodies, and wildlife habitats, it assists in conservation efforts, sustainable development, and disaster preparedness.
3. Public Engagement and Transparency: The GIS map fosters transparency and public engagement by making crucial information readily accessible. Citizens can explore data related to their communities, understand environmental issues, and participate in decision-making processes.
4. Improved Emergency Response: The GIS map is a vital tool for emergency management and response. It helps visualize potential hazards, track the spread of emergencies, and coordinate rescue efforts, ensuring efficient and effective responses during critical situations.
5. Economic Development and Growth: By providing insights into land availability, infrastructure, and market trends, the GIS map supports economic development initiatives. It assists businesses in identifying potential locations for expansion, investment, and job creation.
6. Education and Research: The GIS map serves as an invaluable resource for educators and researchers. It provides a platform for exploring geographic concepts, conducting spatial analysis, and developing innovative solutions for various challenges.
Exploring the GIS Map: A User’s Guide:
The Wisconsin GIS map is a user-friendly platform, offering a variety of tools and functionalities to navigate its vast data:
1. Interactive Mapping: Users can zoom in and out of the map, pan across different areas, and explore specific features by clicking on individual points or areas.
2. Layer Control: The map allows users to selectively display or hide different data layers, enabling them to focus on specific areas of interest or conduct comparative analysis.
3. Search and Query: Users can search for specific locations, features, or data points using keywords or geographic coordinates.
4. Measurement and Analysis: The GIS map provides tools for measuring distances, areas, and volumes, facilitating spatial analysis and data interpretation.
5. Data Download: Users can download data in various formats, including shapefiles, CSV, and GeoJSON, enabling further analysis and integration with other applications.
6. Collaboration and Sharing: The GIS map facilitates collaboration by allowing users to share maps, data, and insights with others.
FAQs on the Wisconsin GIS Map:
1. What types of data are available on the GIS map?
The GIS map encompasses a wide range of data related to the state’s geography, including land cover, water bodies, roads, infrastructure, population density, economic activity, and environmental conditions.
2. How can I access the GIS map?
The Wisconsin GIS map is typically accessible online through a dedicated website or portal maintained by the state government or relevant agencies.
3. Is there a cost associated with using the GIS map?
Access to the GIS map is usually free of charge, but some advanced functionalities or data downloads might require registration or a subscription.
4. How can I contribute to the GIS map?
Individuals and organizations can contribute to the GIS map by providing data, reporting errors, or suggesting improvements.
5. Are there any privacy concerns associated with the GIS map?
The GIS map generally adheres to privacy regulations and avoids sharing sensitive personal information. However, users should be aware of the data they are accessing and use it responsibly.
Tips for Utilizing the Wisconsin GIS Map:
1. Define your objective: Before exploring the GIS map, clearly define your research question or goal. This will help you focus your analysis and identify relevant data layers.
2. Explore the available data: Familiarize yourself with the different data layers available on the map and their respective attributes. This will enable you to make informed decisions about which layers to include in your analysis.
3. Utilize the map’s tools: Take advantage of the various tools and functionalities offered by the GIS map, such as search, query, measurement, and analysis, to extract meaningful insights from the data.
4. Be mindful of data accuracy: Remember that all data has limitations and inaccuracies. Verify the data sources and consider potential biases when interpreting results.
5. Share your findings: Communicate your findings effectively through maps, reports, presentations, or other visual aids to engage a wider audience and foster collaboration.
Conclusion:
The Wisconsin GIS map stands as a powerful tool for understanding, managing, and promoting the state’s diverse resources and assets. Its comprehensive data, user-friendly interface, and analytical capabilities empower various stakeholders to make informed decisions, manage resources effectively, and contribute to the state’s continued progress and development. As technology advances, the GIS map will continue to evolve, offering even more sophisticated tools and insights for navigating the complexities of Wisconsin’s landscape and its future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Wisconsin’s Geographic Information System (GIS) Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!